Have you had accidental unprotected sexual contact with an unknown partner? Has the condom broken or is it known that your partner has sexually transmitted diseases? Then you urgently need drug prevention after an accidental relationship!
In fact, neither a condom nor antiseptics used after sexual intercourse protect against sexually transmitted diseases with 100% probability. We know of many tragic cases of infection with syphilis, gonorrhea, pubic lice and scabies in patients who used a condom and were treated with an antiseptic solution.
Drug prevention
Drug prevention is a complex of treatment and preventive measures aimed at destroying pathogens of sexually transmitted infections that are still in the incubation period, i.e. not yet showing themselves. If the patient has complaints, no prophylaxis is carried out. In this case, a detailed diagnosis of STDs is already necessary. The optimal period for prevention is 1-3 days. But some diseases (syphilis, chlamydia) have longer incubation periods and can be prevented for up to 3-8 weeks, but in this case prevention should be preceded by diagnosis. If the clinic has express tests, this can be done within 30 minutes.
The essence of prevention is a short course of antibacterial, antitrichomoniacal and antiviral therapy directed against the main pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases.
In our clinic, a full course of prevention after casual sex includes injections, IVs, tablets and instillations into the urethra in men or vaginal treatment in women. This type of prevention provides protection against sexually transmitted diseases in 100% of cases.
Tablet treatment used independently at home leads mainly to chronic infections.
Be more attentive to your health, consult a specialist and protect yourself from serious complications of sexually transmitted diseases.
Treatment of chlamydia
It is important to note that any sexually transmitted disease, including chlamydia, is prohibited from being treated independently! The treatment regimen for chlamydia is drawn up by the doctor, based on the symptoms and research results.
This disease does not require hospitalization, provided that the infection is not in a pregnant woman and there is no threat of pregnancy.
It must be remembered that for the treatment of chlamydia to be effective and to prevent re-infection, a course of therapy is necessary for both partners. After treatment, repeat tests are recommended to assess its effectiveness.
When treating chlamydia in both men and women, complex therapy is used aimed at combating chlamydia and supporting the body as a whole:
- antibiotics - the most commonly used drugs are erythromycin and azithromycin; broad-spectrum antibiotics are used, as there are often difficulties in making an accurate diagnosis
- immunomodulators (increasing a person’s own immunity)
- enzyme therapy (enzyme therapy, stimulates the liver and kidneys to reduce the intoxication of the body with antibiotics)
- hepatoprotectors (protect the liver and increase resistance to antibiotics)
- vitamin therapy (increasing the immune response) – vitamin E, ascorbic, glutamic acids
- probiotics (prevention of dysbacteriosis)
The choice of drug, its dosage and duration of treatment is determined by the doctor depending on age, gender and type of chlamydia.
In the absence of adequate treatment, chlamydia can provoke dangerous complications: arthritis, changes in the nervous system, decreased immunity, various types of vascular diseases, as well as asthma and allergic reactions. The spread of infection through the bloodstream can cause inflammation of the liver, manifested by abdominal pain, which is often mistaken for inflammation of the gallbladder or pancreas.
You can get a qualified consultation with a gynecologist at our Dynasty clinic by making an appointment by phone or using the feedback form at the bottom of the page.
Prevention after casual relationships for men
Many people believe that after casual sex it is enough to get tested for STIs and, if the results are negative, to calm down and live a normal life. But it's not that simple. Each sexually transmitted infection has its own incubation period and time when it is not fully detected by laboratory tests. Therefore, if you come to see a venereologist a couple of days after contact, you should not rely only on diagnosis; at the same time, you need to do prevention after casual relationships in men. Then the likelihood of contracting most STDs is reduced to almost zero.
Prevention after unprotected intercourse in men is most effective within 72 hours of possible infection. During this period, preventive treatment of all sexually transmitted infections, even HIV, can be carried out.
Of course, prevention after casual relationships in men is carried out at a later date; with syphilis, it is possible up to 2 months from the moment of contact, provided, of course, that tests for syphilis are still negative. But the more time has passed after unprotected sex, the higher the likelihood of the infection transitioning from the incubation stage to disease. And accordingly, prevention will no longer be indicated, but specific treatment for a specific STD is necessary. Therefore, the sooner the better.
