Causes of structure failure
Can a dental bridge fall out immediately after installation? The reasons that a permanent dental bridge falls off after a few days, weeks (less often, months) most often lie in errors in its manufacture or fixation. But the patient’s own fault may also be present here. Let's take a closer look at the factors that cause loss in the early period:
- the use of low-quality cement or its incorrect application,
- the presence of a gap between the inside of the prosthesis and the supporting teeth on which it is placed,
- caries under crowns: this may be undetected caries - it was not noticed during preparation for prosthetics. Or when the supporting tooth was overheated during turning. If, during the passage of root canals, they are poorly processed or sealed, then over time this leads to the spread of infection,
- allergy to prosthetic materials,
- if the patient chewed something very hard with his teeth (including artificial ones), chewed toffee, toffee.
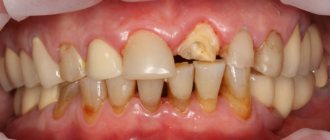
Another reason for loss is poor oral hygiene, when a large amount of plaque and stone accumulates around the crowns. This in itself can lead to the destruction of the ceramic or composite coating of the bridge and partial crumbling of the cement composition. If we consider that dental deposits are inhabited by bacteria that have a negative effect on the gums and roots of the teeth under the prosthesis, then loss can occur due to progressive caries on the supports.
Relationship between loss and service life
Dental bridges can fall out due to natural wear and tear or the end of their life. On average it is 5 years. And with good oral hygiene and careful treatment, the bridge will last up to 10 years. If the bridge is supported by implants, the service life increases. For ceramic and metal-ceramic it is at least 10 years, and for zirconium dioxide and ceramic-composite – from 20 years.
“My mother built golden bridges for herself back in the 90s. So, they stayed with her for almost 20 years. Either the doctor was such a good one, or she was taking care of her teeth. But she definitely never ate nuts. And I installed metal-ceramic ones in 2014. And they fell out after only 6 years. The doctor was able to glue them in place, but I understand that it is no longer so convenient. We'll probably have to change it."
Anastasia G., review from gidpozubam.ru
Technique for predictable removal of cemented implant-supported dentures
Show menu
- Lectures
- Conferences
- Courses
- Publications/Scientific work
- Abstracts of foreign articles
Abstract compiled by: Abstract compiled by: Bisyaev G.K.
Schweitzer DM, Berg RW, Mancia GO. A technique for retrieval of cement-retained implant-supported prostheses // J Prosthet Dent., 2011.-Vol.106(2).-P.134-8.
The ability to remove prostheses is an important aspect of treatment due to potentially unpredictable biological or mechanical complications. Cement-retained implant-supported dentures with predictable removability increase the clinician's ability to care for, repair, and, if necessary, replace these dentures. The procedure can be performed on either custom abutments or factory abutments for single or bridge restorations. This technique requires metal at the interface between the abutment and the crown and involves the use of a flathead screwdriver to facilitate removal of the prosthesis.
Technique. Make a model of self-polymerizing acrylic resin for a castable screw-retained abutment, with the ideal dimensions of the prepared tooth (Fig. 1). Make a lingual-palatal shoulder approximately 1 mm above the gingiva and follow the contour of the gingival margin (Fig. 2). Mill the lingual-palatal groove in the abutment (Fig. 3).
Prepare a slot at least 1 mm deep and 3 mm wide (mesiodistal), creating enough space to insert the functional tip of a flathead screwdriver to be used for removal (Figure 4). Pack and cast a custom type 4 gold alloy abutment. After unpacking and cleaning, mill the custom abutment to the ideal size and shape using a milling machine, then sand and polish it. Make a substructure of self-polymerizing resin over the custom abutment with a minimum thickness of 0.5 mm. Heat the functional tip of the screwdriver over a fire and place it within the light wax along the length of the abutment arm. Apply pressure until it contacts the axial wall of the milled abutment (Figure 5), creating an open crown edge that is approximately the size of a screwdriver (Figure 6).
Clean, pack and cast gold alloy wax modeling for cermets. Immediately after casting, unpack and process the frame. Apply ceramic as usual. After fitting, fitting and final polishing, secure the denture intraorally with cement. Remove excess cement from everywhere, including the groove. Fill the groove with resilient composite material (Fig. 7).
