Computed tomography – technologies of the future for the health of your teeth!
Do you know what complex diagnostics is? What modern diagnostic methods allow you to obtain the most accurate data and the best results?
In modern dentistry, not only treatment methods are being improved, but also diagnostic methods. Any competent treatment begins with a full comprehensive examination of the patient. Dental computed tomography of the teeth has long become a mandatory and priority method for examining the jaws.
Improved devices provide unmatched accuracy and reduce the X-ray burden on the patient's health. This improves the quality of the examination and its safety.
Is it possible to do a CT scan with dental implants?
Unlike magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography allows for the presence of implants and dentures in the mouth. The material from which the structure is made matters.
Modern implants consist of inert metals (titanium, zirconium) and ceramics. They do not create interference and do not distort the final model with spots and shadows. Previously used “simple” metals change the appearance of the image, but a qualified specialist takes this into account when decoding.
When answering whether it is possible to do a CT scan with dental implants, let’s say yes, but be sure to notify the x-ray technician about the presence of fixed structures in the mouth.
Sign up for the study
What are CT scans and CT scans?
Previously, as part of a standard examination, patients were given a targeted X-ray of the tooth and an orthopantomogram. The latter is a panoramic image of the dental system, where you can see all the teeth, but this image has distortions.
With the advent of computed tomography, diagnostic options for doctors have expanded significantly. This is a method of x-ray examination that allows you to obtain a layer-by-layer image of the object under study. A computed tomogram (CT) is the result of an examination, a finished layer-by-layer image.
What is an x-ray?
This is one of the types of radiation. If you think that X-ray radiation is present only in the X-ray room, then we can say right away that you are very mistaken. Let's remember physics lessons. We receive small doses of radiation every day:
- outdoors, from a natural source of radiation - the sun;
- at home from household sources located in the apartment: from a TV, various gadgets, a refrigerator, etc.
Radiation is measured in sieverts. What is the rate of radiation that a person can consume? Acceptable is 1000 sieverts per year.
Now let's remember mathematics and calculate how many X-rays can be taken for a person. A targeted image of one tooth is equal to 2-3 microsieverts. You can take 300-500 x-rays per year. A panoramic photograph (all teeth) is equal to 16-18 microsieverts. You can take 60-70 x-rays per year.
Now let's look at computed tomography. 1 photo taken on this device is equal to 60-80 microsieverts. You can take 16-20 x-rays per year.
We are now considering the maximum dose limits for X-ray equipment. Our clinic has a radiovisiograph and a computer tomograph of the latest generation made in Germany. The load on the devices is reduced to a minimum.
Previously, when taking an x-ray, the exposure time (you hear it as a beep) was approximately 2-3 seconds. Now this time has been reduced to 0.05 seconds.
Now let's talk about household radiation. If you watch TV for 3 hours at a distance of less than 2.5 meters from the screen, you get approximately 0.5 millisievert, i.e. Watched TV for 5 days, get 1 x-ray. If you sit in front of a computer monitor for more than 3 hours, you get 1 microsievert, 1 x-ray. We flew by plane to Turkey, where the flight is 3-3.5 hours, you get 10 millisieverts or 5 targeted shots. And add radiation from TVs, refrigerators, microwave ovens and you will understand that you will not receive terrible radiation in the X-ray room.
What are the advantages of CT?
This examination gave rise to the study of the dental system not only externally, but also internally.
The most important aspect here is the ability to see the jaw from all angles, to objectively assess the size of any parts and objects, be it a tooth or an implant. CT also allows you to plan and simulate various situations in the oral cavity, for example, you can simulate dental implantation and see what size implants are exactly suitable for a particular patient.
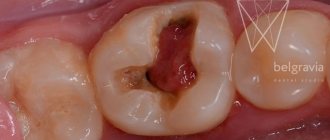
Often, a computed tomogram can detect cysts and neoplasms, as well as foreign bodies in the canals of teeth or see supernumerary teeth located in the jaw. Often, timely identification of such objects preserves the health of patients. If any deviations are detected, it is possible to prescribe targeted, adequate treatment as quickly as possible.