Prevention of STDs after a casual relationship for men has several stages, but usually it goes away in 1 doctor’s visit:
- Examination by a venereologist
- Conducting express blood tests for syphilis, HIV, hepatitis and urethral smears within 20 minutes
- Taking scrapings from the urethra for PCR diagnostics of latent bacterial and viral STIs to determine further treatment tactics after prevention.
- If rapid blood tests and a normal smear are negative, prophylaxis itself is carried out after casual relationships for men. Its duration is about 40-60 minutes. Intravenous and intramuscular administration of drugs that destroy pathogens of sexually transmitted infections in the incubation period
- Instillation of silver preparations into the urethra, which have a strong antiseptic effect, but are safer for the mucous membrane, unlike other antiseptics. If necessary, solutions are injected into the rectum and pharynx if anal or oral sex has taken place.
- A short course of therapy with tablet forms of antiviral and antibacterial drugs.
Prevention after unprotected intercourse in men is almost always well tolerated. Despite the simultaneous administration of several groups of antibiotics, antiviral and antifungal drugs, any side effects are rare and are usually associated with individual intolerance to the drugs. But these are always much smaller doses of drugs and a shorter course than when treating an already developed venereal disease, which undoubtedly will not pass without leaving a trace on the body.
Some patients are faced with the question of whether they need STD prevention after a casual relationship for men or whether they can be tested for infections in several stages and, if something is found, then treated. With this approach, several factors need to be taken into account:
- Not all sexually transmitted diseases can be cured if they are already deeply embedded in the body. HIV, viral hepatitis, herpes, papillomavirus infection, sometimes chlamydia and trichomoniasis are easier to prevent than to be a carrier or a sick person all your life, putting your family and friends at risk.
- The detection period for many STIs is several months, HIV sometimes up to a year. Accordingly, during this period it is necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse, especially without a condom, which is not always possible, especially in the case of married men.
- After many sexually transmitted diseases, serious complications and consequences remain in the form of chronic prostatitis, urethritis, balanoposthitis, vesiculitis, damage to the nervous system and internal organs, which could have been avoided by carrying out prevention after casual relationships in men.
- After suffering from syphilis, antibodies to it remain in the blood forever, so every time you take tests to undergo any medical examinations, for hospitalization, the results will be positive, despite the treatment, which raises a lot of questions from doctors conducting examinations and from employers who need employee medical records . And this, too, could have been avoided if preventive treatment of syphilis had been carried out at the stage of the incubation period.
Prevention after unprotected intercourse in men is carried out against most known STIs: syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, gardnerellosis, candidiasis, HIV, hepatitis, viral infections.
The cost of prevention after casual relationships in men usually ranges from 1000 rubles. for 1 infection. There are complex preventive measures that include procedures against several STD pathogens at once: 3,500-10,000 rubles. for major infections. In order to protect the immune system, liver, and kidneys, cover-up drugs are prescribed, but then prevention becomes more expensive.
Prevention after casual relationships for men is carried out in our clinic every day. The selection of drugs and types of emergency preventive treatment for STDs is carried out by a venereologist after a thorough survey of the patient and the results of express diagnostics.
Prevention after casual relationships for women
Protecting yourself from the consequences of sexual intercourse with a casual partner is quite possible for a woman at any age and in any state of health. Competent and experienced medical specialists know how to do this competently, safely and with a high probability of a positive result.
Not a single woman is immune from unplanned sexual intercourse, as well as from the infections that can be obtained from them. And if this has already happened, you should take care to minimize the possible consequences. Our clinic provides prevention of sexually transmitted diseases in women who have had a relationship with an unverified partner no earlier than 2-3 days before visiting a dermatovenerologist. Therefore, it is not worth postponing a visit to the doctor indefinitely: it is in the patient’s interests to seek help as early as possible.
STDs that can be treated preemptively include:
- syphilis;
- gonorrhea (gonorrhoea);
- chlamydia;
- ureaplasmosis;
- mycoplasmosis;
- trichomoniasis;
- candidiasis;
- molluscum contagiosum.