To remove the denture, remove (if necessary) excess composite material from the groove using hand tools such as a scaler or probe. Then install a flat-head screwdriver with a torque wrench into the groove, press with your finger and apply a force of 32 Ncm while controlling the force. The cement will break and the prosthesis will be removed (Fig. 8, 9).
Discussion
. The presented technique describes the production of cemented prostheses on implants with predictable removal. The release slot allows the flathead screwdriver, when rotated in the slot, to simultaneously apply force coronally away from the abutment and an apical force onto the abutment sufficient to break the cement and separate the two components. Also, the groove can be placed in the area of the angle of the mesiolingual line of the lateral crowns to improve clinical access. During bridge fabrication, this type of crown removal mechanism can be incorporated into multiple parallel milled abutments with a convergence of 4 to 6 degrees each to allow successful removal of the prosthesis when necessary (Figure 10). To remove the bridge, the grooves can be used one at a time to ultimately destroy the entire cement layer (Fig. 11,12). The use of higher hardness gold-containing alloys for the custom abutment and for the prosthetic framework helps in preventing significant distortion of the groove. These alloys are also more resistant to corrosion and have less potential for local toxicity to the tissue around the implant.
Conclusion. The predictability of removal of cemented implant-retained prostheses is a clinical problem. The presented technique includes a design feature that allows these prostheses to be easily and predictably removed to facilitate required maintenance and repair or replacement of the prosthesis by the physician.
Rules of conduct when a bridge falls out
What to do if a dental bridge falls off? Often people get lost and don’t know how to behave. Someone almost begins to panic, someone hastily throws the fallen orthopedic structure into the trash. The list below includes simple and understandable rules that will tell you what to do when a dental bridge falls out:
- carefully spit everything out of your mouth onto a napkin if it falls out while eating,
- rinse your mouth with water and then with some solution (chlorhexidine or mouthwash),
- rinse the bridge in clean water, you can clean it with a soft bristle brush: when rinsing and cleaning, make sure that it does not fall into the sink or onto the floor,
- place the prosthesis in a clean handkerchief or piece of sterile bandage,
- put the bridge in a small, clean container so as not to accidentally break the product (in case it can be glued back, although this is unlikely). You will need to take the prosthesis to the clinic in the same container,
- try not to chew on the “affected” side, and also rinse your mouth after each meal (if there is still a lot of time before your visit to the clinic).
When the bridge falls out from clenching the jaws, from pressing with the tongue - that is, when there was no food in the mouth, then immediately go to point number “2” of this list.
If it suddenly turns out that the bridge was swallowed along with food or liquid, then you need to immediately contact a clinic - for example, a therapist, pediatrician, or a hospital emergency room. The sharp edges of the structure can injure the gastrointestinal tract; the bridge can get stuck in the esophagus or intestines. Therefore, you will need to undergo an x-ray or ultrasound. It is important not to make active movements, not to bend over and to adhere to the diet prescribed by the doctor - so that the structure leaves the body naturally. Otherwise, you will have to undergo emergency surgery.
Is it possible to glue the bridge in place yourself?
What to do and how to secure a dental bridge if it falls out at home? Let us immediately point out that putting a fallen bridge back on your own is not the best idea. Since this can injure the supporting and neighboring teeth, harm the gums (if you suddenly decide to glue the bridge with pharmaceutical cement or household glue). The consequences can be unpredictable - up to the removal of “damaged” teeth or implants. Therefore, it is better to entrust your teeth to a professional dentist.
Repair of dentures
General dentist Viktoria Aleksandrovna Vetrenko tells. The doctor conducts an appointment in orthopedic dentistry.
Daily chewing stress, inappropriate hygiene products, improper care or injury can lead to failure of the orthopedic structure.
Why does a denture break?
Here are the most common causes of breakdowns:
- Poor quality prosthesis care;
- Excessive chewing load on the denture;
- Injuries, blows;
- Falling of the prosthesis onto a hard surface;
- Destruction or loosening of the supporting tooth;
- The service life of the prosthesis has expired;
- Initial design defects or poor quality materials;
- The technology for fixing the prosthesis is broken.
What to do if your denture breaks?
Contact the dental clinic and describe your situation. As a rule, administrators know which problems require immediate solutions. They will tell you whether you should wait for a convenient time with your doctor or whether it is better to make an appointment at the earliest available time.