Experts highlight the following advantages of computer diagnostics:
- High level of quality and detail of the resulting image. Allows you to objectively assess the size of any formations, which affects the choice of treatment methods.
- The ability to create a three-dimensional model on a computer for further diagnosis and treatment planning. With this model on the computer, the doctor can at any time once again examine the analyzed area in detail from all sides.
- Identification of hidden inflammatory phenomena, foci of infection and foci of the pathological process, which may become a contraindication to one or another treatment method.
- More opportunities for implantation planning; implants can be placed on a 3D model and the required size and length can be calculated based on the individual characteristics of the jaw structure
- Expanded capabilities for orthodontists to assess occlusion and jaw relationships. This is very important for competently drawing up a treatment plan and selecting the necessary orthodontic treatment methods.
CT scan before implantation
Diagnostics using a computed tomograph before installing implants allows, first of all, to determine whether implantation is necessary at all. The image will give a complete picture, and the doctor will see where the teeth are missing, whether there are problem units, and whether they can be cured.
The 3D tomogram will show:
- hidden carious cavities;
- unerupted and “extra” teeth, which may interfere with the installation of artificial pins;
- properties of roots, canals - curved, narrow and long canals require a special approach, which should be taken into account before implantation;
- bone dimensions in height and width, on the basis of which the type and size of the implant is selected;
- condition of bone beams, partitions, voids in the jaw bone;
- the presence of inflammatory processes in the root area - cysts, granulomas, abscesses where implants are planned to be installed. All this needs to be treated or removed before surgery;
- inflammation in the paranasal sinuses and lacrimal ducts, which can become a temporary obstacle to implantation;
- density, size, inclination of the alveolar process, thickness of the cortical bone layer, taking into account which the optimal type of artificial pin is selected;
- the physiological structure of the maxillary sinuses, the mandibular canal to determine the angle of inclination of the implant rod;
- defects and anomalies in the structure of the dentofacial apparatus;
- quality of installation, strength of fixation of implants after surgery for their implantation;
- severity and nature of traumatic injuries in fractures.
Based on the results obtained, a virtual operation to install the rods is performed. The appropriate size of the titanium pin is selected, its inclination and the point of implantation are determined, bypassing the anatomical structures. Thus, the final outcome of implantation is modeled.
Next, the tomographic data is loaded into the computer, and the program creates a three-dimensional model. The patient’s personal surgical template is printed on a 3D printer - an overlay with guide holes for inserting rods.
During implantation, the template is placed tightly on the gums, and the placement of the pins is carried out with extreme precision.
What types of CT scans are there in dentistry?
Depending on the type of device, CT diagnostics is divided into:
- Cone beam
- Multispiral
- Sequential processing of layers
Only the doctor chooses which device to perform the diagnostic procedure on. This depends on the planned manipulations, since in some cases, diagnostics on another device can provide the doctor with all the necessary data for an accurate assessment of all possible risks.
Prices for cone beam magnetic tomography of the jaw in Moscow
A cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scanner at the LaLaDent dental medical center in Moscow allows you to perform a CBCT scan on the day of your visit.
The price list does not contain hidden fees: our patients will immediately find out the final price for diagnostic procedures on the website or in the dentist’s office. The cost of cone beam CT in the clinic is indicated in the price list. The cost of the study includes:
- dentist consultation;
- CBCT of both jaws;
- decryption by a specialist.
The results of the study are recorded on a CD, which is subsequently provided to the doctor for study. You can pay for diagnostics by card or cash.
Cone beam computed tomography can be booked online through a convenient feedback form or by phone. To do this, just call the contact number listed on the website. Our administrator will select a convenient day and time for your visit. Discounts on services are provided upon initial contact.
When is a CT scan performed?
