Why does gum recession develop?
Recession can be either an independent disease or a symptom that accompanies a certain pathology. It occurs for various reasons:
- Improper hygiene procedures. If you brush your teeth with a hard brush or press hard on it, you can damage the tissue. As a result, inflammation develops and the periodontal structure is disrupted.
- Bad habits. Smoking causes blood vessels to narrow because they are exposed to toxic substances from tobacco smoke. In this case, the blood supply is disrupted, which provokes tissue sagging.
- Bite pathologies, dentition defects. In such cases, the chewing load is distributed unevenly. Therefore, on the one hand, the dental system experiences increased stress, crowns wear off, and gums recede.
- Anatomical imperfections. With a shortened frenulum of the tongue, upper and lower lips, a small vestibule of the oral cavity, short strands of the mucous membrane, as well as in the case of other disorders, recession may occur.
- Incorrect prosthetics. If the gums recede only in the area of the crown, this symptom often indicates an allergic reaction to the materials used to make the dentures, or its incorrect installation.
- Errors when implanting orthodontic structures. If a patient's teeth quickly shift while wearing braces, this causes excessive pressure on the gums, which exposes the roots.
- Age-related changes. People who have reached older ages are more susceptible to the disease.
- Vitamin deficiency, in particular lack of vitamin C.
Regardless of the causative factor, treatment must be started as quickly as possible. Only a doctor can tell you what to do in each specific case.
Causes of recession
The prerequisites that provoke the development of the disease can have a different nature:
- inflammatory process: gingivitis, periodontitis;
- trauma to the gums: improper brushing technique;
- congenital pathologies of the frenulum;
- malocclusion and functional overload of teeth;
- incorrect prosthetics and orthodontic treatment;
- age-related changes occurring in the body;
- lack of vitamins leads to tissue degeneration;
- smoking, which leads to vasoconstriction and disrupts normal blood circulation in the tissues.
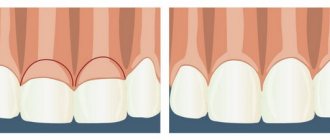
Clinical picture during the development of recession
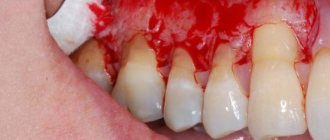
As the disease develops, the gums on the lower teeth recede and those on the upper teeth rise. The roots are gradually exposed. They are not covered with enamel, as a result of which they lack protection. Because of this, tooth sensitivity increases. Visually they look elongated, their color changes at the gums. Interdental gaps form, in which food constantly gets stuck, which brings a lot of inconvenience. In advanced cases, bleeding appears and the gums become inflamed.
The pathology can be localized, that is, affect 1-2 teeth, or generalized, when the entire dentition is involved in the painful process.
What will happen if you do nothing?
If you ignore the problem and do not take any measures to eliminate it, the disease will progress and lead to more serious problems, such as:
- formation of periodontal pockets;
- cervical caries (the most dangerous type of caries);
- tooth mobility.
If you are not satisfied with the aesthetics of your smile or are worried about tooth sensitivity, do not put off visiting the doctor! You can make an appointment with a dentist by calling the numbers below:
+7 or
What is the problem?
Because the part of the tooth that is not covered by enamel is exposed, the risk of developing root caries increases. In this case, it is difficult to cure, since ensuring a high-quality fit of the filling material to the root tissues is very problematic due to their hydrophilicity. Over time, teeth can become loose because there is not enough tissue available to hold them in place.
In addition, gum recession is an aesthetic problem, especially when the disease is advanced. People suffering from the disease develop complexes, which leads to social isolation.
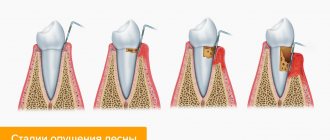
Stages of disease development
As with other dental diseases, it is important to notice and treat gum recession as early as possible. The more advanced the disease, the more difficult it will be to treat. There are several common types of damage to the body:
- Initial stage. Characterized by slight receding gums. It can only be noticed in the place where the gum adjoins the crown. In this case, the disease can be cured easily and quickly.
- Drop by 1-2 mm. It is considered the second stage of prolapse. The influx of tissue occurs from the inside or front side, without affecting the space between the teeth.
- Drop by 3-5 mm. There is a gradual exposure of the dental necks. Bleeding and pain may develop.
- Descent of more than 5 mm. It is considered an advanced form of the disease, which is the most difficult to treat dentally. The roots are greatly exposed, the teeth become very mobile.
It is usually very difficult to notice the first stages of gum recession. Therefore, it is important to come for routine preventive examinations at the dentist. This is the only way to find early manifestations of the disease and effectively eliminate them.
Diagnosis of gum recession
First, the doctor will conduct a visual examination and collect anamnesis. This may be enough for a specialist to make a diagnosis. To confirm it, the following studies are additionally prescribed:
- CT scan;
- inoculation of smears taken from the oral cavity to establish pathogenic microflora;
- clinical tests that are aimed at determining mineral deficiency.
Only after a thorough diagnosis will the dentist recommend how to treat the pathology.
How is gum augmentation performed?
