Pediatric dentist: what he does and what he treats
Content:
What does a pediatric dentist do?
What is special about the work of a pediatric dentist?
When should you visit a pediatric dentist?
Why do children need fissure sealing?
Diagnostics in pediatric dentistry
Why is it important to treat baby teeth?
Advice from a pediatric dentist
A pediatric dentist diagnoses, prevents, and treats oral diseases in patients under 18 years of age in a dental clinic.
Who is a dentist and what are his responsibilities?
In fact, the specialty of a dentist implies a fairly wide range of responsibilities, despite the fact that they study for this profession for only three years.
What does a dentist do:
- examines a person’s oral cavity and makes a diagnosis;
A dentist has the right to examine a person’s oral cavity and make a diagnosis, but does not have the right to remove teeth
Many people are interested in the question: can a dentist remove teeth? Despite the fairly wide range of services that he has the right to provide, he cannot do this because he does not have enough knowledge and qualifications.
Read also: Folk remedies for acute toothache
What does a pediatric dentist do?
- examination of the oral cavity, filling out a dental formula;
- diagnosis and treatment of caries and its complications;
- fissure sealing;
- reading x-rays, interpreting computed tomography results;
- removal of baby teeth;
- providing assistance with dental injuries;
- carrying out professional oral hygiene;
- teaching competent home hygiene to children and parents;
- diagnosis of diseases of the mucous membrane;
- referral to dentists of related specialties (to an orthodontist to correct malocclusion).
What parents need to know!
I want to reveal a little the secrets of dentistry for those who care about the health of their children.
The photographs taken of my patients will clearly explain “what we are talking about.” During the examination, the doctor must collect an “amnesis” - a complete picture of the child’s health status and past dental treatment. The doctor will note any pathology of the oral cavity (be it changes in bite or adenoiditis) and refer you to other specialists, if necessary. He will also definitely send your child for an x-ray (sometimes even one picture is enough). When developing a treatment plan, your doctor will offer you different alternatives so that you can choose for yourself. This constitutes the “conscious consent” of the parents to treatment. During treatment, parents take part - they are not “kicked out” of the office, as before. They are helpers (mostly psychological). Treatment is necessarily accompanied by the application of a rubber dam (a rubber curtain over the mouth that protects the child’s oral cavity). The International Association of Pediatric Dentists prohibits treating young children without it in 90% of cases! The site after tooth extraction must be preserved. To do this, a “space saver” is placed, which is removed only when the permanent tooth erupts. Initially, children undergo canal filling and then prosthetics. Crowns specially produced for children are cemented so that the baby tooth falls out along with the crown. “Silvering” does not have such an effective effect as previously thought! To prevent caries, as well as treat superficial caries, fluoridation using mouthguards is necessary. If you see a dark or yellow spot of caries, this is already medium or deep caries. Superficial caries looks like a white spot! Destruction of the front teeth from caries cannot be restored only with fillings. For front teeth, there are special “caps” made of light-curing material. Tooth extractions should be performed by a pediatric dentist, not a surgeon (as well as prosthetics, placement of a space saver, etc.). Children can only get used to one specialist! Orthodontic treatment should follow complete sanitation of the oral cavity! A competent orthodontist will not begin treatment without an appropriate document from a pediatric dentist confirming the completion of dental treatment for the child. And now the last and main secret of a professional dentist is that at the end of treatment, the child should want to come to this clinic again, because he was not in pain and was understood.
What is special about the work of a pediatric dentist?
It is difficult to get young patients ready for treatment. All children are afraid of people in white coats: they associate them with injections and unpleasant sensations. They are especially afraid of visiting the dentist's office. Therefore, one of the features of the work of a pediatric dentist is the ability to find contact with all children and encourage them to undergo treatment.
Many young patients already have negative experiences at the dentist, when the doctor performed treatment through crying. These unpleasant impressions remain in the memory for a long time. When dental treatment is needed again, the child refuses to enter the dental office.
Finding contact with any child, calming him down, and conducting competent treatment are the main tasks of a doctor in pediatric dentistry.