Diagnosis of a specific area or the entire jaw depends on the purpose of the study and the suspected disease. Most often, CT is done in the following cases:
- Studying the structure of bone tissue before implantation
- Identification of hidden inflammatory processes in the peri-root zone of teeth
- Detection of hidden foci of inflammation and infection in the bone tissue of the jaws
- Diagnostics of soft tissues for neoplasms
- Determining the location of the injury
- Complete diagnostics of the dentofacial apparatus before starting orthodontic treatment
With the advent of new diagnostic methods, treatment methods have also improved. With the help of computed tomography of the upper and lower jaw, simultaneous implantation surgery became possible, and the risks of complications were reduced to a minimum. Accurate calculations and a clear vision of the actual situation allows complex operations to be performed with the lowest risks of complications both during and after the operation.
3D CT – what is this procedure and what is it for?
3D imaging of the jaw is one of the main dental procedures used in diagnosis. The data obtained allows us to assess the condition of a specific maxillofacial area and plan further treatment.
This diagnostic tool is universal; it is used by both therapists and orthopedists, periodontists and implantologists. Using a 3D image, the therapist assesses the condition of the roots and canals of the tooth, and clarifies the localization of the inflammatory process.
An orthopedist can examine the anatomical structure of the temporomandibular joints, an implantologist can examine the volume and density of bone tissue in the area of the upcoming operation, as well as the parameters of the maxillary sinuses (maxillary sinuses).
Sometimes a large part of the tooth remains, as they say, “behind the scenes”, and the dentist simply cannot see it. Then computed tomography comes to the rescue, which allows you to examine the hidden area and prevent unpleasant consequences for the patient.
Until recently, the “gold standard” for instrumental diagnostics was a panoramic image. Today there is a more advanced method in which the maxillofacial area is scanned using computer technology.
How is CT diagnostics performed?
Diagnosis begins with patient preparation. The specialist asks to remove all metal objects and jewelry to avoid interference and distortion of the results obtained. To protect internal organs from radiation, a special lead apron is worn.
To obtain the best image, keeping the patient still during the examination is very important. The chin is fixed on a special stand.
Then, after starting the device, a scanner with an emitting tube rotates around the patient’s head. At this time, the image begins to be transferred to the computer.
This procedure does not require any special preparation on the part of the patient.
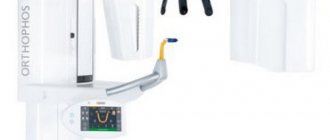
CT diagnostics in Dr. Lemberg’s dentistry means there are no contraindications, including for pregnant women and children. Doctors carry out diagnostics using the Planmeca device - this is 3D imaging with a lower radiation dose to the patient than with standard two-dimensional panoramic imaging.
Multispiral or cone beam?
A multispiral tomograph performs layer-by-layer scanning of an object along a spiral trajectory caused by the continuous movement of the table and the X-ray tube relative to each other.
Most often, MSCT - multislice computed tomography - is used in maxillofacial surgery for facial injuries and pathologies of the temporomandibular joint.
In dental practice, especially when planning implantation, this method is not widely used due to insufficient data accuracy. Since the patient lies down during the examination, the jaw connection is distorted.
In addition, the radiation level of MSCT can reach 1000 μSv, which is unacceptable, since implantological treatment involves more than one procedure over several months.
Cone beam CBCT is a more modern, accurate and safe method compared to MSCT. Its radiation exposure is less, about 25-50 μSv, which makes it possible to carry out the procedure several times a year.
Interpretation of computed tomogram
The doctor can evaluate and interpret the results immediately. Initially, the specialist evaluates the overall picture based on images of 3D models of the jaws. Then moves on to the area of interest. It is important to assess the condition of the tooth and adjacent tissues if a CT scan of one tooth was performed. Determine the number of roots and their condition, the structure of the bone tissue near the tooth, and also consider the presence of inflammation around the roots of the tooth. This determines treatment tactics and helps assess possible risks.
Before starting orthodontic treatment, the doctor evaluates the occlusion on a computer model, and also selects the necessary angles of layer-by-layer images and makes calculations to select an orthodontic apparatus or system.
The quality of the images obtained directly affects the objectivity of the assessment of the actual condition of the oral cavity. And it can radically change the intended treatment plan.