Unfortunately, HPV, genital herpes and hepatitis viruses, as well as HIV, are resistant to any medical preventive measures and procedures. Emergency measures that are recommended to be taken in the first hours after contact (mainly washing and douching with antiseptics) also do not reduce the likelihood of infection with the above diseases. This is also why the doctors at our medical clinic recommend not delaying the decision to visit a doctor, because timely tests and identified infections allow you to begin treatment in the early, uncomplicated stages of the disease.
For each patient who contacts our dermatovenerologists, an individual treatment regimen is developed taking into account existing concomitant diseases, contraindications and intolerance to certain groups of drugs.
As a rule, the prevention of STDs after a casual relationship for women is carried out according to the same protocol as the treatment of corresponding diseases that occur in an uncomplicated form. For example, preventing gonorrhea includes the same medications as treating it. The same applies to all other infections.
Preventive medications in this case are antibiotics, which the patient receives orally, vaginally or by injection in a loading dose. Therefore, prescribing such drugs to yourself and taking them without the supervision of a doctor is dangerous and can cause significant harm to the body.
Two weeks after the prophylaxis, our doctors suggest that the patient undergo tests. They will help make sure that the infection has not “taken root” in the body.
A casual relationship is not an event you want to be proud of. But there is no point in being ashamed, much less hiding what happened from the attending physician. By turning to our medical center for help, every woman receives:
- qualified assistance from competent specialists at a reasonable, adequate cost;
- the opportunity to take control tests in a modern high-precision laboratory;
- no queues, delays or delays;
- absolute confidentiality;
- friendly attitude from the clinic staff.
Did something unexpected happen? Contact one of our doctors at any time of the day and get effective help at a professional level!
Prevention after casual relationships Gardnerella Gardnerrella vaginalis
Prevention of gardnerella is necessary when there has been contact with a man or woman in whom gardnerella was detected in an STI test, or it is not known at all whether this sexual partner is healthy.
Standard comprehensive prevention of STDs after casual sex usually includes drugs to kill Gardnerella. But sometimes it is necessary to carry out isolated prevention of gardnerellosis, when there is a risk of contracting only this particular infection.
Gardnerella is an opportunistic infection that causes bacterial vaginosis in women, and can provoke balanoposthitis and prostatitis in men. But very often gardnerellosis occurs latently and asymptomatically, which leads to a massive spread of infection.
Prevention of gardnerella is carried out for all men who have sexual contact with women with bacterial vaginosis, and for all women who have had sexual intercourse with a partner who has gardnerella urethritis, prostatitis or balanoposthitis.
Before preventing gardnerellosis, a gardnerella test is performed. Ideally, a smear on the flora and PCR diagnostics are done, but in some cases they are limited to an express smear, which provides information about the inflammatory process and the presence of gardnerella in the vagina, urethra or on the skin of the penis within 20–30 minutes.
If gardnerella is not detected in the smear, then prophylaxis is carried out. If it is found, then prophylaxis is not prescribed, but its specific therapy is developed.
Typically, STD prevention after a casual relationship is carried out on the day of the patient’s initial appointment. The same applies to measures to prevent gardnerellosis.
It is important to carry out the procedures while the pathogen is in the incubation period and is not detected in tests.
Chlorhexidine Pharmland, solution for external use 0.5 mg/ml
In patients with open traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injuries, or perforation of the eardrum, contact with the surface of the brain, meninges, and the cavity of the inner ear should be avoided.
In case of contact with the mucous membranes of the eyes, they should be quickly and thoroughly rinsed with water.
Contact of hypochlorite bleaches on fabrics that have previously been in contact with chlorhexidine-containing medications may cause brown stains.
Use Chlorhexidine Pharmland with caution in conditions where the systemic effect may be dangerous, especially in children, if the skin is damaged over large areas.
Special precautions. Given the lack of information on transdermal absorption, systemic effects cannot be ruled out. The likelihood of their occurrence increases with repeated applications, especially when a large area is treated, the surface under an occlusive dressing or mucous membranes, in the presence of damage to the skin (in particular burns), as well as in the case of treating the skin of newborns (taking into account the ratio of the surface area and body weight of the child and occlusive effect of diapers).