Text checked and approved by an expert
Mikhailova Natalya Aleksandrovna
Children's dentist
20
years of experience
Children's dentistry. Treatment of caries. Treatment of pulpitis. Oral hygiene. Fissure sealing
What is the difference between pediatric and adult dentistry?
In terms of its anatomical structure, the developing dental system in children differs from the formed teeth of an adult. This explains the peculiarities of the course of dental diseases and methods of their treatment.
There are also a number of features in dental treatment itself.
- The need for the doctor to work quickly. Small children are physically unable to sit still for a long time, much less keep their mouth open. The duration of dental treatment for a child 3–5 years old is 10–15 minutes. If a lengthy procedure is required, treatment may be carried out in several doses or with sedation.
- Use of drugs and materials. Dental treatment for children may involve the use of medications, restorative materials, and anesthesia. Before starting treatment, the dentist must always make sure that there are no risks to the baby’s health.
- Choice of treatment method. One of the main reasons for a child’s fear of dental treatment is the drill. Modern clinics at the early stage of caries can use gentle methods of therapy that do not require enamel preparation. If it is still necessary to use a drill, the doctor must correctly explain to the child the features of the device, the necessity and safety of manipulations.
The difference between pediatric and adult dentistry lies not only in the treatment process and approach to the patient, but also in the arrangement of the clinic. A children's clinic should accommodate the child, so the interior often uses such maneuvers as colorful design, playrooms, children's pictures, and the presence of a TV for watching cartoons. The dentist’s office also follows a “children’s” design; there may be special toys and other elements. A small patient should feel comfortable and pleasant in the dentistry.
When should you visit a pediatric dentist?
Timely prevention and treatment of caries helps to prevent the development of complications (acute pain, swelling). It is recommended to take your child to the dentist from the age of 2. If nothing bothers the baby, there are no visible changes, a doctor’s examination is necessary:
- To introduce your child to visiting the dentist's office. During the examination, the little patient retains in his memory the positive emotions from visiting the doctor, because the examination is quick and painless. The inspection takes place in the form of a game.
- Pathologies of the dental system do not always have characteristic symptoms. Initial caries may not bother children, but treatment is already required.
- The doctor tells parents about the timing of changing baby teeth and how to properly perform home hygiene.
Prevention of the development of caries in primary teeth depends on how carefully home hygiene is carried out. Dental services include training in the rules of rational hygiene and individual selection of oral care products.
A visit to the pediatric dentist is necessary every six months in order not to miss the development of caries and other pathologies of the dental system.
What does an orthopedic dentist do?
A prosthodontist is often called a prosthetist, or the doctor who places crowns on teeth. Indeed, both restoration and implantation involve replacing the lost part of bone tissue with artificial materials. During the treatment process, many different manipulations are performed on the patient. What kind of actions does the orthopedist perform?
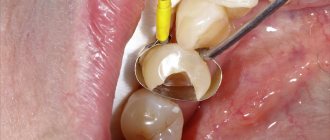
Installs crowns
Of all types of prosthetics, the most common is the installation of crowns. The strength and durability of the crowns depends on the material chosen. Based on the type of material, crowns are divided into:
- Metal. They are made by an orthopedist from steel, titanium, gold, and also platinum.
- Metal-ceramic. This is a combination of metal and ceramic. They are reliable and look good.
- All-ceramic. A high level of reliability of such a crown is achieved by including zirconium dioxide in the composition. It is quite expensive to install such a prosthesis, but the crown looks beautiful.
- Plastic. The doctor inserts them temporarily.
Advantages of installing crowns:
- the root remains alive;
- the shape of the tooth surface can be adjusted;
- this method is cheaper than implantation.
Disadvantages of restoring teeth with crowns:
- the tooth, together with the nearby teeth adjacent to it, has to be filed down;
- there is a risk of inflammation;
- tooth destruction is possible in case of unsuccessful prosthetics.
Installs dentures and bridges
The doctor, as a prosthetist who inserts the implant, decides on the method of restoration. We are talking about implants, bridges and removable dentures.
An implant is a completely artificial tooth. It has a number of advantages over other prostheses:
- set for life;
- there is no need to grind adjacent teeth;
- painless operation;
- identical to the real ones in their structure and functions.