Indications
Computed tomography is prescribed to identify:
- hidden carious lesions;
- defects in the structure of the jaw and dentition;
- fully or partially unerupted teeth;
- dystopic dental units with incorrect location or direction of growth;
- supernumerary teeth;
- damage to the dentition due to jaw fractures and other injuries;
- pathologies of the temporomandibular joint TMJ;
- tumors, cysts and other neoplasms in the jaws;
- condition of periodontal and periodontal tissues in case of gum disease, inflammation in the root area;
- number of roots, canals of teeth;
- cracks in the roots of teeth;
- features of the structure of bone tissue before jaw surgery (installation of implants, bone augmentation).
A 3D photo must be taken before dental implantation. The fact is that the jaw bone is clearly visible on a regular x-ray, but it does not allow assessing the soft tissues. On a three-dimensional tomogram, you can see in detail not only the bone, but also the nerve of the lower jaw, as well as blood vessels.
A 3D tomogram is much more informative than a panoramic image or targeted photographs of all teeth.
How much does a CT scan of teeth cost in Moscow dentistry?
At Dr. Lemberg's Dentistry, the service of cone beam tomography of teeth costs 4,000 rubles. When conducting such diagnostics, the quality of diagnostic equipment and the professional knowledge of the medical personnel performing this examination are very important.
When thinking about where else you can get a dental CT scan in Moscow, you should mention specialized diagnostic centers. If diagnostics are carried out outside the clinic, the time required to transfer the results to the doctor and interpret them increases significantly. If you carry out the diagnosis immediately in the clinic, you can develop a competent treatment plan during the consultation and make a correct diagnosis.
Advantages of the method
CBCT has many advantages that set it apart from other diagnostic methods. First of all, tomography provides high information content and accuracy of the study without distorting the data, thanks to which the doctor receives sufficient information about the shape, size, structure and anatomical features of the patient’s dentofacial apparatus.
Other benefits:
- insignificant radiation exposure, which is comparable to air travel: 10 cone-beam scans are allowed to be safely performed per year;
- safety for children and adults, including pregnant women (the procedure is allowed to be done in the 2nd trimester);
- minimal time to complete the study - the procedure itself takes only half a minute (so even a child can withstand it), another quarter of an hour is required to load, process and save data;
- absence of discomfort - to conduct the study, the patient only needs to clamp a special bite block with his teeth;
- the ability to save data, due to which the doctor can return to the study results at any time and re-examine the area of interest.
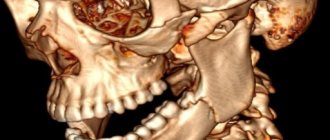
The use of a tomograph makes it possible to obtain an accurate three-dimensional reconstruction of teeth and maxillofacial structures, including the TMJ, bones of the facial skeleton and the base of the skull, which no other x-ray diagnostic method can provide.
Thanks to CT, the doctor can see the structure of interest in the required projection, at the desired depth and at any angle. Such diagnostics help the doctor make an accurate diagnosis, draw up a treatment plan, and predict the outcome of manipulations or illness.
How often can a CT scan be done?
The radiation dose for this type of research reaches only 70 μSv. While the figures for established standards for adults reach 1000 μSv, for children under 15 years of age it is 300-400 μSv. Thus, this procedure can be repeated up to 14 times a year. Most often, CT scans are performed for dental implantation at the planning stage and then after surgery. And it is completely harmless to health. The radiation dose is very low, allowing multiple examinations to be performed in short periods of time.
In order to prevent the development of complications and inflammatory processes after operations, CT scans are performed 1-2 times a year. Observation in dynamics makes it possible to evaluate the course of healing processes and see changes in the structure of the bone tissue of the jaws.
Thus, computed tomography as a diagnostic method is often mandatory. It allows you to make the correct diagnosis as quickly as possible and begin adequate treatment. Allows the doctor to see more detailed information about the health of specific teeth and the dental system as a whole. It also helps to identify inflammatory and tumor processes at the initial stages and minimizes their harm to the patient’s health.