If a crack appears on a denture of any kind, you should see a doctor as soon as possible. Try to use the denture as little as possible: chew on the other side of the jaw, and remove the denture if possible.
Which doctor repairs dentures?
To have your denture repaired, contact your orthopedic dentist . He can solve some minor problems right there at the reception. Others will require the work of a dental technician. And if retreatment of abutment teeth is required, the doctor will refer you to a dentist-therapist, but will first cover the abutment teeth with temporary material to isolate them from the chemical effects of food.
Urgent repairs - if there is a laboratory
Check with the administrator whether this clinic or this branch has its own dental laboratory. Then the doctor will be able to immediately put the prosthesis to work, and after 1-2 hours the structure will be repaired and returned to its proper place in the oral cavity.
Ceramic crowns, bridges, veneers and inlays
Here we will talk about situations where repair of permanent structures made of metal ceramics, press ceramics and zirconium dioxide is required.
Appearance has deteriorated. During wearing, scratches, yellowing and other aesthetic defects may appear. The doctor will quickly fix this at your appointment: he will clean and polish the surface.
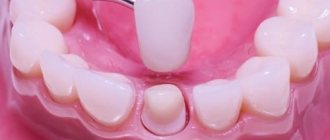
Cracks and chips . If the supporting tooth is not damaged, then the help of a technician is not required to repair a chipped ceramic or crack. The doctor will glue the crack, return the fallen piece to its place, fixing it with a composite, or recreate the lost fragment from photopolymer material. It is important to understand that after such repairs the prosthesis will be less reliable, and another chip may soon occur.
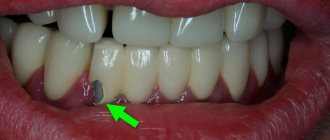
Loss, decementation. These are cases when the prosthesis is not damaged, but has fallen off the supporting teeth. The doctor will examine the condition of the teeth: if they have not suffered much from contact with the external environment, then the prosthesis can often be glued back. If it was not possible to notice and eliminate the problem in time, because of which the tissue damage went deep, you will have to first treat the teeth, and then make a new prosthesis in the laboratory and install it. The same applies to situations when a crown or other prosthesis has become mobile and dangles on the tooth.
If you see that the crown has fallen off or is loose, consult a doctor as soon as possible. These are the most urgent problems.
Relocation
if the prosthesis becomes uncomfortable over time, its shape can be adjusted
In half
Even if the prosthesis is completely broken, it can be repaired
Removable dentures
Now let's look at what can happen to a prosthesis made of acrylic, acry-free or elastic acrylic, as well as temporary plastic structures and clasp dentures. But nylon prostheses, unfortunately, are almost impossible to repair.
Loss of one tooth. An artificial tooth on a removable denture can chip or wear away from chewing. The new tooth can be glued in: they are standard and can be easily replaced in the laboratory. The same procedure occurs when, after a natural tooth falls out, it is necessary to install an artificial tooth on a prosthesis in its place.
Crack or fracture. Rigid dentures made of acrylic and plastic are more likely to chip than flexible ones. In the laboratory, removable dentures are repaired by milling the edges of the fracture and gluing them together with self-hardening dental resins or adhesives. However, if the cast frame of a reinforced prosthesis is damaged, then such a product cannot be repaired.
The fastening is broken. Fasteners may become bent, broken, or otherwise fail. This mount can be replaced or adjusted. If the prosthesis was fixed with locks, then the lock must be replaced. All these manipulations are carried out in the laboratory.
The prosthesis became uncomfortable. Most likely, the problem is not in the prosthesis, but in the changed contour of the gums. Strictly speaking, adjusting the prosthesis to the gum is not a repair; this procedure is called relining. It is carried out based on the results of a warranty examination, when the doctor notices an insufficient fit. But if you feel discomfort before the examination, consult a doctor.
Prosthesis on an implant
The prosthesis broke. A removable denture on an implant is repaired in the same way as dentures on teeth.
The abutment broke. This element connects the prosthesis and the implant and can be replaced. This will take several days, as a standard abutment of the required manufacturer and size must be ordered and delivered.
If the patient had a digital individual abutment installed, and its parameters were saved in the laboratory database, then a replacement can be made immediately, within 2-3 hours.
