- From the moment of pregnancy, a complex of changes occurs in a woman’s body, which covers the functions of all organs and systems, is observed throughout pregnancy and is within the physiological boundaries characteristic only of the state of pregnancy.
The set of changes includes:
- cessation of menstruation (changes occur in the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity caused by changes in the functional state of the ovary);
- prolonged low-grade fever (the influence of progesterone, an ovarian hormone, on the thermoregulation center in the brain);
- formation of the placenta - a new endocrine gland;
- change in a woman’s appearance;
- the emergence of a pregnancy dominant in the cerebral cortex, which ensures clear coordination of the functions of all organs and systems in the interests of the developing fetus;
- changes in the function of the endocrine glands;
- changes in the uterus (the greatest changes compared to other organs);
- changes in metabolism;
- changes in hematological (blood) and hemodynamic (blood movement) parameters;
- change in circulating blood volume;
- changes in the blood coagulation system;
- changes in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
That is, with the onset of pregnancy, your body begins to completely restructure its functioning. He is preparing to bear the fruit, give birth and feed the child. Therefore, such a restructuring is a normal state for a pregnant woman.
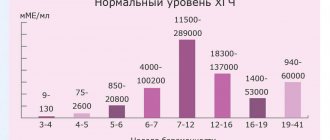
| A healthy person has the same indicators (the numbers you see on the analysis form are normal), for example, blood indicators, urine indicators, etc. |
| For a sick person , there are indicators; they vary depending on the patient’s condition and his disease. |
| A pregnant woman is her own story. Her laboratory values may vary depending on the physiological course of pregnancy. Moreover, in different trimesters of pregnancy, each indicator has its own norm, and these norms for a pregnant woman do not coincide with the norms for a healthy person. |
Moreover, sometimes what is normal for a pregnant woman is considered pathological in a non-pregnant woman. But for a man it’s generally fatal; you can’t live with something like that.
We answer popular questions
The COVID-19 pandemic, announced by WHO in March 2022, has made serious adjustments to the life of modern society. News reports are full of figures about the number of people infected, recovered and those who could not cope with the disease. The infection itself and its complications can cause serious harm to the adult body. What will happen to the fetus, does COVID affect pregnancy, how to protect yourself? These and not only these questions are often asked by young couples who are just planning to become parents or are already waiting for a miracle. Let's talk to the experts at the SM-Clinic Reproductive Health Center about how to behave correctly.
Treatment
If you notice any symptoms of the disease, you should not delay visiting a doctor. Self-medication is a risk not only that the disease will not go away, but that the pathology will become chronic.
Only a specialist will select the optimal treatment option for the disease for the expectant mother.
The primary task is pain relief. Most often, gels and ointments are used for this purpose for the eruption of the child’s first teeth. Such drugs are absolutely harmless for a pregnant woman, and at the same time, very effective. In addition to the analgesic effect, such products have an antiseptic effect.
The viral type of pathology is treated with the mandatory use of antiviral agents.
If the disease is caused by a fungus, then it should be treated with antifungal drugs that are suitable for the expectant mother.
Is coronavirus dangerous for pregnant women?
Pregnancy during the coronavirus period is especially dangerous if a woman is at risk. In this case, the likelihood of a more severe course of infection compared to the population is increased due to existing immune disorders and concomitant diseases.
Although the infection is new and much is still being studied, risk factors have been identified. These include:
- anamnestic indications of blood clots in arteries and veins before pregnancy;
- an established diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome - a condition in which antibodies to the cell membrane are formed in the body;
- inherited forms of thrombophilic disorders - increased blood clotting caused by genetic characteristics;
- confirmed autoimmune diseases, in which the immune system “works” against the cells of its body;
- diabetes mellitus of any type;
- obesity;
- metabolic syndrome is a pathological complex that includes impaired glucose tolerance, excess weight and a number of endocrine disorders;
- lung diseases characterized by a chronic course (bronchial asthma, chronic bronchitis, etc.);
- pregnancy resulting from the use of assisted reproduction methods;
- oncological processes in the body.
