The quality of dental treatment depends on the accuracy of the diagnosis. A panoramic photograph of teeth helps to find the cause of dental diseases. However, some patients are concerned about X-rays, fearing harm to their health. In the article we will consider the need for such images, harm to the health of the body and other issues related to this procedure.
What is an orthopantomogram?
A panoramic photograph of the teeth, or abbreviated as OPTG from the word “orthopantomogram”, is a two-dimensional cross-sectional image of the patient’s jaw. In fact, this is an ordinary x-ray, since it is x-ray radiation and an orthopantomograph x-ray machine that is used to take the picture. This is where patients begin to fear for their health, because X-ray radiation is harmful to the body.
What you can see in the image:
- both jaws;
- all teeth including roots;
- condition of bone tissue;
- jaw joints;
- maxillary sinuses.
The doctor receives a panoramic picture of the patient’s skull and can make the most accurate diagnosis.
However, a panoramic image still differs from the usual x-ray and other hardware diagnostic methods: teleradiography, tomogram.
When an X-ray is taken, a visiograph works. With the help of such hardware research, you can see a maximum of two adjacent molars. That is, a targeted image is obtained in a two-dimensional plane. An x-ray can be taken at any public clinic.
Orthopantomogram
An orthopantomogram is done using a computed tomograph. The result is a panoramic image of the jaw in two dimensions. Diagnostics can be done in any public or private clinic. The price is several times more expensive: from 1000 rubles.
Teleradiography
Teleradiography is also performed on a computed tomograph. However, compared to an orthopantomogram, the doctor already sees the entire skull in front and profile. Accordingly, this is a more informative diagnosis than the first two. The examination method is used to resolve surgical and orthodontic issues. The procedure costs from 2000 rubles.
Tomogram
A tomogram (or computed tomography, CT) is also performed on a CT scanner. However, the doctor already sees a three-dimensional three-dimensional image: not only bone tissue, but also soft tissue. This examination is carried out to resolve issues regarding implantation and surgery. The photo is taken in private clinics, the price for the work starts from 1,500 rubles. You can do a segmental tomogram (a separate section of the jaw): it will be cheaper.
Which method is better
Which examination method is preferable? It depends on the issue that needs to be resolved. To place an implant, it is better to take a 3D image. If only one molar needs to be treated, a simple x-ray examination is sufficient.
In private clinics, patients are offered a panoramic photo at their first appointment. This is necessary to track the dynamics of changes in the condition of the jaw and teeth. The image will be stored along with the patient's record. Sometimes this service is provided free of charge, it all depends on the clinic.
Stages of the procedure
To carry out the procedure, a separate room, equipped accordingly, is required. The procedure itself does not cause virtually any discomfort and consists of several stages.
- The position of the person in the chair, the doctor’s clarification of the location of the problem.
- It is imperative that the patient wears an apron that protects against harmful radiation.
- Fix your head to get a good shot.
- Taking an image with the patient in a stationary position.
The entire procedure from taking a photo to receiving it in electronic or printed form takes a short period of time - about 20 minutes.
Analysis of the finished image
The dentist himself or a radiologist is responsible for describing the image. If the image quality does not meet the required quality, the procedure is repeated. The specialist examines the patient’s teeth, roots, and jaw bones in detail. If there are light and dark areas, this indicates the appearance of inflammation, cysts and other neoplasms.
In the pictures you can see inhomogeneities, damage to bone tissue, damage to the enamel, cement and root part, damage to the septum and other abnormalities that indicate the presence of a particular disease.
Features of performing a targeted shot for children
The younger generation needs this procedure more than adults, because caries develops more intensively in children. Another reason is to identify deviations and defects at an early stage of tooth growth. If any are detected, the necessary preventive and therapeutic measures are taken.
But it is not advisable to use the targeted photo procedure for children under 2 years of age. It is prescribed only in cases of birth or mechanical injuries, or to monitor the development of teeth.
Advantages and disadvantages
Each research endeavor has its pros and cons.
