Pulpitis and periodontitis: clinical picture of the development of caries and its complications
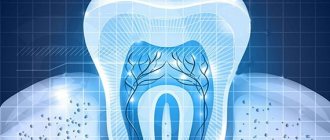
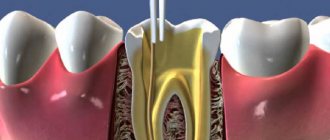
If we talk about the structure of a tooth in a simplified way, then it has a crown part that protrudes above the gum, and a root (or several roots) that hold the tooth in the bone tissue of the jaw.
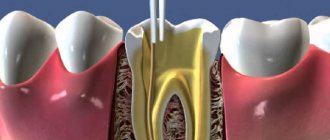
Inside, under the enamel layer, the tooth is filled with dentin, in the thickness of which there is a small space. There are nerve endings and blood vessels that supply the tooth. They enter the root canal through the apex, fill it from the inside, and also occupy a small space in the crown of the tooth. The neurovascular bundle inside the tooth is the pulp. If you delay the treatment of caries, pathogenic microorganisms will begin to penetrate the pulp, causing its inflammation. This complication caused by caries is called pulpitis. With this disease, the pulp swells and puts pressure on the nerve. This is why the pain is so intense. The difficulty of pulpitis in root canal treatment sometimes lies in the fact that the teeth are connected by nerve endings and it can be difficult to immediately determine which of them is causing the pain.
When the pain does not go away, and also intensifies at night, this indicates that the inflammation has gone further - into the root canals of the tooth. If you do not treat the tooth canals during pulpitis, and try to drown out the pain with medications, then the infection from the root canals will spread to the bone tissue of the jaw.
The inflammatory process that begins in the bone around the apex of the root is called periodontitis. Treatment of canals for periodontitis and elimination of bone inflammation itself is much more difficult. Here you absolutely cannot delay contacting a specialist, otherwise the inflammation will quickly spread and intensify. Or it will become chronic, in which the infected area of the bone is replaced by granulomatous tissue or granuloma. As a result, the tooth most likely cannot be saved. This process is very dangerous: you can not only lose a tooth, but also provoke serious health problems.
Deep caries is a potential pulpitis, followed by periodontitis. A simple examination 1-2 times a year will preserve the health and beauty of your teeth, nerves and money. Since canal treatment for pulpitis and periodontitis is not the easiest, and also not cheap. In addition, there is a high risk of complications and tooth extraction in advanced cases.
Different clinics mean different prices for services: what exactly are you paying money for?
Depending on the price-quality indicator for the services provided, all dentistry can be divided into three categories:
- Budgetary organizations (clinics, hospitals);
- Private economy class clinics;
- Private business class clinics.
Advantages of a budget organization:
- Free treatment or low price for services (as a rule, only the cost of paid materials is taken into account);
- There is no need to sit in a chair for a long time, the reception is as quick as possible.
Minuses:
- In general, the quality of services is relatively low due to the constant rush of the doctor, insufficient technical equipment, lack of materials and often the professionalism of the dentist himself.
- Long waits in queues, where you can often hear things that will dissuade any desire to go to the doctor.
- Rudeness and poor attitude towards patients are, unfortunately, not uncommon in many clinics and hospitals.
- There is no guarantee for root canal treatment or permanent filling.
As a result of poor-quality treatment of three-channel pulpitis in a budget organization, the following problems may arise in a short time:
- pain in the tooth due to poorly washed, unfilled canals or due to removal of the filling material beyond the root (it will be painful to bite);
- swelling of the gums and cheeks due to missed canals (with infection), or a fragment of a dental instrument left in the canal, which is also not uncommon (see photo below);
and etc.
The mistakes of a budget doctor can be listed endlessly, but it is worth remembering that there are many doctors, even in hospitals and clinics, who are provided with materials and have a high level of professional qualities that allow them to treat even three- or four-channel pulpitis at a fairly high level, although today This is rather an exception to the rule.