However, the presence of risk factors alone does not mean that in 100% of cases COVID during pregnancy will be severe. Coronavirus during pregnancy can go unnoticed (asymptomatic). Only positive results of an antibody test will help determine that a pregnant woman has had a new coronavirus infection.
Predisposing factors in the development of genital varicose veins in women
Varicose veins on the labia have a genetic predisposition - the mechanism of the disease is similar to varicose veins of the lower extremities. The basis is dysfunction of the valves of the gonadal veins. Physical activity, frequent pregnancies, engorgement of the genital organs during prolonged sexual intercourse contribute to vascular stretching with the development of venous stagnation. The appearance of varicose veins of the labia during pregnancy usually occurs in the second trimester and reaches a maximum closer to childbirth. After childbirth, these varicose veins, which developed during pregnancy on the labia, most often regress, but sometimes remain for life due to changes in the structure of the vascular walls.
How do expectant mothers cope with COVID-19? Course of the disease during pregnancy
COVID-19 during pregnancy can occur in different ways. The symptoms of coronavirus during pregnancy are in many ways similar to the clinical manifestations in “ordinary” patients. Women note a decrease in sense of smell or its complete loss, an increase in body temperature, a cough (mostly dry), body aches and severe weakness. As with any viral respiratory infection, a severe runny nose is not typical.
However, pregnant women have one important feature. COVID during pregnancy can suddenly worsen, even if the disease was relatively stable and mild before. Therefore, you should not self-medicate and hope that “maybe it will pass.” Only a doctor can notice the alarming symptoms of COVID during pregnancy and take preventive measures in time to avoid serious complications.
Coronavirus in the 1st trimester
COVID and early pregnancy can act like a common cold. If a woman’s immunity is sufficiently tense, then there will be no negative consequences for the fetus. If the immune system malfunctions, the risks of an adverse effect of a viral infection on the developing chorion, that is, on the future placenta, which is responsible for feeding the fetus until the due date, increase. Severe consequences of COVID in the early stages of pregnancy may include spontaneous and failed (fading pregnancy) miscarriage, fetoplacental insufficiency, which can subsequently lead to fetal growth retardation and oxygen deficiency at the intrauterine stage of development.
Coronavirus in the 2nd trimester
Does coronavirus affect pregnancy at 14-28 weeks? Yes. And the degree of this influence depends, on the one hand, on the infecting dose, and on the other, on the state of the mother’s body. A favorable scenario is a common cold without obvious consequences. An unfavorable scenario is the development of complications in the mother (pneumonia, “long COVID”, etc.), complications from the feto- and utero-placental complex (placental insufficiency, fetal growth restriction, intrauterine hypoxia, shortening of the cervix).
Coronavirus in the 3rd trimester
How does coronavirus affect pregnancy in the 3rd trimester? According to epidemiological studies around the world, pregnant women who have had COVID-19 for 28 weeks or more have a 2-3 times increased rate of preterm birth. Coronavirus in late pregnancy either increases the contractile activity of the uterine body or promotes dilatation of the cervix, which ultimately ends in premature birth.
There are still no reported cases of intrauterine infection of the fetus with coronavirus. All situations where newborns test positive for COVID are associated with infection after birth.
The structure of the external (and internal) genital organs changes
- The external genitalia become swollen and hyperemic. Cyanosis of the mucous membranes of the vaginal part of the cervix, vagina and its vestibule occurs, which indicates vasodilatation and blood stasis, facilitating serous permeation of the tissues necessary for the deposition of nutrients at the site of attachment of the fertilized egg to the uterine wall.
- The vagina expands and lengthens somewhat during pregnancy. The walls of the vagina are swollen and thickened. The discharge becomes more abundant, mucous in nature, milky white or yellowish in color with an acidic reaction. In a healthy pregnant woman, the vagina has I-II degrees of cleanliness.