Advantages:
- Safety.
- High image quality.
- A large amount of information received.
- Convenient storage.
- Speed of execution.
Disadvantages for dentists include:
- It is impossible to detect cracks in the roots.
- Pictures of only one plane.
- Small viewing area.
- Narrow survey area.
- Limitations for use
The procedure is considered harmless and therefore has no visible contraindications for its implementation. Considering the minimum level of radiation (the permissible dose is 1000 microsieverts per year, i.e. about 100 images per year), a targeted image can be taken even during pregnancy. But, nevertheless, it is not recommended to resort to the procedure under the age of 2 years, in the presence of bleeding, reduced immunity, or in poor health.
A radiovisiograph provides a lower dose of radiation, an X-ray machine.
Price of the procedure
| Click to sign up for a FREE consultation |
Imaging services are provided in almost every hospital. Its cost will vary from 150 rubles and above. Sometimes the procedure is included in the cost of treatment.
In public clinics, under the compulsory medical insurance policy, you can take an x-ray and print the image for free.
Thus, a targeted image is a safe and effective procedure that can identify problems with the dental elements in the early stages if the patient seeks qualified help in a timely manner.
Minuses
Every medical procedure has its pros and cons. Let's consider them in relation to panoramic diagnostics:
- OPTG does not always provide accurate information, since the image is not three-dimensional, but two-dimensional. In this regard, CT is still much more informative.
- Sometimes image distortion reaches 30%, which negatively affects the diagnostic accuracy.
- OPTG does not provide complete information about the three root teeth, as it produces a two-dimensional image in a slice. The roots of such teeth are located in three planes at once, and the image is only two-dimensional.
Accordingly, many dentists refer to OPTG as a rough diagnosis that only gives a general idea of the condition of the teeth and jaw. When it is necessary to see a crack in a root canal or to fill a curved root canal, they resort to other forms of examination.
Orthopantomogram or panoramic photograph...
In the daily practice of a dentist of any specialty, for the most correct and complete diagnosis, there is often a need to obtain a panoramic X-ray of the patient’s oral cavity (survey X-ray, orthopantomogram). What kind of research is this, why do it, and what can be seen in such a picture? The answers to these and other questions can be found below in the article, which its author, Moscow colleague Stanislav Vasiliev, kindly shared with me.
What is an orthopantomogram and why is it needed?
An orthopantomogram (or “OPTG”, “panoramic image of the dental system”) is one of the types of diagnostic radiography. In dentistry, OPTG is of key importance - many types of treatment cannot be started without this diagnostic method. Technically, it is carried out as follows: the beam source (X-ray tube) and its receiver (film or digital sensor" move around the object under study in opposite directions. As a result, a very limited part of the object of study is in focus, everything else is blurred. Depending depending on the settings, we can get clear only a specific layer that interests us, and everything else in the image will be blurred. Panoramic images are taken using orthopantomographs. There are different orthopantomographs - film and digital. Film OPTG are almost history, while “digital” takes more and more place in modern dentistry. A modern orthopantomograph looks something like this:
This photo shows a Planmeca dental tomograph with a cephalostat. The latter is needed for teleradiography, a study that is widely used in orthodontics and maxillofacial surgery.
There is a widespread belief that this type of research is harmful. In fact, the volume of radiation even from a film orthopantomograph is such that it is possible to take panoramic photographs every day for a month without significant harm to health. And the radiation from digital devices is several times less than that of film devices, and the radiation dose received is much less than what you receive, for example, during a two-hour flight.
When is an orthopantomogram needed?
In principle, it is always needed. In dental treatment, prosthetics, orthodontic treatment, in surgery and implantology, even in rhinology when examining the paranasal sinuses, the value of panoramic images cannot be overestimated. However, in some cases it is impossible to navigate only by OPTG - nevertheless, we are transferring a three-dimensional image to a plane, and therefore distortions are possible. But orthopantomography should be considered as a primary x-ray examination, based on the results of which the tactics of both further, more in-depth diagnosis and treatment are built.