Repairing a prosthesis at home is dangerous
What happens if you try to repair the prosthesis yourself? In cases with fractures and cracks, patients sometimes try to seal the prosthesis themselves using office or household glue. Such adhesives are unsafe for health:
- may cause allergies,
- can lead to intoxication of the body,
- cause inflammation of the gums,
- corrode elements of the orthopedic structure.
Only a doctor can restore the shape and smoothness of the prosthesis, and ensure proper fit and closure with the opposing teeth. Unprofessional repairs will lead to health problems, and the prosthesis will most likely have to be completely replaced rather than repaired.
As soon as you notice problems with your denture, consult a doctor immediately. Some breakdowns need to be repaired urgently, otherwise the harm to health and financial costs will increase.
| Price, ք | With a discount, ք |
| Repairing a broken base or welding a clasp or tooth | 2115 |
| Installation of new artificial teeth on removable dentures (1 tooth) | 375 |
| Relining of a removable denture with Mucopren material (Germany) | 2000 |
| Restoring one chip of metal ceramics with photopolymer material | 3300 |
What will the doctor do?
Which doctor is best to see if a dental bridge has fallen off? In general, dental prosthetics is the domain of an orthopedic dentist. If the prosthesis is on implants, then you will need to visit both an orthopedist and an implantologist, because The problem may be with the implant. Will the doctor be able to fix the old prosthesis? Here you will first need to undergo diagnostics, incl. tomography of the jaw, which will help determine the condition of the bone around the roots, the quality of root canal filling, and identify cracks in the roots.
Read on the topic: features of dental bridges - who is suitable for them, how they are made and installed.
If the support is in order and suitable for prosthetics, and the prosthesis itself has no flaws (i.e., the problem of falling out was only due to low-quality cement), then you can try to glue the old bridge in place. Of course, using new and high-quality cement.
If the doctor considers that the support needs treatment or removal, and also if the prosthesis is made incorrectly or is broken, then in addition to the main treatment, it will be necessary to make a new orthopedic bridge structure or, in principle, a different type of prosthesis.
What to do if a temporary bridge falls out
If the temporary bridge falls out, then there is nothing to worry about. After all, it is glued to temporary cement, which has weaker fixing properties. Therefore, you need to contact an orthopedist to glue the structure in place. Or, if a permanent prosthesis is already ready or the implants have taken root, then the temporary bridge will not be put back, but the permanent one will be fixed immediately.
Complex on 4 OSSTEM implants with delayed loading - from RUB 170,000.
Complex implantation Osstem (South Korea) with delayed loading after 4-6 months.
Guarantee for the doctor’s work - unlimited Call now or order a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
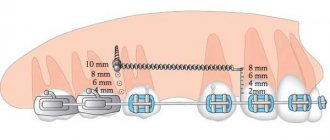
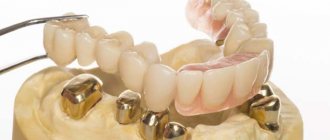
Types of dental bridges
Bridges come in different types; they are divided into main types depending on the material and method of manufacture, as well as installation. Let's take a closer look at the types of dental bridges.
Metal bridge structures
Recently they are rarely used due to unsatisfactory aesthetic characteristics. However, dental bridges, consisting of all-metal crowns on the supporting teeth and metal artificial teeth between them, are perhaps the strongest and relatively inexpensive. But at the same time, such a dental bridge can cause a number of inconveniences in addition to its unaesthetic appearance: since the structure is quite heavy, the supporting teeth under it can be destroyed, a metallic taste may be present in the mouth, and the soft tissues of the mucous membrane may undergo an allergic reaction.
Metal-ceramic bridges
are considered as durable as metal structures, but at the same time surpass them in aesthetic qualities, since the ceramic lining of a metal-ceramic crown ideally imitates the natural color of tooth enamel and can be matched to the shade of neighboring teeth. At the same time, a metal frame that runs through the entire structure and connects its parts allows the prostheses to be made quite extensive. But at the same time, it shines through the ceramics, which does not look very aesthetically pleasing in the smile area. In order to solve the problem, recently bridges have increasingly been made from zirconium dioxide, a white metal.