The disadvantages of implants are their high cost and long period of survival in the jaw. However, implantation is the best method for restoring teeth.
A bridge is a stationary system that is installed when several teeth are missing in a row and is secured to the supporting teeth on both sides of the missing teeth. Types of bridges:
- solid cast - cast from cobalt-chrome alloy;
- metal-ceramic - identical to metal-ceramic crowns;
- ceramic - made from zirconium dioxide based on a model that is developed by a special computer program.
Read also: Ulcer on the inside of the lip treatment
Removable dentures are installed in case of loss of an entire row of teeth. They can be completely or partially removable. Advantages:
- no age restrictions;
- low price;
- quick addiction;
- short installation time.
- require regular care;
- have a short service life.
Why do children need fissure sealing?
Chewing teeth have deep grooves on their surface - fissures. They become clogged with food debris and bacteria develop. When home hygiene is inadequate, bacteria remain on the surface. They produce acid and destroy the tooth, causing tooth decay.
Prevention of caries is by sealing fissures at the dentist. It is carried out from the moment the first permanent molar erupts (from 6-7 years). The pediatric dentist carefully examines the fissures. If caries has already appeared on them, then sealing is contraindicated. It is necessary to treat caries and put a filling.
During the consultation, the doctor will tell you about all the features of the procedure, indications and contraindications.
Why does a child need a dentist?
AT WHAT AGE IS IT NEEDED TO VISIT A PEDIATRIC DENTIST FOR THE FIRST TIME?
From the very early days. We recommend that you do not wait until your child has formed all of his baby teeth or has problems. As soon as the first tooth appears, welcome to us, pediatric dentists. Moreover, today many pediatricians recommend being examined by a dentist from the age of one month. And here's why: only a specialist can identify anomalies of the dental system at an early age and help prevent their consequences. Let me give you a simple example: a child does not latch on to his mother’s breast well, hardly gains weight, the mother cannot understand what the reason is, and it may be trivial - a shortened frenulum of the tongue. It is this small, easily removable defect that prevents the baby from eating properly. Only a specialist can discern such a problem, and he will correct it: this is a simple procedure that does not even require pain relief. Meanwhile, a shortened frenulum can not only interfere with the baby’s proper nutrition, but also play an even worse role in the future: he may have problems with speech and an incorrectly formed bite. And truncation of the frenulum, say, at the age of 7, is both stressful for the child and a more painful procedure, because by this age the structure of the frenulum itself becomes denser, so this problem must be solved at a very early age.
WHY DOES CARIES APPEAR IN SMALL CHILDREN?
A few reasons. This could be genetics, stress, or illnesses of the mother during pregnancy, but baby teeth are formed in the first trimester. But the main reason is poor oral hygiene and nutrition. Do not give a pacifier to a child unless absolutely necessary, but there are cases when children use it until they are two or three years old! You should not buy sweets for babies; they get all the necessary carbohydrates from breast milk and other foods, including cereals, vegetables and fruits. Children under three years old should not know the taste of candy at all. But, alas, parents hardly listen to the advice of specialists. That’s why we often see the following picture: a one-year-old baby in a stroller happily sucking a lollipop on a stick, or a two-year-old baby with cotton candy and a chocolate bar. Unfortunately, childhood caries has recently become much younger. If previously children of 4–5 years old were brought to us for the first time, now they are one and a half year old children. In my practice there was a 9-month-old child who had already developed caries.
IS IT TRUE THAT IT IS NOT NECESSARY TO TREAT CARIES IN CHILDREN; IT IS BETTER TO EXTRACT THE SICK TOOTH?
A categorically false statement! Early tooth extraction leads to disruption of the maxillofacial system; malocclusions and problems with the gastrointestinal tract may occur. And then, untreated caries is a source of infection, a gateway for bacteria. Many parents believe that baby teeth do not hurt, and are very surprised when they find out that they have roots and nerves. Yes, they hurt just as much as adults! The tooth hurts because it has both a nerve and a root, under which is the germ of a permanent tooth. Therefore, it is important to come to an appointment with a pediatric dentist as soon as possible, without waiting until life with bad teeth turns into torture for the child.