Orthopantomography of an adult.
For example, here's a snapshot:
Pay attention to the shape of the dentition. It turns out that the person in the picture seems to be smiling))). If we don’t see a smile (on the contrary, a “sad form”), then the picture was taken incorrectly and the amount of distortion in it will be very high. Such an image is not suitable for a good diagnosis.
They look at an orthopantomogram not as if in a mirror, but as if they were looking at another person. That is, the left side is on the right, and the right side is on the left. Sometimes, for convenience, the letter L (left) is placed on the left side or the letter R (right) on the right side. Or they sign the picture so that the patient’s data can only be read on one side.
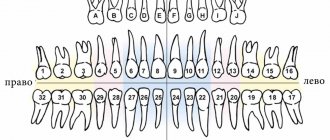
An adult normally has 32 teeth. But you have repeatedly seen on my blog that we are discussing, for example, the treatment of the 44th tooth or the removal of the 48th tooth... How does this happen?
The fact is that each tooth, in addition to its name, has a number. According to the WHO classification accepted throughout the world, the dentition is divided into four segments. The top right segment is tens. Upper left - twenties, Lower left and lower right, respectively - thirty and forty. The numbering comes from the center of the dentition. It turns out that the right upper central incisor is the 11th tooth, the tooth following it (the right upper lateral incisor) is 12, the lower left second premolar is 35, and the lower right wisdom tooth is 48 teeth.
Although my friend, Valera Kolpakov, who now lives and works in the USA, said that they have a different classification: teeth are simply designated by a clockwise serial number. In our country such designations are very rare. Europe is still...
In the picture, yellow numbers indicate the numbers of an adult’s teeth. Now you can surprise your dentist by telling him that your pain is not just some lower molar, but specifically the 36th tooth. He will understand everything and look at you with such respect...
Some doctors name teeth by segment number. For example, “four, two,” lower left lateral incisor. This account is being vigorously imposed in institutes and universities, mainly by teachers of pre-retirement age. This classification is fundamentally incorrect. Why? Because initially this teeth counting system was intended for machine processing, and the machine works with the number “forty two” and not with the number “four two.” Therefore, you need to name the teeth correctly.
Most dental materials are made radiopaque. This is done so that the volume and location of this material on x-rays can be controlled. For example, filling materials for root canals are indicated by the letter A in the picture.
When an orthopantomogram of the dental system reaches a nearby ENT doctor, the latter immediately notices the penetration of the roots of the teeth into the maxillary sinus (letter B in the picture). Moreover, old dental textbooks mention this. In fact, the roots of teeth very rarely penetrate the maxillary sinus. Most often, they go around the edges of it so that the bottom of the sinus is between the roots of the teeth.
Orthopantomography gives a good idea of the location of wisdom teeth (letter C in the picture). Even targeted photographs do not provide a complete picture of the structure and localization of figure eights. Therefore, without performing an OPTG, I highly do not recommend undertaking the removal or treatment of “wise” teeth
In addition to teeth, OPTG also shows other structures that may be of interest to the dentist. For example, the mandibular canal, which runs through the thickness of the lower jaw and contains a neurovascular bundle, is highlighted in green. The latter innervates the teeth, the corresponding half of the lip and chin. This bundle exits through the mental foramen (indicated in dark green), which some “specialists” sometimes confuse with a cyst.
The borders of the maxillary sinuses and nasal passages are indicated in red. The image shows a curvature of the nasal septum and, as a consequence, asymmetry of the nasal passages. This is an indirect sign of chronic rhinosinusitis, including allergic nature.
The temporomandibular joints are indicated in blue. Normally, they should be symmetrical and have a certain shape. A noticeable difference in the shape of the joints, as well as their asymmetry, is one of the signs of chronic arthritis. In this image, the joints are almost symmetrical, therefore, the patient has no problems with the joints.
Radiopaque materials are highlighted in purple. The pictures clearly show all the fillings, the quality of the canal fillings, etc. The thin purple stripe on the front teeth are retainers installed after orthodontic treatment.