At Dr. Lemberg's Dentistry, multidisciplinary specialists with extensive experience will not only conduct a full-fledged comprehensive diagnosis, but also draw up a professional treatment plan with the involvement of doctors of all necessary specialties to ensure that your treatment is as effective as possible.
CT scan of the jaw: what it shows, how it is done, radiation doses
Dental computed tomography is an important part of diagnostic procedures in the dental field. This is a very informative method that allows you to see the structural features of the jaw, dentition, and also identify pathological processes. Previously, X-rays were used for this, but CT is a more advanced diagnostic method that allows you to get the most accurate picture.
3D dental diagnostics are carried out using a tomograph. In one procedure, you can obtain detailed information regarding the condition of the dentition. The main feature of this method is a three-dimensional image that allows you to see the object under study in full. This is extremely important for making an accurate diagnosis and drawing up a detailed treatment plan.
Content
- The main advantages of dental tomography
- Indications for CT scanning
- Main contraindications
- Is it harmful to have a dental CT scan?
- How often can a dental CT scan be done without harm to health?
- Basic rules of preparation
- How are dental CT scans done in specialized clinics?
- What does this procedure show?
- Computed tomography after implant installation
- Which is better - CT or X-ray?
- Computed tomography of the jaw in St. Petersburg
The main advantages of dental tomography
Compared to other diagnostic methods, computed tomography has the following advantages:
- The entire procedure lasts no longer than 1 minute.
- High level of information content.
- CT is safe for the patient’s health, so it can be performed repeatedly if necessary.
- The high quality of the image in the image allows you to clearly see the structural features of bone tissue.
- The radiation dose received is minimal.
At the end of the procedure, the resulting 3D image is recorded on a CD with universal software, which is installed automatically on the attending physician’s computer for the purpose of further diagnosis.
Indications for CT scanning
The information obtained after a CT scan is necessary to solve a number of problems in the field of dentistry.
The procedure is carried out in the following cases:
- Damage to the jaw after minor injuries. It is with the help of CT that dislocations and fractures can be determined.
- Detection of pathologies in the structure of the dentition. This procedure is commonly used before any type of orthodontic correction.
- Drawing up a computer model of the jaw for the manufacture of an individual brace system.
- As a preparatory procedure before the upcoming operation.
- Presence of neoplasms in the jaw.
- Diagnosis of hidden caries.
- Complications in the dental canals.
- Monitoring the success of previous treatment.
A CT scan is performed before dental implantation, because based on a 3D image, a suitable implant is selected, its installation is carried out and the quality of the procedure is checked.
Main contraindications
During the procedure, the body is exposed to a certain dose of radiation, so computed tomography is not performed during pregnancy. As for women during lactation, the procedure is possible, but after its completion it is forbidden to breastfeed the baby for 24-48 hours.
It is prohibited to perform dental CT scans on preschool children. In this case, alternative diagnostic methods are used. The same applies to patients with a pacemaker.
Is it harmful to have a dental CT scan?
Computed tomography is based on the principle of passing x-rays, with the help of which a series of layer-by-layer images are produced. Accordingly, a certain radiation dose is present during a CT scan of the jaw. It depends on the number of images and the total area of study.
When examining the chest and abdominal cavity, this figure is 11-14 mSv. The critical level for one procedure is 50 mSv (the maximum permissible annual dose is 150 mSv). If this figure is exceeded, there is a high risk of developing cancer.
So is it harmful to have a CT scan of your teeth? The study of this area is considered the most gentle, because the radioactive dose during the procedure is only 0.1-0.3 mSv. Therefore, computed tomography is absolutely safe for the health of patients (except in cases of contraindications).
How often can a dental CT scan be done without harm to health?
Despite the fact that a dental CT scan exposes the body to a minimal dose of radiation, there is no need to overuse this procedure. The frequency of the procedure depends on the degree of need for this, but it must be taken into account that radiation can accumulate in the human body. Therefore, the standard frequency of procedures is no more than 2 times a year.
But there are times when it is necessary to exceed the permissible limit. Based on the permissible radiation exposure, CT scans of the face and jaw should be performed no more than once every 2-3 months.