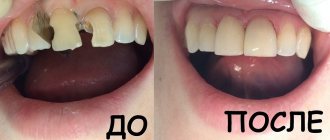
An example from my experience: a 4-year-old patient whose central teeth were all affected. The boy was embarrassed to smile; he was teased in kindergarten. After we fixed all of the baby’s teeth, it was very nice to see his smile. Unfortunately, such advanced cases are becoming more and more common.
Before and afterPhotos courtesy of the Enger Dental Clinic
HOW TO PREPARE YOUR BABY FOR A VISIT TO THE DENTAL CLINIC?
First of all, the parents themselves need to prepare - don’t be nervous, don’t show excitement. It happens that the mother herself begins to lament how scared she is. At home, in a playful way, explain to your child how his tooth will be treated. But the best time to start getting to know the dentist is during preventive visits. The first visit to the doctor plays a big role. The baby meets a doctor who will simply count his teeth, look at him, make a joke, and give him a ride in a chair - at the Enge clinic we have special chairs that can be lowered and raised, the child perceives this as a game. The child sees that nothing bad happened to him, and next time he will come with pleasure. Moreover, in our clinic we give gifts to all children - even for a preventive examination. And for treatment, little patients also receive certificates and medals for courage. And what young “hero” doesn’t want to receive a medal?
AT WHAT AGE SHOULD CHILDREN BE TAUGHT TO BRUSH THEIR TEETH?
From the appearance of the first tooth. Of course, parents should do this. And already on their own, under the supervision of adults, children are taught to brush their teeth from the age of one and a half years, of course, without gels and pastes for now. A child under 2–3 years old only needs a “magic” toothbrush dipped in warm water.
WHAT TO DO IF A CHILD’S TOOTH SICK SUDDENLY?
See a doctor immediately. But the main thing is to prevent such developments. The fact is that caries develops rapidly in children - it may be that on the outside the tooth looks healthy, but inside there is an inflammatory process that is already affecting the nerve. Therefore, I recommend visiting your pediatric dentist regularly.
WHAT IS THE APPROACH DIFFERENT IN TREATING CHILDREN FROM ADULTS?
A pediatric dentist must be not only a very professional doctor, but also a psychologist, love children, be able to communicate with them, have patience, and be able to win over the child. Not everyone can persuade a small patient to simply open his mouth. And if it bites, endure it: by the way, the bitten hands of doctors in pediatric dentistry are a common occurrence. We must also take into account that children have very little perseverance: not every child can sit still for 15–20 minutes, but what if treatment requires a longer time? Therefore, all manipulations must be done clearly, quickly and efficiently. This is jewelry, painstaking work. In addition, the doctor must carry out the treatment so as not to damage the buds of permanent teeth. And then, a dentist for adults communicates only with the patient, and a dentist for children communicates with both the small patient and his parents. And sometimes the whole family comes along with grandparents. Everyone needs to be talked to, if necessary, and reassured. This is why pediatric dentists are especially valued in a professional environment - not every doctor, even a very competent one, can work with children.
HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT PEDIATRIC DENTIST, WHAT SHOULD YOU PAY ATTENTION TO?
As for professionalism and experience, it would be a good idea to inquire about the availability of a special certificate. If you notice that the doctor is indifferent, does his job mechanically, is rude, and tries to force the child into a chair - leave. Treatment by such a doctor can instill a lifelong fear of the dentist. At the Enger Clinic, the attitude towards small patients is special. We communicate with the child, encourage, praise, involve children in the treatment process, turning it into a game. For example, a child can choose a filling for himself - we have special colored fillings for baby teeth - and then in kindergarten he will brag about how cool his fillings are. Children feel that this aunt in a white coat is a true friend who wants to help.
WHAT SHOULD A CHILDREN'S OFFICE BE LIKE IN A DENTAL CLINIC?