The uterus changes the most during pregnancy compared to other organs.
Its size increases during pregnancy in all respects:
- weight - from 50-100 g to 1-2 kg!!!
- length - from 7-9 cm to 50 cm,
- volume - 500 times, reaching 2-3,000 cm3 (liters) or more.
Accordingly, changes occur in all tissues, blood supply and innervation of the uterus:
- The shape and position of the uterus changes during pregnancy. As the uterus grows, it emerges from the pelvis into the abdominal cavity, rising in the 9th month of pregnancy to the xiphoid process. The shape of the uterus is asymmetrical due to the bulging of the part where the placenta is attached.
- Thin arteries and veins of the uterus turn into powerful trunks, which become corkscrew-shaped, tortuous, which allows maintaining normal blood supply during pronounced changes in the uterus during pregnancy and during contraction of its muscles during childbirth.
- The volume of blood circulation in the uterus during pregnancy increases tens of times, providing uteroplacental blood flow, which is carried out according to the principle of blood supply to vital organs and remains relatively optimal even under various stresses (blood loss, anemia). This ensures the survival of the fetus in extreme situations.
- The receptor system of the uterus changes: during pregnancy, the sensitivity of the uterus to stimulating factors decreases, before childbirth, the excitability of the uterus increases, some of the nervous structures are lost in order to reduce pain information from the uterus during childbirth.
With the appearance of the placenta, a pregnancy dominant arises in the cerebral cortex, which ensures clear coordination of the functions of all organs and systems in the interests of the developing fetus.
Women note a decrease in performance, increased drowsiness, or vice versa, they are irritated, they have nausea, drooling, periodic vomiting, which is classified as mild and the occurrence of which corresponds to the phase of functional changes in the nervous system.
Pregnant women have increased suggestibility and self-hypnosis, which is taken into account when conducting psychoprophylactic preparation for childbirth.
Phenomena of paresthesia, neuralgic pain, spasms of muscle groups, numbness of the fingers and other disorders may occur. Increased excitability of peripheral nerves is also manifested by increased knee reflexes.
With all this, sexual excitability decreases , and you, dear husbands, must be prepared for this. No need, under no circumstances!!! (remember about increased suggestibility and self-hypnosis) do not show your grievances that your wife is cold and inattentive to you, which means she has stopped loving you. She still loves you, she is already carrying your child and she has a dominant in her cerebral cortex - to endure pregnancy at all costs. And there is no escape from this.
- In a pregnant woman, the functions of some analyzers change - hearing, vision, smell!!! A pregnant woman's sense of smell can become so strong that the woman will react to the lightest (hardly perceptible) odors.
Please keep in mind, dear men, when a woman feels bad, feels sick, and the world is generally in shades of grey, for some reason unhappy thoughts come into her head, which can lead to a deterioration in her condition and, as a consequence, to termination of pregnancy.
During pregnancy, changes affect other organs as well.
The adrenal glands increase in size during pregnancy due to cortical hyperplasia, and the glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid function of the adrenal glands increases accordingly.
Strengthening the function of the adrenal cortex during pregnancy is aimed at increasing protective and adaptive mechanisms, including during childbirth.
The thyroid gland increases in volume and function increases. Goiter in pregnant women is observed, especially in areas endemic for goiter (little iodine in soil and water) and hyperthyroidism without thyrotoxicosis. Strengthening the function of the thyroid gland is associated with the influence of placental hormones on it. Clinical thyrotoxicosis does not develop due to increased binding of free hormones by plasma proteins. The protein-bound form of the hormone is subsequently utilized by the fetus and the mother’s body, since the need for it increases with the development of pregnancy, before the onset of fetal thyroid function.