There are also structures on the OPTG that are not very interesting, but are still visible:
For example, the earlobes are highlighted in red, and the spinal column is highlighted with a blue dotted line against the background of the lower jaw. On either side of it is the hyoid bone. It comes into focus only in a lateral projection, and therefore is visible as two separate parts.
The horizontal line above the upper jaw is the hard palate, and on the sides of it the zygomatic bones are clearly visible. In the contour of the earlobes, one can distinguish the styloid process, the mastoid process and the opening of the external auditory canal. Thus, a panoramic image, although distorted, can give an almost complete picture of the state of the dental system - due to this, it is simply necessary in the high-quality diagnosis of dental diseases.
Orthopantomogram of a child.
Oddly enough, children have more teeth:
But the principle of their numbering is the same. Unless baby teeth are designated not by tens or twenties, but by fifties, sixties, seventies or eighties - as indicated in the picture. For example, tooth 75 is the left lower primary molar.
Under the milk teeth are the rudiments of permanent teeth (indicated by yellow numbers). At different ages they look different and have different shapes. In this image, for example, you may not see the crowns of the forming teeth 15, 25, but you can see the contours of the rudiment - therefore, there will be teeth.
The blue color in the picture indicates the mandibular canal.
Blue color - temporomandibular joints. Note how the relative position of the joint head, articular tubercle and socket differs from the structure of the adult joint.
The purple line is the contours of the maxillary sinus. In children it is relatively less than in adults. Therefore the voice is quieter and higher.
Green color - nasal septum and nasal turbinates. While relative symmetry is observed, however, due to injury, chronic rhinitis, allergies, or simply due to uneven growth, a curvature of the nasal septum is possible. As I already wrote, this is a risk factor for the development of chronic rhinosinusitis (sinusitis).
Red arrows and the letter A indicate artifacts from earrings. In some cases, jewelry in the form of piercings, chains, etc. can introduce significant distortions and complicate diagnosis. Therefore, before performing orthopantomography, it is better to remove all jewelry from the face and neck.
Of course, experts see much more ordinary people in the photographs. And radiologists are much more than ordinary specialists. It would be great if any radiologist would comment on this post.
In general terms, the diagnostic picture from panoramic images looks exactly like this. Now you can take your panoramic photo, look at it carefully and no longer say: “I don’t understand anything here.” After all, it’s better to see once than to hear a hundred times, right?
Indications
In what cases is it necessary to do without an x-ray? There are several such situations:
- before starting orthodontic treatment;
- for detailed diagnostics of the maxillofacial apparatus and dentition;
- before planning an operation;
- to detect the localization of the focus of the inflammatory process;
- when diagnosing periodontitis;
- in implantology.
Orthodontic treatment
Orthodontic treatment is always preceded by an examination of the jaw apparatus. The image clearly shows the root system and its condition. Based on the information received, the orthodontist will select a bite correction method. A panoramic photograph of the teeth must be taken for children, since the doctor must see the anatomical features of the structure of the jaw system and the rudiments of unerupted molars. It is important to see in advance in which direction the teeth will grow, in what condition the root system is - its stability.
In what cases is a comprehensive diagnosis of the entire dental system performed? This examination method allows:
- identify malocclusion pathologies in young children;
- promptly detect hidden foci of the inflammatory process and unmanifested problems;
- detect the beginnings of the formation of tumors and neoplasms;
- control the quality of filled root canals;
- check the condition of bone tissue;
- see other hidden problems.
It is very important for adult patients to undergo annual examinations and take panoramic photographs in order to promptly identify pathology.
Hidden caries can also be seen on the x-ray.
Before surgery
Radiographs are extremely important before planning dental surgeries. The surgeon needs to see nearby molars, the condition of their roots, and the proximity of the nerve endings of neighboring molars. Also, before the operation, it is necessary to identify the presence of root fractures, foci of the inflammatory process and other nuances. Otherwise, the surgeon will operate “blindly”. So it is in the best interests of the patient to go and take a panoramic photo.