The method of performing the operation is chosen by the doctor. To do this, the specialist first evaluates parameters such as the width and thickness of the gums. To restore its volume, patient tissue taken from the area of the extracted tooth or a palatal flap can be used. Along with this, artificial materials are also used, which are considered a progressive means of restoring the soft tissues of the oral cavity. These are collagen matrices or membranes.
Stages of gum growth:
- Antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity. If necessary, the manipulation area is isolated.
- Carrying out infiltration or conduction type anesthesia. For this purpose, injections of painkillers are used.
- Gum plastic surgery. If surgery is performed before the root replacement is installed, tissue incisions are made. When two operations are performed simultaneously, there is no need for additional dissections of the gums.
- Stitching. The edges of the cut fabrics are connected and sutured.
The entire operation takes 40–60 minutes. If collagen membranes are used for extensions, the time for plastic surgery is reduced by approximately three times.
What treatment methods are used for receding gums?
Can gums heal on their own? Unfortunately no. But stopping the pathological process is quite possible. Treatment is a rather complex undertaking that requires an integrated approach. In addition, it is not always possible to guarantee a 100% result.
At the initial stages of treatment, it is important to eliminate the cause that caused the gums to recede. In this case, physiotherapeutic procedures, oral hygiene, correction of orthodontic or orthopedic structures, prosthetics, plastic surgery of frenulum, cords, and vestibule of the oral cavity are carried out. If the deviations are caused by a malocclusion, the orthodontist carries out appropriate treatment, which may take several years, but only in this way will the root cause be eliminated.
How to deal with the disease is determined depending on the degree of neglect of the problem. Different techniques can be used:
- Drug therapy. It helps only in the initial stages of the development of the disease. It is aimed at combating concomitant periodontal pathologies, somatic diseases, and helps strengthen the gums and exposed areas of the teeth. Patients are prescribed immunomodulators, anti-inflammatory, hormonal agents, and vitamin complexes.
- Cleaning and polishing of tooth roots. It is carried out in several stages. First, the doctor removes dental plaque above and below the gum, after which he polishes the roots. Thanks to such actions, the gums will be able to “fix” to the surface of the teeth again.
- Gum plastic surgery. The operation is performed using different techniques. The flap method involves cutting the gums. The resulting flap is lifted to gain access to the roots, which are cleaned and polished. The gum is then reattached to the tooth. In some cases, regenerative materials such as membrane, a protein that has the ability to stimulate tissue, are used. When the loss of gum tissue is large, to restore it, the doctor may recommend transplantation (a section of the mucous membrane is taken from the upper palate and transferred to the problem area).
How to lift the gums is determined in each individual case by the doctor, carefully analyzing the clinical picture.
How to fix the problem?
To achieve 100% gum regeneration, you need to consult a doctor as soon as you notice a shift in the gingival margin. The type of treatment for gum recession depends on the stage of the disease.
If the drooping is insignificant, does not exceed 2-3 millimeters, the roots are not exposed, then they speak of an early stage. In this case, drug treatment of gums is indicated - protein preparations based on amelogenins are prescribed, which help restore damaged and form new healthy dental structures. Thus, the natural forces of the body are used. The advantage of drug treatment for gum recession is its safety and good effectiveness, but in severe forms it is useless.
Another method of treating gum recession without surgery is to inject collagen into the affected tissue. Collagen is a natural substance for our body and does not cause allergies or rejection. It stops inflammation and promotes tissue restoration at the initial stage. Collagen treatment is most effective for gum recession caused by severe inflammation. If the cause of prolapse is injury, then collagen will not help here.
In the moderate and severe stages - the tissues drop to 6 mm - treatment is carried out only surgically. There are 3 ways:
- Transplantation of a flap of your own healthy tissue onto the affected area. It is used in most cases and is highly effective. The disadvantages include discomfort in the area where the flap was taken and the risk of rejection.
- The placement of fibrin membranes formed from the patient’s own blood allows for complete tissue restoration, significantly reducing the risk of relapse, reducing postoperative swelling and shortening rehabilitation time.
- Implantation of separation membranes between gingival and dental tissues. A rigid membrane promotes better bone tissue restoration and eliminates prolapse by more than 70%. The disadvantage of this method is that later you will have to undergo a second operation to remove the membrane.
How and how to treat gum recession is decided only by the treating dentist. The cost of treating gum recession depends on the severity of the disease and the amount of work performed.
Causes of receding gums
Gum recession can be caused by various factors. Self-diagnosis is the first step to identifying the problem, so as not to pay too high a price for inattention. Below are the most common causes of recession:
- improper
oral hygiene. For example, too aggressive brushing of teeth: using a hard toothbrush, mechanical damage during dental care; - lack
of oral care. If plaque is not removed, it will lead to the formation of tartar, which in turn causes gum disease and recession; - periodontal disease
. This gum disease is often accompanied by gum recession. If treatment is not done in time, this will lead to tooth loss; - natural aging
of the body; - bad habits
: biting lips and nails, biting pens, pencils, smoking; - traumatic, inaccurate dental treatment
, including whitening procedures.
In addition, structural features
oral cavity, jaw (bite pathology, arrangement of individual teeth, shortened lip frenulum, etc.) and somatic diseases (metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, etc.).