Where does the treatment of dental recession begin?
Treatment of recession must begin, first of all, by eliminating the cause - what caused it, what caused the gum recession.
After this, depending on the Miller class, surgical treatment is performed - closing the exposed area. Since gum recession occurs in conditions of a broken bite, it is logical to begin treatment in order to stop the process of recession itself. And here we should note the professionalism of our orthodontists.
We, at the German Implantology Center, effectively follow the approach: first we correct the bite and stop the recession, and only then we treat the recession itself and restore the gum level. To immediately restore gums without eliminating the cause is a symptomatic treatment, extremely ineffective and, in fact, useless.
Our clinics value the time of our patients and offer only proven treatment methods that meet the principles of reliability and effectiveness in the long term.
Potential Complications
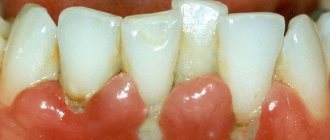
Recession of gingival tissue is an independent disease that requires competent therapy. If left untreated, it can lead to much more serious consequences than a violation of the aesthetics of a smile.
First, food gets clogged into the gaps between the teeth, causing bad breath. Next, inflammation develops, which can be accompanied by severe pain, discharge of pus and loosening of the teeth.
Increased sensitivity and soreness develop in the area of the gum margin, which makes eating difficult.
Teeth and roots are affected by caries. In advanced cases, lack of treatment can lead to the loss of one or several dental units at once.
The easiest way to notice when the gums on the front teeth recede, what to do in this case is well known - sign up for a consultation with dentistry to choose a treatment method.
About orthodontic treatment to stop gum recession
These can be orthodontic structures: braces, or aligners, or something else - this is what the orthodontist will choose, it is he who determines which technique for correcting the bite in a given case of recession will be best applicable for each specific patient. There are no universal treatments. The only question that is subject to discussion is how long orthodontic treatment will take in one way or another.
As a result of treatment, the orthodontist must place the teeth in a physiological occlusion so that the tooth/teeth do not bear such a load that they experience excessive chewing stress at the time of contacting the doctor.
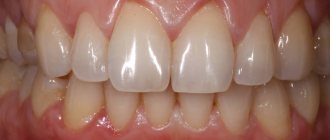
And then, when the tooth is placed in the functionally correct position, the following happens to the gum. Gum recession stops. And again, if it stops at such a level that closing the recession is possible, then the gums subsequently rise and the recessions close.
And after some intervention, perhaps the gums will return in full.
Cases where orthodontic treatment eliminates recession
We cannot always close all gum recessions with the help of orthodontics. We remove the cause of the recession, that is:
- malocclusion,
- we correct occlusal contacts that lead to this recession,
- eliminating improper stress on teeth,
- We eliminate the lack of load in the case of an extracted tooth and the overload, in turn, of neighboring teeth.
And after the doctor has normalized the patient’s bite and normalized the correct closure of his teeth, we refer him to a periodontist who will perform gum plastic surgery.
In any case, the pathological process of gum loss stops after our treatment; it no longer progresses. And we always wait after removing braces (or other orthopedic structures) from 3 to 6 months
for the gums to recover and calm down. And after this, if necessary, plastic surgery of the frenulum, plastic surgery of the vestibule of the oral cavity is performed - all this is done only after orthodontic treatment.
Why is plastic surgery done AFTER, and not BEFORE, bite correction?
Because a scar is formed inside the operated tissue, which in the future can interfere with the movement of teeth when correcting the bite.
HOW TO STOP GUM RECESSION?
If you suspect you have gum recession, contact your dentist for an examination and appropriate treatment.
There are various treatment options for gum recession:
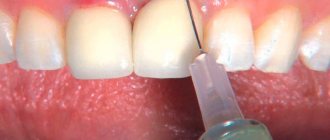
Cleaning and polishing the surface of tooth roots
If you have gum recession, your dentist may recommend a procedure to clean and plan the surface of the roots of your teeth. This procedure consists of two stages and is carried out by a dentist. In the first stage, the doctor removes plaque and tartar in the area of the gum line (above and below it). Then the surface of the tooth roots is polished, so that the gums can “attach” to the teeth again. Treatment may be performed under local anesthesia and may require several visits.
The procedure for cleaning and polishing the surface of the roots of teeth is quite effective. After this, you will need to visit your dentist regularly. He will check the condition of your gums and will be able to spot possible problems in time. To protect your gums, be sure to practice good oral hygiene.
Gum operations
For more severe cases of gum recession, your dentist may recommend surgical procedures. These include the following:
- Gum flap surgery: If non-surgical treatments have not been effective, your dentist may suggest flap surgery. During this operation, incisions are made on the damaged gum, then the resulting flap is raised, allowing access to the roots of the tooth. They are cleaned and polished. After this, the gum is reattached to the surface of the tooth.
- Regeneration: This surgical procedure helps regenerate damaged jaw and gum tissue. First, the area above and below the gum line is cleaned to remove bacteria and plaque. A material that stimulates tissue regeneration—a membrane, a tissue-stimulating protein, or a graft—is then attached. This triggers bone and tissue growth in the damaged area. The gum is then securely attached to the root of the tooth.
Gum transplantation
If you have lost gum tissue, your dentist may recommend a gum tissue graft. A section of gum is taken from the upper palate and sewn to the damaged area of the gum so that it covers the roots of the tooth.