The use of chlorhexidine solution in newborns as a skin antiseptic before invasive procedures is associated with a certain risk of developing a chemical burn. Based on spontaneous reporting and literature data, a higher risk of skin reactions has been identified in preterm neonates, particularly those born before 32 weeks of gestation, in whom chlorhexidine was used during the first two weeks of life.
Before performing invasive procedures, it is necessary to remove all materials soaked in chlorhexidine: bandages, sheets, napkins, gowns, etc. Do not use excessive amounts of solution. The solution should not be allowed to accumulate in skin folds, under the patient’s body, or on materials that are in direct contact with the child’s skin.
If an airtight dressing (occlusive dressing) is to be applied to skin that has previously been exposed to chlorhexidine, ensure that there is no excess chlorhexidine solution on the skin before applying the dressing.
After opening the polymer container, there is a risk of microbial contamination of the drug.
How is gardnerellosis prevented?
- After examination by a venereologist and a negative test for gardnerella, the patient is sent to the treatment room.
- A drug, usually from the group of imidazoles, is administered intravenously at the maximum therapeutic dose.
- Next, in the urology office, the doctor instills a silver preparation into the urethra or a vaginal bath with an antiseptic solution and imidazole. An antibacterial cream or gel is placed in the vagina.
- Tablets may also be given to your home.
- A week later, a gardnerella test is taken to check the effectiveness of the prevention.
Prevention of Gardnerella is especially important for women with impaired vaginal microflora. If their sexual partner introduces gardnerella into the vagina, then a relapse of bakvaginosis will occur, which will require long-term complex treatment.
Prevention of gardnerellosis after casual relationships is effectively carried out only in a clinic under the supervision of a venereologist or gynecologist. Self-medication and self-prevention with medications usually lead to the development of chronic STDs.
The cost of STD prevention is from 1000 rubles. Instillation into the urethra and vaginal bath - 800 rubles.
Prevention after casual relationships Herpes Herpes viridae
Prevention of herpes and other viral infections after sexual intercourse is much more difficult than bacterial STDs.
It is very difficult to achieve complete elimination of the virus if it has already penetrated into cells, and even more so into nerve nodes. That is, prevention of genital herpes is possible only in the first days after infection, before the virus reaches the node along the nerve trunks and remains there forever, manifested by periodic exacerbations of herpes infection.
As for effectiveness, the prevention of herpes is very much inferior to the usual prevention of STIs for the sole reason that at the moment there are no drugs that can kill the virus located in organs and tissues. All medications only inhibit its activity and reproduction in cells.
The usual standard prevention of STDs after a casual relationship does not include measures against herpes.
Prevention of genital herpes is included in the already expanded version. Although sometimes it is performed in isolation, when it is known that the sexual partner is sick only with this infection.
When is herpes prevention indicated after an accidental relationship?
- In principle, always if there was contact with an unfamiliar partner. Because herpes is very widespread and even in the absence of visible manifestations can be found in the mucous membrane of the genital tract and oropharynx.
- Definitely, if you have sexual contact with a person who has sores, crusts, or blisters on the genitals, then there are clinical manifestations of herpes.
- During oral contact with a partner who has symptoms of a “cold on the lips,” that is, labial herpes.
- During anal intercourse, if there are erosions in the anal and perianal area.
- Of course, herpes rashes can be deep in the vagina, rectum, or on the oral mucosa and not be noticeable. Therefore, it is very difficult to focus on symptoms. And that's why herpes is very common. A guarantee can only be a trusted permanent partner or timely prevention after sexual intercourse.
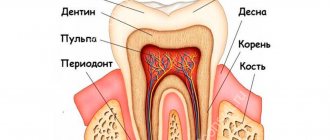
Symptoms and manifestations of chlamydia
Most sexually transmitted infections are easy to detect and diagnose. But this is not the case with chlamydia. A very important problem is the asymptomatic course of the infection (in most cases, with a normal immune system of the body). This is the reason for the lack of timely treatment, the possibility of complications when the immune system weakens, and, in addition, unconscious further infection of sexual partners.