Basic rules of preparation
There are no special requirements that must be strictly observed before tomography of the dental jaw. It is better not to eat for three hours before the procedure.
The remaining requirements are standard, as in the case of x-rays. You will need to remove all jewelry and objects containing metal. This is necessary to obtain the most accurate research results.
How are dental CT scans done in specialized clinics?
Compared to the old X-ray machine, the tomograph is much more compact. A CT scan can be performed lying down, standing, or sitting. The choice depends on the physiological characteristics of the person, his age, as well as the type of pathology itself.
In cone beam computed tomography, the patient's head is placed between two scanners. To ensure maximum immobility, clamps are provided for the jaw, chin and temples. To understand how a dental CT scan is done, we will describe the procedure in stages:
- The procedure is carried out standing, the platform for fixing the jaw, chin and temples is set in accordance with the patient’s height, and a protective lead vest is put on before the procedure. The head is placed on a special tomograph stand and pressed against the equipment rack. And in this position it is fixed by means of stabilization.
- After preparing the patient, the specialist turns on the tomograph. The moving part of the device rotates around the patient's head. During the entire procedure, about 200-300 images are obtained, which are immediately displayed on the monitor.
- During the procedure, the patient may hear noise - this is quite normal and there is no need to be afraid of it. When it subsides, you do not need to immediately remove your head from the platform or make other movements; you must wait until the x-ray technician reports the end of the study and asks you to leave the scanning area.
During the procedure, the patient does not experience pain or any discomfort. The only discomfort is the forced need to remain immobile. Also, for 10-20 seconds during the image, the patient can feel the heat emanating from the moving scanners.
CT scan of the jaw: what does this procedure show?
The resulting CT image of the teeth is a three-dimensional image of the jaw, which is obtained using hardware positioning and the use of a three-point fixation system.
Computed tomography of teeth allows you to clearly see all pathological processes and disorders in the structure of bone tissue. With this study you can see:
- Crowns and fillings.
- Condition of the paranasal sinuses.
- Location of canals, roots and unerupted molars.
- TMJ condition.
- Various pathologies of the jaw.
The high accuracy of the results obtained allows us to accurately determine the nature of the pathology. If a CT scan is performed for dental implantation, then layer-by-layer images allow you to get the clearest picture of the condition of the maxillofacial area in different projections. The specialist sees the maxillary sinuses, canals, TMJ and blood vessels.
This type of research is the most accurate source of information about the dental system. Only with the help of CT can you correctly plan the upcoming implantation procedure. If you do not use CT, there is a high risk of installing a smaller implant, which will lead to unnecessary stress on the bone tissue.
Computed tomography after implant installation
Quite often the question arises: is it possible to do a CT scan with dental implants? Unlike magnetic resonance imaging, when foreign bodies can produce a “phonic effect,” there is no such problem with computed tomography. Moreover, it is not only allowed, but recommended after implantation.
CT is necessary in the following cases:
- Identification of the reasons for the instability of the installed structure.
- If you need to determine whether the artificial root has taken root or not.
- Determination of the quality of implantation performed. This is especially necessary if computer modeling of the jaw was not carried out at the preliminary stage.
- Identification of complications hidden during visual examination.
If the patient has metal crowns installed, then preliminary consultation with a specialist is necessary. The fact is that metal elements can create unwanted optical effects in images, which will complicate diagnosis and diagnosis.
Which is better - CT or X-ray?
Computed tomography is considered one of the most informative diagnostic methods used in dentistry. Using this method, it is possible to obtain a multilayer image of the area under study. A 3D image is much more informative compared to a conventional X-ray, which only provides a planar image.
From the point of view of affordability, x-rays are preferable, but they do not always provide an accurate picture of the condition of the dental-maxillary system. As practice shows, if a CT scan is performed, then in 99% of cases it is possible to accurately determine the cause of toothache and other symptoms.
Computed tomography of the jaw in St. Petersburg
If the doctor has prescribed a CT scan for you, but you don’t want to wait and sit in lines, then X-ray will offer you to undergo this study on their newest tomographs. The procedure takes no more than a minute, is absolutely painless and effective.