Ceramic dental bridges
, or in other words, all-ceramic, are bridge-like structures that do not have a metal frame. They are inferior in strength to a metal-ceramic bridge, but at the same time superior to it in aesthetic qualities, since ceramics have almost the same transparency as natural dental tissue.
Plastic dental bridges
are the most cost-effective orthopedic structures. At the same time, modern dental plastics are absolutely hypoallergenic and can imitate the natural color of enamel and the anatomical shape of dental fissures. However, a plastic bridge is more of a temporary measure, since its service life is relatively short, and its strength is significantly inferior to that of ceramic and metal-ceramic structures. In modern dentistry, dental bridges made of plastic are installed as temporary structures for the period of production of permanent dentures or for a short period in case of limited financial capabilities of the patient.
Metal-plastic bridges
– stronger and more durable structures than plastic ones, which, however, are also inferior in service life to metal-ceramic and all-ceramic prostheses. A dental bridge made of plastic on a metal frame will last on average about two years, the maximum limit does not exceed five years, by which time the plastic crown part of the structure will most likely change its color under the influence of pigments, saliva and the aggressive acid-base environment in the oral cavity.
According to the manufacturing method, bridges are divided into solid, stamped and adhesive. A pressed bridge is made from single crowns and artificial teeth that are soldered together, so another name for this design is a soldered bridge. This production method is becoming a thing of the past, as it is inferior in strength to the casting method, and also combines several dissimilar metals, which can cause discomfort when wearing the structure. Cast bridge structures are much stronger and more convenient. An adhesive bridge is made directly in the patient’s mouth from modern composite materials and requires minimal grinding of the teeth adjacent to the defect. Such a prosthesis does not have supporting crowns; it consists of a fiberglass arch, its ends resting on protrusions drilled in the supporting teeth, and an artificial tooth grown on this arch. Since this design is inferior in strength to bridges with abutment crowns, it can be used to replace only one lost tooth.
How much does a re-restoration cost?
How much does it cost to put a dental bridge in place if it falls out? If the supports do not need to be treated or removed, then fixation with new cement will cost approximately 1000-1500 rubles. If the screws on dentures on implants have come loose, then fixing them with new screws will cost about the same. If the patient needs to treat/remove supports, install new pins or inlays - and, as a result, make a new prosthesis, then the cost of restoration starts at 30 thousand rubles. And the final cost is calculated individually.
What needs to be done to make the bridge last as long as possible
In order to extend the service life of the bridge, we must not forget that although it is an artificial structure, it should be treated like “natural” teeth. That is, do not load the bridges with excessively hard and stretchy food, regularly brush your teeth with a brush and toothpaste. Another important rule is that you need to visit an orthopedic dentist every 6 months. During a preventive examination, the doctor will examine the condition of the oral cavity and installed dentures, and will carry out professional removal of tartar and plaque.
1Yamamoto M. Basic technique for manufacturing metal-ceramic dentures, 1998.
Your questions and answers
QUESTION Hello, the bridge fell out of the teeth along with the pins. Can it be put back or not? And what is the best way to do this? Oksana
ANSWER Hello, Oksana. It's best not to try to glue the bridge in place yourself, because... This is fraught with complications, and consult an orthopedic dentist. Because there are many nuances due to which the old prosthesis can either be put back or not be used further (i.e., a new one can be made). But, given that your bridge fell out instead of the pins, most likely you won’t be able to put it back in place.
Author: Sambuev B. S. (Thank you for your help in writing the article and the information provided)
What should you do if a dental bridge falls out?
First, you should make an appointment with your dentist as soon as possible.
Before visiting a doctor, you can temporarily glue the crown yourself with a special compound that can be purchased at a pharmacy. You need to act in the following sequence:
- Clean the surfaces of the crown and tooth thoroughly;
- Dry with sterile gauze;
- Apply cement inside the prosthesis and install it.
With its help, a layer is created that will allow the structure to be tightly secured for some time. Before application, ensure that surfaces are dry and clean. If moisture remains, integrity will not be restored.
With a serious approach to solving the problem, you can get the desired result.
To ensure that the crown glued in this way holds:
- The load on the problem area should be reduced as much as possible;
- Oral hygiene should be carried out carefully.
It will not be possible to solve the problem in a global sense in this way, but it is possible to temporarily prevent the development of an inflammatory process in the mouth and protect the tooth from destruction.