Symptoms of chlamydia appear mainly with weakened immunity in 25% - 50% of cases.
1. Venereal granulomas
The disease begins with the appearance of small blisters at the site of infection (on the genitals). After 2 - 6 weeks, the inguinal lymph nodes enlarge, which can become denser and adhere to each other. In case of complications, the formation of a fistula (pathological canal) of the scrotum (in men), urethra, rectovaginal fistula (in women), elephantiasis of the genital organs, narrowing of the rectum is possible.
2. Chlamydia in women
Chlamydia in women can cause inflammation of the urethra, cervix and mucopurulent proctitis (inflammation of the rectum). Symptoms of chlamydia in women include:
- redness and swelling of the vagina, accompanied by pain, burning during urination, and a feeling of an incompletely emptied bladder;
- with inflammation of the cervix: mucopurulent discharge, redness and swelling of the vaginal part of the cervix, delay and increase in the duration of menstruation, bleeding between them;
- pain during intercourse;
- elevated temperature;
- nausea.
Chlamydia in women can cause many complications. With an ascending infection, chlamydia can spread to the upper parts of the reproductive system, causing inflammation of the mucous membrane of the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, cervical erosion, and inflammation of the Bartholin gland.
Pelvic inflammatory processes can lead to difficulties in conceiving.
Infection with chlamydia can also negatively affect pregnancy.
In these cases, there is a higher rate of ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous abortion, premature rupture of membranes, preterm birth, and increased perinatal neonatal mortality.
3. Chlamydia in men
Infection in men most often manifests itself as inflammation of the urethra, proctitis (mainly in homosexual men) and pharyngitis (sore throat) in the case of orogenital contact.
Symptoms of chlamydia in men appear 7-21 days after infection. Most common symptoms:
- clear or milky white, serous or mucus-like discharge from the urethra;
- temperature increase;
- redness and excessive heating of the skin of the perineum;
- burning pain when urinating;
- acute epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis).
When the inflammatory process affects the inguinal glands, a dull pain appears in the groin, radiating to the groin, testicles and back.
The spread of infection can lead to inflammation of the testicle (orchitis), which can cause infertility. In addition, untreated chlamydia can cause chronic prostatitis and narrowing of the urethra.
All of these symptoms may not necessarily appear together. Some of them are similar to symptoms of other diseases and are not always associated with sexually transmitted infections. As a result, a person finds out that he is a carrier of chlamydia many years later, for example, when trying unsuccessfully to have a child.
Common complications of chlamydia infection for men and women include:
- inflammation of the rectal mucosa;
- conjunctivitis;
- sore throat;
- pneumonia;
- inflammation of the brain;
- inflammation of the meninges (meningitis).
How is herpes prevented after casual relationships?
It is advisable to start it immediately after contact, treating the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs with antiseptic solutions of miramistin and chlorhexidine. You can also apply one of the antiherpetic creams and immediately consult a venereologist at the clinic, where they will carry out full prevention after sexual intercourse, which includes:
- Examination by a doctor to check for STD symptoms.
- Express smear for flora.
- Express tests for syphilis, HIV, hepatitis.
- PCR analysis for STIs and herpes including.
- Blood test for antibodies to herpes viruses.
- Intravenous or intramuscular administration of abnormal nucleosides, interferon, interferon inducers to block the reproduction and spread of the virus in tissues. Dosages and course duration are determined by a venereologist. The results of laboratory diagnostics are taken into account.
- If there are no manifestations of herpes infection, after 3 weeks, blood is donated for immunoglobulin M for all types of herpes, and a month later the blood test is repeated with the addition of immunoglobulin G.
- If the results are negative, prevention of genital herpes is considered effective.
Prevention of STDs after a casual relationship should be carried out exclusively in a clinic under the supervision of a venereologist. Doing this at home is unacceptable! The result of self-medication can be unpredictable - from the transition of the infection to the chronic stage, to anaphylactic shock to drugs.
The cost of herpes prevention is from 1000 to 5000 rubles, depending on the chosen regimen and route of drug administration.