Tumor detection
Detection of the localization of the inflammatory process is of particular interest to the doctor and the patient himself. Because in most cases, patients complain not about a bad tooth, but about nearby healthy molars.
A panoramic photograph is also taken when wisdom teeth are difficult to erupt.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a dangerous gum disease that also destroys bone tissue. A panoramic (circular) image allows you to see the depth of tissue damage, the depth of periodontal pockets and make the correct diagnosis.
Implantation
Implantation is a modern method of restoring the smile line and functionality of the jaw system. Panoramic diagnostics (it is better to do a computed tomogram) before implantation will help identify pathology of the maxillary sinuses, in which implantation is strictly prohibited.
CT scans are also performed after implantation to monitor the quality of work. The image shows the condition of the bone tissue, which is especially important when implanting titanium elements.
Contrasting types of research
There are contrast radiological types of studies: arthrography, angiography, sialography, dacryocystography. They are worth mentioning separately, because... To obtain data on the condition of the maxillofacial apparatus and oral cavity, doctors inject a water-soluble contrast agent with iodine into the patient’s body.
During a contrast study, doctors inject a contrast drug with iodine into the patient's body.
Until recently, the methods were actively used in dental practice; now this happens much less frequently, because they are quite labor-intensive and even uncomfortable, painful for the patient, and some require anesthesia. In addition, these methods have contraindications (for example, iodine intolerance), as well as narrow indications. Thus, sialography is used to determine the condition of the salivary glands and in cases of suspected salivary stone disease.
How pictures are taken
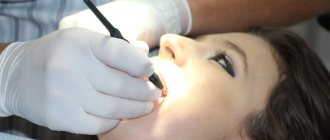
The pantomograph diagnostic procedure does not take much time and is easy to perform. A special stick made of medical plastic is placed in the patient’s mouth, which he must squeeze with his teeth. Before the procedure, you must remove all metal accessories: rings, earrings, watches, necklaces. The patient is asked to wear a lead apron, which protects against harmful radiation.
After turning on the device, a digital sensor begins to rotate around the patient’s head, which scans the jaw and temporal area. The whole procedure takes no more than a minute. Then the doctor analyzes the data received, enters the information into a computer or onto a flash card, and takes a picture.
How is an orthopantomogram done?
No special preparation is required for the study. You will need to remove glasses, earrings, hair clips, other metal objects, and dentures. An orthopantomogram is usually done in a standing position. A special X-ray protective apron-cape is put on the chest. The position of the head is fixed with special clamps. As directed by the doctor, you will need to bite a special plastic mark (which is located in a disposable cover) - this will allow the image to be correctly centered. The tongue should be kept pressed to the palate. During an orthopantomogram, the module will move around the head, this will take 15-20 seconds, and during this time you must stand strictly still in order for the image to be of the proper quality.
You can get an orthopantomogram in Moscow at Family Doctor JSC.
Sign up for diagnostics Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Other types of diagnostics
An image of the jaw is taken using a special device called an orthopantomograph. This device is an X-ray mechanism for scanning the entire jaw and temporal area. There are two types of pantomographs: digital and film (analog). Film mechanisms require a darkroom, while digital mechanisms require a computer. Digital pantomographs are more convenient to use, and their radiation dose is several times lower.
In modern dentistry, film orthopantomographs are used less and less often, since the pictures are unclear and quickly erased. The latest equipment is based on digital technology, and examination methods do not harm the body. The resulting digital image can be printed on photo paper or saved on any medium.
However, some public clinics still have old film-type equipment. If you take a panoramic photograph of your teeth under compulsory medical insurance, be prepared for such a turn of events.
The image can also be obtained using other hardware tools. Therefore, a panoramic test is also done using:
- computed tomography;
- teleroentgenograms.