Today we told you how a CT scan of the jaw and teeth is done without negative consequences for your health. You can also record the examination results on a CD, send them by e-mail and make an online appointment. You can find out more detailed information by phone.
Sign up for a study by phone
+7 (812) 332-52-54
How to read the results of a CBCT scan of the jaw?
After the patient receives a disk with a CBCT study, he must give it to the doctor for decoding. A person without special knowledge will not be able to independently understand what is depicted on layer-by-layer sections. In addition, to view the information saved in the file, you need a special program - a CT viewer.
However, CBCT data can provide the doctor with the following information:
- the presence of carious lesions and the depth of damage to dental tissues;
- information about the number, length and location of root canals, their anatomical features;
- the presence of foreign bodies in the root canals and jaw bone;
- quality control of root canal filling;
- condition of dental roots and periodontal tissues, presence of cysts, granulomas, abscesses, fistulas;
- condition and type of bone structures of the upper and lower jaw, location and condition of the paranasal sinuses;
- assessment of the readiness of the dental system for implantation and sinus lifting;
- planning surgical interventions on teeth and bone structures of the jaw;
- condition of the temporomandibular joint to identify functional and morphological disorders.
Having deciphered this information, the doctor can plan treatment and make a prognosis regarding the outcome of the disease. Changes after therapy may also be monitored.
Raw result
The raw result is an uncompressed array of information of several hundred megabytes about the layer-by-layer scanning image in the form of voxel models (allowing you to create 3D objects with insides) obtained during the research process.
Volumetric images allow you to reconstruct the structures of the area under study. Having studied them, the doctor can draw a conclusion about the morphological and functional state of the anatomical structures.
Processed result
The processed result is the visualization obtained after opening a file with a voxel model using the CT viewer. This is a program that allows you to view files saved in the universal general medical format DICOM.
By opening the image, the doctor can take the necessary measurements and view structures in different projections. If necessary, the dentist can build three-dimensional models and sections of structures included in the area of interest.
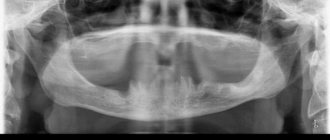
Sample pictures
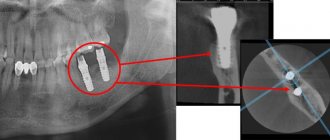
The picture shows sections of the lower jaw with a zone of interest in the area of 33 – 36 teeth. They show the bone structure, the configuration of the root canals, and the location of the teeth relative to each other.
This 3D image was taken in connection with the removal of the 36th tooth. The condition of the alveolar socket is visible, as well as the anatomical and structural features of the bone and adjacent teeth of the lower jaw. In addition, the images visualize the mandibular canal.
The photographs were taken to control the position of 5 upper jaw implants (14, 15, 16, 24, 26) and 4 lower jaw implants (45, 46, 35, 36), as well as monitor the condition of the bone tissues of both jaws. The images show the distance from the upper implants to the bottom of the maxillary sinus and from the lower implants to the mandibular canal. Also visible on the lower jaw is a fixed structure supported by teeth 33–34 and 43–44.
Interpretation of results
There are no standard descriptions of CBCT examination results. This is explained by the variety of anatomical and structural features of the structure of the dentofacial apparatus of each person. Therefore, in each case, when receiving three-dimensional research results, the doctor interprets them taking into account the picture he sees.
The dimensions, location, shape, symmetry, structure, structural features of certain dentofacial and facial formations are described. Pay attention to the presence of pathological changes on the roots of the teeth and in the bone tissue of the jaws, the condition of the paranasal sinuses and soft tissues of the oral cavity.
This takes into account the presence of structures in the oral cavity that can distort the picture (for example, metal-ceramic crowns), as well as the influence of the human factor on the scanning results. The sum of this information describes the real picture of the dental system, on the basis of which the doctor draws appropriate conclusions, analyzes the treatment performed or plans further treatment.
Author: Family doctor Chervenakova Vladislava Gencheva