If there was unconventional sex
If you have practiced oral or anal contact during casual sexual intercourse, you must inform your doctor about this so that the appropriate tests can be prescribed for you.
In these cases, on the same 7-10 days after the first unprotected sexual intercourse (if there were several), a scraping from the mucous membrane of the back wall of the pharynx and anus is needed for analysis. From these places, the same PCR method is used to determine the presence of pathogens such as chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, and gonococci.
In 4−6 weeks . It is this period after casual sexual contact that the doctor will prescribe for donating blood to be tested for the presence of antibodies for syphilis and HIV. Antibodies will not be detected earlier than this period. So there is no need to rush to donate blood “for HIV” immediately after unprotected sexual intercourse, no matter how scared you may be. During these periods, the test will be negative, when in fact HIV may be present.
The importance of cytomegalovirus prevention
Cytomegalovirus can remain in tissues for a long time without detecting itself. Most often, the disease is transmitted through saliva, through casual sexual intercourse. However, infection does not always occur after the first contact.
Pathogenic bacteria can remain in a “dormant” state in a person for a long time and become active after provoking factors - a decrease in the defense of the immune system, colds, hypothermia, stress, illness. Cytomegalovirus cannot be completely cured and can affect vital organs and systems, which is why prevention after casual relationships is so important. Signs of the disease may be:
- general weakness;
- frequent headaches;
- fever;
- persistent mild runny nose;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- temperature increase;
- muscle soreness.
Drug prophylaxis after unprotected intercourse is the primary treatment to help prevent the spread of the disease. It can affect the respiratory tract, lungs, pancreas, and kidneys. Sometimes the virus invades the lymph system, retina, and liver. As a result, not only the functioning of the listed organs is disrupted, but also those nearby. As a result, a person’s condition can worsen to critical, even death.
Tests after unprotected sexual intercourse
On days 7-10 after the first unprotected sexual intercourse, the doctor will prescribe scrapings from the mucous membranes of the genital organs for both the man and the woman. Please note that for correct analysis you need not smears, but scrapings. For women, they will be taken from the vaginal mucosa and from the cervix - cervical canal.
In men, a scraping is taken from the urethral mucosa. Keep in mind that while scrapings are painless for women, for men this procedure is noticeable and some discomfort in the urethra will be felt for several hours.
The scraping data will be used to determine sexually transmitted infections using the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method. These are the following infections - chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, gonococci, trichomonas, human papillomavirus.
The PCR method makes it possible to identify these pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases most effectively. And it’s better to get tested using scrapings rather than blood.
Diagnosis and prevention of the virus
Prevention methods are divided into “home” and medicinal. In the first case, you may not only not get rid of the virus, but also provoke the development of other pathologies. Even after measures taken at home, it is necessary to be diagnosed for the presence of the virus. It can only be detected using laboratory tests. Our clinic has modern equipment that eliminates misdiagnosis and helps to quickly detect the disease.
Prevention of cytomegalovirus is carried out with medication for several days. This is the most reliable way. Our clinic employs highly qualified specialists who successfully prevent infection after casual relationships:
- Drugs are prescribed to prevent the activation of the virus or the development of infection.
- Antibiotics are selected individually, taking into account contraindications and other medications.
- The genitals (externally and internally) are treated with special solutions, which significantly reduces the risk of infection. Douching is done, followed by the prescription of agents that restore the vaginal microflora.
- A vitamin complex is selected to restore or strengthen the immune system.
- Prophylactic treatment is provided for several days.
- An examination is carried out by a venereologist and urologist-andrologist.
- All laboratory tests are performed (blood, saliva, urine testing, smears are taken). The results will be ready within 24 hours.
- Intramuscular and intravenous administration of necessary drugs. Patients undergo allergy tests in advance.
Our specialists will inform you about effective ways to prevent possible infection and recommend medications that can be taken after casual relationships without harm to health.
Cytomegalovirus, once it enters the body, is practically incurable. However, it is possible to prevent the activation of the pathological process. We suggest visiting our Private Practice clinic and completing a full course of prevention with the involvement of all the necessary specialists. Due to the presence of our own laboratory, test results are guaranteed to be accurate and fast.