CT scan
Cone beam tomographs allow you to take panoramic images of the jaw, which facilitates the work of dentists and orthodontists. A panoramic image of the entire oral cavity helps to make a correct diagnosis, prescribe bite correction and implant implants. However, this type of diagnosis is contraindicated for persons suffering from claustrophobia and pathological mobility (cannot sit quietly in one place). Pregnant women should refuse this procedure; breastfeeding women should refrain from breastfeeding for two days after the examination.
Teleradiogram
Teleradiography is prescribed when installing braces or implants, bridges. The procedure is also part of orthodontic treatment and surgery. The radiation exposure during this type of examination is minimal and does not pose a threat to the patient. This procedure is performed even on young children if there is a suspicion of an anomaly in the structure of the dental system.
Types of teleroentgenogram:
- frontal;
- lateral;
- axial
In frontal diagnostics, images are taken from the front and back. A lateral teleroentgenogram is done in case of malocclusion; this procedure is mandatory when installing braces. The chin (axial) radiograph is clarifying (additional). It is necessary for a complete picture of the structure of the patient’s skull in a three-dimensional image. This procedure is mandatory when installing upper jaw implants.
Advantages of teleradiography:
- the resulting image is as close as possible to the actual dimensions of the patient’s skull;
- the result of the study is ready within a few minutes after the image;
- The radiation dose to the patient is negligible.
This type of examination is preferable for patients with claustrophobia who are frightened by the appearance of the tomograph cabin. This type of diagnosis has virtually no disadvantages. However, the doctor’s literacy factor should also be taken into account: you need to be able to correctly decipher an x-ray.
Sight shot
With this type of study, a general photograph of the oral cavity is not taken; the image captures only the area of one or several teeth. The picture shows their root system, the condition of the canals and the bone tissue surrounding the tooth, as well as the gums. An indication for a targeted image is, for example, the presence of caries or pulpitis.
The study is performed using a device called a visiograph. This equipment allows you to obtain a two-dimensional flat image.
The procedure is carried out as follows: the patient is given a lead apron and seated on a chair next to the device. A sensor, which is wrapped in film, is applied to the diseased tooth. It must be held in the mouth, pressed against the tooth and gum with a finger, for about 10-20 seconds. Done – the pictures are taken. The doctor can only process them on a computer, after which they can be sent to print or saved in a special program for viewing.
The image captures only the area of one or more teeth
The study is also called intraoral, but it is important to understand that a targeted shot is the most popular, but not the only method of intraoral radiography. There are others:
- interproximal: allows you to study the crown of a certain tooth in detail, identify hidden processes under a filling or on supporting teeth under fixed artificial orthopedic structures (bridges, crowns),
- occlusal or in bite: this is an addition to the targeted photograph in cases where it does not give a clear idea of the processes occurring in the desired area. Allows you to obtain an image over 4 teeth, to clarify the features of the pathological process on impacted teeth or in the area of cystic formation. This type of study is also indicated for patients with an increased gag reflex or impaired mouth opening,
- shooting with parallel beams or long-focus: it allows one to assess the condition of the bone tissue structure and identify signs of periodontal disease.
Cost – from 250 rubles for 1 photo.
Common Questions
How safe is X-ray diagnostics?
Doctors responsibly declare that this diagnosis can be carried out several times a year without harm to health. A lead apron does not mean that the examination is mortally dangerous for the patient. The apron is worn to protect the thyroid gland from radiation. It is customary to wear aprons in dentistry, traumatology, etc., since the patient receives a dose of radiation annually during a fluorogram.
How often is irradiation allowed?
Since the radiation exposure to the body during an orthopantomogram is small, studies can be done as needed. That is, how much is needed for treatment. However, there is a limitation: no more than 80 images per year. This figure takes into account preventive fluorograms, and not just dental photographs.
How dangerous is x-ray for pregnant women?
X-rays are taken for pregnant women only as a last resort, if it is required to save the life of the woman and the fetus. However, in the first trimester, any manipulations with X-rays are prohibited: this will negatively affect the condition of the embryo. The second trimester is relatively safe, when all the internal organs and systems of the baby are formed. In the third trimester, taking an X-ray is very dangerous, as it can lead to premature birth.