As joyful as a playroom. These are the rooms at the Enger clinic - with funny posters of your favorite children's characters on the walls, toys and cartoons. And if we talk about filling, then our clinic has specialized equipment, materials, anesthetics intended specifically for children. Even the instruments have a rubberized surface so that their knocking does not frighten the child. A dental unit with a radiovisiograph allows you to take dental photographs without leaving your chair. After all, sometimes there is a dilemma: keep the tooth or remove it, in which case the image allows you to see a more accurate picture. In addition, the office is equipped with a sedation unit - this is not anesthesia or painkiller; this unit allows you to relieve the feeling of fear and anxiety in some cases. And, of course, children's rooms are equipped with first aid kits for first aid. All staff - assistants, nurses - have undergone special training. And most importantly, the clinic must have a special license for pediatric dentistry.
WHAT DO YOU ADVICE TO PARENTS?
There is no need to wait until your child starts having dental problems. As I have already noted, inflammatory processes in children occur very quickly, and parents may not notice the carious cavity. Come for preventive examinations at least once every six months; the sooner you introduce your child to the Tooth Fairy, the fewer problems he will have in the future.
Why is it important to treat baby teeth?
A common misconception is that baby teeth do not need to be treated because they will soon fall out. Like permanent ones, milk ones are destroyed, hurt, and bother the child.
Why treatment is necessary:
- Caries reaches the nerve: acute pain appears, the baby’s well-being deteriorates sharply, and appetite is lost.
- If pulpitis is not treated in time, the infection spreads beyond the root and the permanent tooth germ suffers.
- Chronic infection in the mouth affects the development of the dental system and the child’s immunity.
- Inflammatory processes spread faster in children than in adults. Today caries appeared, and a few weeks later: inflammation affected the roots, swelling and severe pain appeared.
- Early removal of baby teeth before the physiological change leads to displacement of the dentition and disruption of chewing function.
Do not self-medicate, consult a doctor!
Don't wait for your condition to worsen!
Sign up
Anesthesia for dental treatment
Treating a child’s tooth while sleeping is much more convenient and safer. Therefore, often in children, dental treatment under anesthesia is preferable to without it. At the same time, dentists are confident that the use of gas as anesthesia does not cause any harm to the body, even of an infant.
Treating teeth under anesthesia for a child aged 2 to 4 years is one of the most convenient and popular methods. The inhalation method is based on the fact that the baby simply inhales a special mixture, and then calmly falls asleep. Doctors provide treatment, and then the child wakes up with no memory or pain or fear of doctors.
To use inhalation anesthesia, the clinic must have a license, the necessary equipment, and an experienced anesthesiologist who knows how to work with children. It is important to remember that under general anesthesia, teeth are treated only for a healthy child - he should not have a cold, and at least two weeks must have passed since the acute respiratory infection, acute respiratory viral infection or other illness. Also, do not use this method immediately after vaccination.
Local anesthesia is another popular method of pain relief. But if it is customary to treat teeth in a dream in young children, then this method can be used in schoolchildren. Its essence is that an anesthetic drug is injected into the gum using a syringe and a needle, which will not allow the child to feel pain during treatment.
All modern technologies that exist in Russia only work to quickly cure teeth at the moment when they manage to persuade the child to open his mouth. But can the quality of such treatment be at its best? It will not be possible to completely remove infected and diseased tissue. Not to mention fillings, whose task is to harden faster in order to somehow cover carious holes. This leads to the fact that soon the parents bring the child to the doctor again, but now with even greater problems.
An equally popular problem is the baby’s fear. Therefore, inhalation anesthesia is an easy way to cure a child’s carious teeth in one visit to the doctor, and then not remember about this procedure until the next preventive examination.
Advice from a pediatric dentist
Below are tips that will help maintain a healthy smile for a young patient under parental supervision:
- A child’s teeth should be brushed from the moment the first baby tooth emerges.
- Change toothbrushes regularly: every 1-3 months, depending on the condition of the bristles.
- Use only children's toothpaste.
- After eating you need to rinse your mouth with water.
- Control the consumption of carbohydrates: sweets, flour products, compotes.
- It is necessary to teach oral hygiene in a playful way, and also to be an example, because children repeat a lot after their parents.
- Visit the dentist every 6 months.