Advantages of an economy class private clinic:
- Availability of services for people with average incomes;
- No long queues;
- As a rule, the doctor’s professional level is quite high;
- Availability of necessary equipment and materials for the implementation of economy class services;
- Guarantee for root canal treatment and filling.
Minuses:
- Lack of maximum quality control of treatment at all stages (the risk of complications after canal filling can be described as average);
- The materials are not good enough for artistic restoration and often do not allow the filling to be completely invisible to others.
A business-class private clinic, unlike previous options, allows us to provide very high-quality services thanks to the availability of modern equipment and highly trained qualified dentists.
The use of a microscope, as an intermediary between the doctor and the patient’s tooth, significantly increases the already considerable price for the treatment of pulpitis of a three-canal tooth. However, thanks to such equipment, the patient can forget for the rest of his life that treatment was once carried out in the canals of his tooth, and he will only occasionally have to come to the dentist to examine the condition of the filling.
There are often situations when a patient, having contacted a local clinic, loses a tooth within a year or two due to a cyst that has developed on the root, and ends up undergoing expensive prosthetics for the missing tooth at a price even higher than the treatment of three-channel pulpitis, but in a business-class clinic .
There are also cases when, for example, 5-7 years after treatment of pulpitis in an economy class clinic (for about 6-7 thousand rubles), it is discovered that against the background of a fragment of an instrument left in the canal, a huge granuloma has developed on the root, due to where it is not possible to save the tooth. In such a situation, it is already difficult to say for the patient what is better for him: to lose a tooth in 5-7 years and deal with expensive prosthetics or implantation, or immediately go to a business-class clinic, where treatment of pulpitis of a three-channel tooth will cost around 12-14 thousand rubles, but such a tooth will last almost the rest of its life.
Interesting video: treatment of pulpitis of the upper tooth, which turned out to be not three-channel, but 4-channel
Root canal treatment
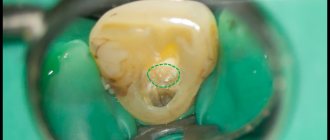
Before you begin root canal treatment, you need to take a photo. The fact is that in order to draw up an effective treatment regimen, the doctor needs to see the individual clinical picture of the disease: how deep the infection has spread and whether changes have begun in the bone tissue, how many roots the tooth has, perhaps the canals are too narrow and/or sclerotic. During treatment, it will be necessary to take more pictures to ensure the quality of the work done and the density of filling the canals with filling material. Only after making sure that everything is done correctly and efficiently will the doctor perform the final manipulations and restoration of the crown.
Treatment of root canal pulpitis
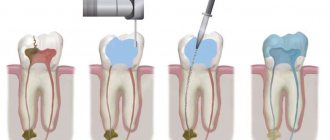
If no pathological changes in the bone tissue near the apexes of the roots are detected, then the canal treatment is performed according to the traditional scheme:
- Anesthesia with modern anesthetics. The drug is selected individually for each patient.
- Using a bur, the dentist removes tissue decay and opens the entrance to the pulp chamber.
- Then he needs to find the entrances to the channels, which is not always easy.
- Using special instruments and medications, the doctor removes the pulp from them, washes them, disinfects them from infection and dries them.
- The canals must be hermetically filled to the full depth with special filling materials - gutta-percha and polymer cement.
- Immediately after filling the canal, you must wait several days. Therefore, first the doctor places a temporary filling, and at a second visit he will restore the anatomical shape of the tooth with a modern photopolymer filling. Restoring the crown of a tooth after root canal treatment is a responsible task, the correct execution of which determines the reliability of the restoration and its service life. Often, the tooth is additionally strengthened with a pin, fixing it in the root canal.
Treatment of canals for periodontitis
It is not always possible to save a tooth if periodontitis has already developed. But with timely seeking help and proper treatment, the chances of a favorable outcome are quite high.