Do children get x-rays?
In dental practice, photographs of baby teeth are taken if a cyst or a hidden source of inflammation is suspected. For diagnosis, a targeted image is sufficient, the radiation dose at which is extremely small. For the body to suffer harm, you need to make 100 such diagnostics in a year, or more than five in a day. Teenagers can already undergo OPTG, as they understand the requirement to stand still and not cry during the procedure.
Is it possible to carry out diagnostics during pregnancy?
According to SanPiN, X-ray examinations are allowed in the second half of pregnancy using protective equipment, provided that the radiation dose does not exceed the same 1000 μSv. However, it is recommended to refrain from taking x-rays in the first and last 12 weeks, i.e. in the first and last trimesters.
Do not be afraid of undergoing diagnostic procedures during pregnancy. Even ordinary caries is an infection that, if not properly treated, can spread throughout the body and lead to infection of the fetus. Therefore, it is better to receive a small and completely safe dose of radiation than to carry out complex dental treatment blindly, not knowing how deep the inflammatory process is.
After the baby is born, i.e. During breastfeeding, dental x-rays can be taken, even more than once (within reasonable limits). Radiation doses are minimal, so radiation does not accumulate in breast milk, and there will be absolutely no harm to the baby. There is also no need to pump or skip feedings.
Bottom line
To properly treat teeth, you need to have an idea of the condition of the jaw and skeletal system. This information can be provided by an x-ray, which is taken with a special orthopantomograph or computed tomograph. The picture is taken in every private clinic and government institutions. The cost depends on the equipment and tariffs of private clinics. In a government institution, you can get an X-ray done free of charge upon referral or for a small fee of 300 rubles.
Orthopantomography is a panoramic image of both jaws in a section in a two-dimensional plane. The absence of a three-dimensional image is a common reason for an incorrect diagnosis. Also, a two-dimensional image does not allow one to see microcracks on the roots of teeth, and in three-rooted teeth only 2 roots are visible. The listed disadvantages speak in favor of computed tomography, although it costs several times more.
Panoramic diagnostics are recommended not only during dental treatment and implantation: it must be performed annually for preventive purposes. This will allow timely detection of hidden caries, internal foci of inflammation, cysts, tumors, and neoplasms.
Sources used:
- Abolmasov N. G., Abolmasov N. N. Orthodontics. – 2008.
- American Academy of Implant Dentistry (AAID)
- Distel V. A. Dental anomalies and deformations. Omsk — 2004.
- “Orthopedic dentistry. Textbook" (Trezubov V.N.)
CT scan
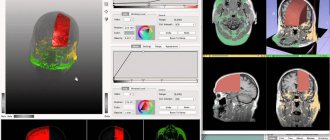
To conduct a computed tomography, or CT for short, you need a machine called a tomograph. Compared to all the previously listed research methods, computed tomography is a volumetric, three-dimensional or 3D image of the oral cavity. Due to the “volume”, the doctor has the opportunity to see the necessary areas in more detail and even layer by layer, which increases the effectiveness of treatment and reduces the likelihood of errors, relapses and complications. In addition, CT reduces the time spent on examining each patient and reduces the total radiation exposure, which allows the technique to be used even in pediatric dentistry1.
Computed tomography produces a three-dimensional image of the jaw
Computed tomography is prescribed before complex surgical interventions; it is required before and after dental implantation. Especially when a comprehensive restoration of all teeth on one or both jaws is expected. This is important for every patient to know, because... even today there are clinics where, instead of CT in such situations, they perform OPTG, which is less informative and may not give an idea of all the nuances and features of the structure of your jaw system.
Computed tomography is mandatory before complex dental implantation, for example, according to protocols with immediate loading. If only 1 tooth is restored, then an orthopantomogram will be sufficient.
The cost of a segment of the dentition is from 1,500 rubles, one jaw – from 3,500 rubles, two jaws – from 5,000 rubles.