- When a child first complains of toothache, immediately visit a doctor to avoid complications (swelling, tooth extraction).
Who is a dentist?
To become a dentist, you must graduate from medical school or college. A specialist with secondary medical education is trained to perform relatively simple dental procedures.
This does not mean that it is not able to cope with more complex cases, but its theoretical and practical basis is limited, and does not involve performing operations on teeth of the highest level of complexity.
Who is a dentist?
Dentist is a unifying definition applied to a dental specialist with higher education. (Stoma, stomatos means mouth in Greek, logos – teaching). To become a dentist, you need to graduate from a medical academy, institute or university.
The duration of their studies is at least 5 years. Along with dental diseases, future dentists study many medical sciences - biochemistry, physiology, therapy, histology, etc.
They are prepared not only theoretically, but also practically, having completed a one-year internship or a 2-year residency.
What is the difference between these concepts?
The difference between a dentist and a dentist is the level of training and the type of treatment they can perform.
The list of works provided for in the job description of a dentist includes:
- A dentist is a specialist in a wide range of diagnostics;
- treatment of relatively simple diseases of teeth and gums - gingivitis, stomatitis, caries and some others;
- removal of teeth not complicated by periodontitis;
- treatment of simple maxillofacial injuries.
- carrying out physical procedures;
- consultation regarding the choice of oral hygiene products;
- cleaning teeth from plaque and tartar, and some others.
In case of more serious dental pathologies - malocclusion, pulpitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, lesions that have caused tooth destruction by more than 50%, and in other cases requiring the participation of a more trained specialist, the dentist gives the patient a referral to a dentist of the appropriate specialization.
A dentist is a general specialist. He has theoretical knowledge and practical skills sufficient to perform therapeutic, orthodontic, orthopedic and surgical operations.
Although, like a dentist, when faced with a particularly difficult case, he can refer the patient to a doctor of a narrow specialization.
Narrower specializations
- The large number and complexity of pathologies of the dentofacial apparatus, the constant improvement of existing treatment technologies and the development of new ones require in-depth, specific knowledge and skills from dentists.
- This feature has found its implementation in the concept of narrow specialization of dentists.
- Depending on the type of work performed, the following specializations of dentists differ:
- therapist;
- orthodontist;
- surgeon;
- orthopedist;
- hygienist;
- pediatric dentist.
Dentists often combine several specializations at once.
Dental surgeon
The prerogative of the profession of a dental surgeon is the following operations:
- Dental surgeons often treat diseases that are within the competence of dentists of other specialties: tooth extraction;
- treatment of neoplasms in the PR;
- elimination of TMJ dysfunctions, diseases of the salivary glands and trigeminal nerve;
- primary treatment of wounds and injuries of the mouth, neck, face;
- plastic surgery and reconstruction of jaw bones;
- operations on periodontal tissues (gingivectomy, gum pocket removal, soft tissue transplantations, gingivoplasty, plastic surgery of the oral vestibule and frenulum);
- correction of tooth position anomalies.
- implantation.
Dental surgeons often treat diseases that are within the competence of dentists of other specialties: phlegmon, periodontitis, sinusitis, periostitis, abscesses, osteomyelitis.
They also diagnose specific diseases, the symptoms of which may appear in the PR - syphilis, tuberculosis, actinomycosis.
Dentist-therapist
Typically, patients who seek help from a dentist first see a therapist.
- Dental therapist is the broadest specialization in dentistry.
- Typically, patients who seek help from a dentist first see a therapist, who in most cases is able to deal with their problem alone.
- The job description of a dental therapist provides for the following work:
- examination of the oral cavity;
- diagnosing;
- treatment of teeth (caries, pulpitis, etc.) and periodontal disease (gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, periodontitis);
- preparation of PR for prosthetics, its sanitation;
- teeth whitening and PG;
- preventive examination and advice on caring for RP.
When pathologies are identified that urgently require the participation of a specialist doctor, the therapist refers the patient to them.
Orthopedist
An orthopedist restores teeth using prosthetics
A doctor of this specialization is engaged in the restoration of dilapidated, missing or lost aesthetic teeth using prosthetics.