The parathyroid glands (calcium metabolism) undergo hypertrophy, their functional activity increases due to the increased need for calcium, which is a plastic material for the formation of the musculoskeletal system of the fetus. If there is insufficient intake or impaired absorption, the fetus receives calcium from the tissues of the mother’s body (bones, teeth), which can manifest itself as osteoporosis, fragility and dental caries. During pregnancy, the concentration of calcium in the blood increases. The content of phosphorus compounds, iron and a number of microelements (cobalt, iodine, manganese, copper) also decreases in the blood plasma. The deficiency of these substances is due to the needs of the fetus and increased metabolic reactions, the enzyme systems of which include some of the micro- and macroelements.
Pancreas – strengthening the function of the insulin-producing apparatus. As a result, carbohydrates are absorbed very well and are deposited in the mother’s liver and in the tissues of the fetus. Women with diabetes always give birth to large children due to the utilization of excess carbohydrates by the fetus. Some pregnant women experience glucosuria (sugar in the urine), which is not pathological and manifests itself with normal or even low carbohydrate levels in the blood.
The pituitary gland in pregnant women increases in volume and is difficult to fit in the sella turcica; hyperproduction of growth hormone (GH) is observed, which, penetrating the placenta, stimulates the growth of the embryo. This hormone also affects the lactogenic function of the mammary gland, causing in some cases an enlargement of the nose, lips, and fingers.
Consequences of coronavirus during pregnancy
Research into how coronavirus will affect pregnancy is still ongoing. The infection is new, so much remains to be learned. And this process for pregnant women is associated with certain difficulties, so new data appears in doses. Today we have the following information.
- Chinese scientists have found that the consequences of COVID during pregnancy may include an increased risk of premature birth.
- Other researchers have found a link between positive COVID during pregnancy and a greater likelihood of fetal growth restriction and distress syndrome (lack of oxygen for the baby in utero).
Observations are ongoing to help analyze how COVID affects the fetus during pregnancy. There are now reports that this virus can lead to low platelet levels and liver dysfunction in newborns. However, this information needs further verification and is not unambiguous.
Dry mouth and sleep disturbances in pregnant women
Rapid weight gain, changes in the position of the diaphragm, weakening of the ligamentous apparatus, and difficulty in nasal breathing due to swelling of the mucous membranes lead to snoring in a pregnant woman. When snoring, the walls of the pharynx vibrate and beat against each other during breathing, which causes injury to them. The next morning the woman wakes up with a dry, sore throat and a hoarse voice. Breathing through the mouth during sleep leads to rapid drying of the mucous membranes, and since saliva is practically not produced during sleep, dry mouth also naturally occurs in the morning.
Snoring, apnea, insomnia or other problems? Contact the Sleep Medicine Center at the Rehabilitation Clinic in Khamovniki. We will definitely help you! Ask questions and schedule a consultation by phone.
If you are pregnant and wake up in the morning with a feeling of dry mouth, check with your family to see if you snore. If yes, then consult a somnologist. You should not ignore the situation, as snoring can develop into a complicated form - sleep apnea disease, which increases blood pressure in a woman, provokes oxygen starvation in the fetus and poses a serious threat to both mother and child.
You can be examined and, if necessary, treated for snoring and apnea at the Rehabilitation Clinic in Khamovniki, where the Sleep Medicine Center has been operating for many years. At the Center you can get professional advice from specialists, regain healthy sleep and get rid of dry mouth.
How can this affect the child? Can his mother infect him with the virus in the womb?
The impact of COVID on the fetus during pregnancy is not completely known. To date, there is no data that would confirm the fact of intrauterine infection (penetration of the virus to the fetus) or intrauterine infection (development of symptoms in the fetus). However, there is no reverse data that would reliably exclude the possibility of vertical transmission of the virus. Coronavirus during pregnancy before childbirth can be dangerous because an infected mother can infect the child immediately after birth. This happens through the traditional airborne or household contact route.
Should you postpone pregnancy?