First of all, it is necessary to ensure the outflow of purulent mass from the inflamed area. Only after its elimination can treatment and filling of the root canals of the tooth be performed. Thanks to modern antiseptic drugs, it is possible to completely eliminate the infection from the affected area. However, in cases where the canal is too narrow to ensure the outflow of pus, it is not possible to save the tooth - it is immediately removed.
After the first stage of treatment, the patient is also given a temporary filling, with which he remains for about a week. You may need to undergo a course of antibiotic therapy. At the follow-up appointment, a thorough diagnosis is carried out. If no complications are identified, then the doctor installs a permanent filling and restores the tooth. Or prescribes further treatment based on diagnostic indications.
How many canals are there in each tooth?
The number of dental canals and nerves is determined by the doctor. Their number does not always correspond to the number of roots of a dental unit. The dentist can determine the exact amount using an x-ray (see also: what is a photograph of all teeth called and how is it taken?). On average, there are from 1 to 3 of them, 4 are less common. The upper “eights” (wisdom teeth) can have 5 canals, which makes their removal extremely difficult. The “eights” of the lower jaw contain no more than 3 cavities.
Root canals are distinguished by structure and divided into different types:
- I. They have a simple anatomy, starting at the base of the pulp chamber and going to the apex of the root. Therapy is not difficult.
- II. Two canals that have a common origin at the bottom of the pulp chamber and merge into one at the apical foramen.
- III. At the base of the pulp capsule, a wide orifice opens, from which one passage emerges. In the lower third of the root, it is divided into two paths, which connect at its base and end in a common exit.
- IV. Two independent canals of simple anatomical shape, each with its own apical foramen.
- V. One canal is located inside one root. Near the top it is divided into two independent entrances. It can be difficult for the dentist to treat them to the apical foramen.
- VI. 2 canals extend from the bottom of the pulp, merge into one at the base and diverge again, opening with separate apical openings.
- VII. The root canal originates from the bottom of the pulp chamber, narrows at the middle of the root, distributing into two cavities that connect at the apex, and again branch into two separate ones (resembling the shape of a chain link).
- VIII. There are three independent direct channels in one root. From a morphological point of view, their structure is very simple, but the frequency of distribution is low.
- IX. The three root cavities of the tooth diverge and merge at the base into one with a single morphological exit. This anatomy is found in third molars.
Upper jaw: incisors, canines, premolars and molars
Lateral, additional branches can depart from the main ones at any level and have a simple and rather complex configuration. Important indicators and characteristics are shown in the table:
“Clinic of Your Dentist”: root canal treatment with care for each patient
The prognosis for the quality of treatment of tooth root canals for pulpitis and periodontitis directly depends on their structure and the degree of development of the disease. Treatment of dental canals in complex cases especially requires good equipment, high-quality medicines and materials, as well as extensive practical experience from the doctor.
“Clinic of Your Dentist” fully meets even the most stringent requirements for the quality of services and the professionalism of its specialists. Conducting effective root canal treatment and saving the patient’s tooth is our main task, which we successfully cope with!
Tooth root: structure, length, purpose
The root of each tooth is located in its own alveolar cavity, hidden by the gum. It (like a tooth) consists of dentin, covered on the outside with cement - bone tissue that comes into contact with the enamel next to the dental neck. The entire structure, together with the connective fibers, forms a shell between the alveolus and cement (periodontium).
Depending on the location, the root can be single or branched. Normally, the maximum number of root cavities is 4. Their length depends on the size of the tooth; it necessarily reaches the bundle of vessels and nerves of the alveoli, from where the unit receives nutrients. It is determined using an apexlorator probe, which is immersed in the hole until it jams.
The main function of the root is to secure the tooth in the gum, for which a strong ligamentous apparatus is provided. Its channels provide access to the nerves, arteries and veins to the coronal part. Thanks to this, the tooth receives nutrition, develops, and is sensitive to external influences. Due to innervation, the tooth is a full-fledged organ located in the oral cavity.