Orthopedist:
- takes impressions of teeth, from which the dental technician subsequently makes a prosthesis;
- tries on, adjusts and secures the prosthesis on the patient.
Prosthetic structures include crowns, bridges, inlays, veneers, and removable dentures.
Orthodontist
The orthodontist adjusts the position of teeth using removable and non-removable orthodontic devices
Orthodontics is a subsection of dentistry dedicated to dental anomalies.
The scope of practice of an orthodontist includes:
- prevention of deformations of individual teeth, dentition and jaws;
- normalization of occlusion;
- correction of jaw development;
- teeth straightening.
Correction of the position of teeth is carried out using removable and non-removable orthodontic devices - mouthguards, braces, braces.
Children's teeth at the stage of formation and growth are most successfully corrected. In adults, this process is much more difficult.
General dentist
The specialty “General Dentistry” was introduced by orders of the Ministry of Health No. 553 and 112. This specialty is of particular importance for rural areas, where it is desirable to have a specialist who can provide assistance in several clinical areas.
However, until now, due to a number of organizational, educational and legal problems, general practice in dentistry has not received proper development.
Children's
Children and adolescents under the age of 17 are patients of the pediatric dentist. A child's teeth have many differences from adult teeth.
- This includes the presence of baby teeth, the constant renewal and formation of the dentofacial apparatus, and the inability to use certain anesthetics for children.
- And the reaction of children to the dental chair creates increased problems.
- A dentist treating children must not only be able to distinguish pathology from the age norm, detect deviations in bite and tooth formation in time, but also be a bit of a psychologist.
Hygienist
The goal of a hygienist is to prevent dental diseases
- Dental hygienist is a relatively new specialization in dentistry.
- Its goal is the prevention of dental diseases, its field of activity is dental hygiene, proper dental care.
- A dental hygienist performs the following work:
- diagnosing RP diseases;
- professional teeth cleaning;
- disease prevention;
- training in proper dental care skills;
- educational activities (inspections in kindergartens, schools, institutions, organizations, enterprises).
Categories of dentists
Dentists are required to confirm their qualifications every 5 years
- Each dentist has a certain qualification category, which is an indicator of the level of his theoretical knowledge and practical skills.
- The procedure for assigning a qualification category is determined by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation.
- Dentists are required to confirm their qualifications every 5 years.
- Those who wish to improve their qualifications themselves must wait 3 years from the date of the last certification.
- Regulatory documents provide for three types of categories in ascending order:
- second (is basic);
- first;
- highest.
Requirements for various categories:
| Category | Requirements |
| Second | Work experience in the specialty for at least 3 years. Successful completion of certification. |
| First | Work experience in the specialty for at least 7 years. For a specialist with secondary education – at least 5 years. Successful completion of certification. |
| Higher | Work experience in the specialty for at least 10 years. For a specialist with secondary education – at least 7 years. Successful completion of certification. |
Popular questions
Here are some answers to some of the most common questions people have about specializing in dentistry:
If treatment is required, it will be painless
If, after all, a child is diagnosed with caries of a baby tooth, then of course it must be cured, and for this our doctors have many modern techniques in their arsenal.
To make the treatment comfortable, the doctor uses a mild, non-toxic anesthetic , which is individually selected for each child, taking into account age and allergy status.
Before treatment, we always refer children with a history of allergies to allergy tests to eliminate the risk of dangerous reactions to local anesthesia.
After the visit, our little patients always receive gifts and certificates for their courage, and parents are confident that the health of their children is under the reliable control of specialists.
How much does Euromed Kids cost?
Pediatric dentistry is different these days. Children need a special approach. The ability to get along with a child is not just important, but a necessary part of the work of a pediatric dentist, without which it will not be possible to earn the child’s trust.
Even the most gentle and anxious little patients will make friends with our dentists.
A calm atmosphere in the office is a guarantee that the child will take good care of his teeth, which means he will be willing to brush them and visit the doctor regularly. And, of course, all Euromed Kids dentists are excellent professionals who regularly improve their qualifications at the international level and follow modern technologies.