There are quite a lot of “blank spots” in the answer to the question of how COVID affects pregnancy in the immediate and long-term period after infection. However, clinical recommendations state that after an illness, conception should be postponed for at least 3 months. This duration of the time pause is explained by 2 arguments. On the one hand, in the 3-month period after an acute infection, there is a possibility of developing delayed complications, especially for thrombosis of various locations. On the other hand, 3 months are necessary for the complete elimination of pharmacological drugs used to treat the infection. Their negative impact can be much more serious than the direct consequences of COVID on pregnancy.
The average spermatogenesis cycle lasts 3 months. In other words, during this time, renewed sperm mature, which do not contain toxic substances formed during the metabolism of pharmaceuticals. In women, the period of folliculogenesis (the complete cycle of egg maturation) is shorter. Therefore, doctors advise focusing on a larger gap, that is, on the male factor.
In what cases do doctors advise terminating a pregnancy?
The impact of coronavirus on pregnancy continues to be studied. Today, there are no direct indications for artificially interrupting the gestational process due to the fact that COVID-19 developed during pregnancy. Interruption can be recommended only for those indications that were previously prescribed in the Order. First of all, this is the cessation of pregnancy, which could potentially be associated with coronavirus. The second is the diagnosis of chromosomal pathology and developmental anomalies incompatible with life. Whether coronavirus causes such conditions or not has not been reliably determined today.
External factors
Sometimes dry skin and mucous membranes have nothing to do with the processes occurring in the mother’s body. It can be called:
- dry indoor air;
- climatic conditions - heat, wind, sun;
- allergies to cosmetics or toothpaste;
- habit of constantly licking or biting your lips.
Most external factors are easy to eliminate: just install a room humidifier and use hypoallergenic cosmetics during pregnancy.
Can pregnant women get vaccinated?
Considering the fact that COVID during pregnancy is especially severe in patients at risk, timely vaccination is recommended for this category. Vaccination is allowed from 22 weeks; the recommended vaccine is Sputnik V.
Experimental clinical studies on animals did not reveal a negative effect of the vaccine on the body of the female and her offspring. Also in world medicine there is data on the impact of anti-Covid immune drugs on the body of pregnant women, who at the time of vaccination were not aware of their “interesting situation.” No negative consequences were registered.
Thus, vaccination during pregnancy is carried out when the expected benefits outweigh the possible risks.
How can a pregnant woman protect herself during COVID?
During pregnancy, even if you have been vaccinated against COVID in advance, you should follow sanitary rules that will help reduce the risk of infection:
- maintain a distance of at least 1.5 meters;
- wash your hands or use sanitizer;
- do not touch your eyes, mouth and nose with unwashed (untreated) hands;
- ventilate the premises;
- avoid crowded places.
When the first suspicious symptoms of a new coronavirus infection appear, you should immediately contact a medical facility. It is easier to prevent complications than to eliminate them later.
Prevention measures
Despite the fact that the exact impact of COVID on pregnancy has not been fully established, one thing is clear - it is worth protecting yourself from the infection in advance. Vaccination is considered the best way. It promotes the formation of specific immunity. Even if the virus enters the body, the immune system will be ready to meet it. The pathogen is immediately attacked by immunoglobulins (antibodies) and most or the entire pool of viruses can be neutralized. Therefore, the consequences of coronavirus during pregnancy in such a situation will be minimal - the infection will not develop or will be mild.
How long does it last?
Hormonal levels will gradually begin to return to normal, and the body will naturally create favorable conditions for the fetus. A woman’s appearance instantly reacts to this, she “prettier” before our eyes. Dry lips go away.
Toxicosis is usually observed in the first trimester of pregnancy. Subsequently, appetite normalizes, and the consumption of necessary food components returns to normal.
What should a pregnant woman do when her lips become very dry? Should you be patient for 3 long months and wait for everything to go away on its own?
No, you don't have to wait. This threatens other, more serious problems. Dry lips are prone to cracking, and infections can enter the body through microcracks.