Surgery to close gum recession
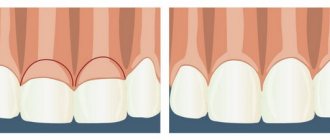
The gum itself, as you understand, will not rise, it will not “bounce into place”, it needs to be put back in its original place, and this is called closing the gum recession.
But I repeat once again: there are also indications and contraindications for the operation, in accordance with certain classes of gum recession according to Miller.
If this is a class one recession, then one forecast. If this is class II gum recession, the prognosis is different. There are many contributing factors to both successful gum recession and failure. That is, at the very beginning of the treatment path, the doctor must determine all the factors for successful closure of gum recession.
Why do gums recede?
Gum loss, or recession (in scientific terms), is very rarely an independent disease. Usually this is a consequence of other diseases and pathological processes in the body, which in one way or another affect the condition of the oral mucosa. The main reasons that provoke poor circulation, atrophy and gum loss are:
- inflammation of periodontal tissues with accumulation of pus and plaque in periodontal pockets;
- poor hygiene, accompanied by the formation of tartar. Gradually, this leads to drooping of the moving part of the gum;
- mechanical, thermal and chemical injuries;
- errors during orthopedic and orthodontic treatment, due to which the gums are injured;
- improper hygiene;
- malocclusion;
- pathologies of the structure of the mucous membrane (the gums are initially thin and weakened) and/or the cortical layer of the bone is too thin, which impairs blood circulation;
- general diseases of the body that affect blood circulation and the functioning of the immune system;
- old age, when gum atrophy may occur.
Miller classification
Today, the generally accepted classification of gum recession is the Miller classification, which is divided into 4 classes
.
First and second classes
according to Miller - root closure is 100 percent possible.
Third class
according to Miller, 100 percent root closure is impossible.
And fourth grade
according to Miller, he is not even being treated.
What treatments are available for each stage of gum recession?
For the first, second and third classes according to Miller - only surgical closure of the exposed necks of the roots of the teeth. The fourth class according to Miller is not treatable, that is, it cannot be treated.
Is there an age limit for treating gum recession?
No.
There is no age limit for treating gum recession.
Symptoms and forms of the disease
Today, when diagnosing the severity of the disease, the Miller classification is used, which involves 4 stages of gum recession.
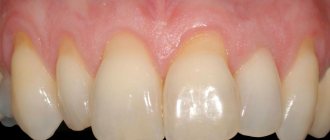
- Visually, gum loss is hardly noticeable (or completely unnoticeable) and appears only in the area of contact between the tooth and gum.
- The defect appears slightly in the area of contact between the gum and the neck of the tooth (the level of the attached gum decreases by 1-2 mm). The gums between the teeth remain at the same level.
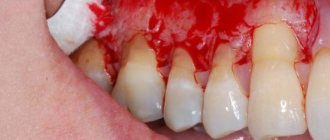
- The gums recede by 3 mm or more. The necks of the teeth are slightly exposed, but the bone level does not decrease. At this stage, the gums often recede and bleed.
- The most severe stage, when the gums recede by 5 mm or more, the roots of the teeth become visible. Mobility of the teeth is observed, which at this stage of the pathology is often generalized and involves several teeth.
At advanced stages, pathology can be noticed visually, especially when the gums on the front teeth recede. If the pathology is at the beginning of its development, a number of additional symptoms help to detect it.
- Inflammatory process, bleeding.
- Formation of periodontal pockets.
- The sensitivity of the enamel has increased.
- The presence of a thick layer of dental plaque.
- Unhealthy whitish tint of gums.
Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis (using modern technologies), so if you have at least one symptom, you should not postpone your visit to the clinic. Of course, everyone is interested in the question of what to do if the gums on a tooth have receded and what treatment should be chosen. There are two directions: therapeutic and surgical. The choice depends on the severity of the pathology and the underlying disease that led to soft tissue atrophy.
What is the problem?
Because the part of the tooth that is not covered by enamel is exposed, the risk of developing root caries increases. In this case, it is difficult to cure, since ensuring a high-quality fit of the filling material to the root tissues is very problematic due to their hydrophilicity. Over time, teeth can become loose because there is not enough tissue available to hold them in place.
In addition, gum recession is an aesthetic problem, especially when the disease is advanced. People suffering from the disease develop complexes, which leads to social isolation.
Prevention of gum recession
- Don't start caries. Place high-quality fillings in a timely manner and prevent the appearance of cervical caries.
- Keep your mouth clean. Follow your teeth brushing technique.
- Have your hair professionally cleaned at least once every six months.
- Avoid injury.
- Massage your gums regularly.
- Take mineral-vitamin complexes with vitamins A, D and group B.
Do not forget that at an early stage it is easier, faster and cheaper to cure the disease. Therefore, consult a doctor as soon as you notice its first signs.
Therapeutic treatment
Conservative treatment is prescribed in the mildest cases, when it is necessary to stop the inflammatory process and potential gum loss due to periodontal diseases (periodontitis or periodontal disease). Usually, the matter is not limited to one procedure: the doctor prescribes a complex treatment, which may include several techniques.
- Professional cleaning.
Removal of hard dental plaque is a basic procedure that precedes the main treatment. - Cleaning periodontal pockets.
To remove pathogenic microorganisms, the closed curettage technique is used. It can be carried out with standard instruments, as well as with the help of a laser and the Vector device (and its analogues). - Rehabilitation physiotherapy.
Used to improve cell health and better restore blood circulation in soft tissues (laser therapy, electrophoresis, current therapy, etc.). - Taking vitamins
, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and preventive therapy.