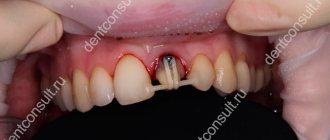
Symptoms of manifestation
Bruises on the face are difficult to ignore. It is characterized by knowledge of all standard symptoms, such as:
- Painful sensations in the facial area. And they are usually felt strongly because the ends of the facial nerves are among the most sensitive;
- Tissue swelling. This manifests itself as swelling of the skin, which may appear thickened upon palpation. The severity of edema depends not only on the severity of the injury, but also on the thickness of the skin and the internal structure of the tissues. Therefore, the area around the mouth and face is most susceptible to swelling;
- Bruises, bruises and hematomas. They arise as a result of damage to blood vessels and the accumulation of platelets in the damaged area. It’s worth saying right away that the deeper they are under the skin, the later the reaction will appear, but, unfortunately, the longer it will take. For this reason, many people start using ointments and gels for bruises even before visible signs appear;
- Feeling numb. This occurs in cases where the fibers of the facial nerve were directly affected during the injury. If nerve damage is very severe, there is a risk that reduced nerve activity may persist;
- Disruption of various areas of the face. Examples include: inability to see if the eye is swollen, difficulty breathing if the nose is injured, difficulty chewing food if the jaw is injured;
- Open bleeding. Observed when the skin is damaged at the site of the bruise and there is an open wound or deep scratch;
- Nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness, convulsions. Such serious symptoms can occur if a bruise of the soft tissues of the face is accompanied by a traumatic brain injury and, as a consequence, impaired brain function.
Bruises and bruises are symptoms of contusion of the soft tissues of the face.
Of course, each of these symptoms may vary in severity in each individual case. Much depends on the individual characteristics of the body, such as the thickness of the skin or the elasticity of blood vessels. So, with one type of injury, one person may only have swelling, while another may have a severe hematoma.
Neck injury
During a strong blow to the back of the head, compression occurs on the jugular vein and the vagus nerve, with which the occipital bone contacts. The vagus nerve travels to the intestines and along the way gives off branches to the heart and lungs. Infringement of the vagus nerve is fraught with constipation - this is the most common option. In addition, tachycardia and arrhythmia are possible, which manifest themselves in adulthood. If the branches of the vagus nerve leading to the lungs are infringed, then a person may develop an unreasonable cough, he will be prone to colds and suffer from something similar to bronchial asthma.
Compression of the jugular vein in the jugular foramen leads to stagnation of fluid in the cranial cavity (after all, it is through this vein that the outflow of venous blood from the head mainly occurs), and intracranial pressure increases. Such people often have a pale, sallow complexion and dark circles under the eyes. Since the occipital bone is directly connected to the sacrum, when it is injured, the sacrum is also blocked. It is especially important to eliminate this problem for women, because a stationary sacrum negatively affects the course of labor.
Severe injuries to the back of the head may be accompanied by visual impairment. Displacement of the occipital bone often leads to impaired blood circulation in the vertebral arteries, which leads to frequent dizziness. The occipital bone determines the position of the temporal bones, and they, in turn, determine the position of the lower jaw. With severe injuries to the back of the head, the lower jaw shifts to the side. A sagging chin also signals an injury to the back of the head: tense muscles under the back of the head compress the lymphatic vessels, which causes stagnation of lymph and swelling under the chin.
First aid
First aid is recommended for injuries to the soft tissues of the face, regardless of the force of the blow. Here are three basic steps in this situation:
- Place something cold on the bruised area. This could be ice, snow, a compress soaked in cold water, or even a chilled metal spoon. Cold helps constrict blood vessels, reducing the risk of bruising under the skin. However, there are two things to keep in mind. Firstly, facial skin is quite thin and cannot be exposed to prolonged exposure. The optimal time is 15-20 minutes. The procedure can be repeated after 2 hours. Use material that protects the receptors from hypothermia. The second point is that the effectiveness of this method is available only in the first half hour after injury;
- If there are signs of skin trauma, be it wounds or abrasions, it is important to treat them with antiseptics. The most common of them are the well-known hydrogen peroxide, herbs, and a very weak solution of manganese solution. This must be done very carefully, since every touch to the wound can cause pain to the victim;
- Anesthesia. If the sensations are strong, you should turn to painkillers. Among them are Ketone, Ketorol, Ibuprofen. Before use, be sure to read the instructions.
First aid for bruised soft tissues of the face includes applying ice.
In most cases, the listed first aid measures for bruises are sufficient. However, if the injury is much more serious and the victim experiences heavy bleeding or convulsions, then the first step is to call an ambulance. When traveling, control bleeding with a tourniquet or position the person so that they do not risk swallowing their tongue.
It is important to remember that the method of providing first aid will affect the result of further treatment of facial bruises and the likelihood of developing complications.
Folk remedies used at home
Many plants and foods common in the daily diet contain components that can quickly heal bruises on the face. This method of treatment, harmless to the body, is suitable for bruises of the 1st and 2nd degree.
For treatment, components with anti-edematous, anticoagulant, and anti-inflammatory properties are used. Folk remedies improve tissue trophism, promote the resorption of blood clots, stimulate local immunity and metabolism, and have a moderate analgesic effect.
Cabbage, potatoes and burdock
For treatment, a green cabbage leaf is washed under cold water, several small cuts are made on the surface and applied to the site of the bruise. The compress can be secured with adhesive tape. The remedy is kept until the leaf dries, the procedure is repeated 4-6 times a day.
To enhance the anti-edematous effect, compresses with cabbage leaves can be combined with the application of raw potatoes. To do this, apply grated potatoes to the surface of the bruise, cover with gauze and leave to act for 30 minutes.
In summer you can use burdock leaf. It is washed with cold water, cuts are made and applied to the bruise with the light side.
Aloe and honey
To prepare the herbal remedy, select a large leaf of a plant that is at least 2 years old. The crushed raw materials are mixed with honey in equal proportions, placed in a glass container and stored in the refrigerator.
Every day, apply a thick layer of ointment to the surface of the bruise and cover it with gauze. The duration of the procedure is 20 minutes, the amount is 2-3 times a day.
If it is not possible to find aloe, the plant can be replaced with grated fresh beets.
Banana and pineapple
To reduce hematoma and swelling, it is enough to apply a banana peel or a slice of pineapple to the bruised surface. The duration of the compress is 30 minutes; to achieve a quick effect, you will need at least 4 procedures per day.
Apple vinegar
To prepare a medicinal solution, vinegar (2 tsp) is diluted in cold water (1 l). A gauze cloth soaked in the solution is applied to the bruise for 30 minutes 2-3 times a day.
Heat therapy
Exposure to heat stimulates local blood and lymph circulation, immunity and metabolism. This accelerates the processes of tissue cell restoration and hematoma resorption.
You can treat with heat 2 days after the injury. To achieve better results, procedures are combined with massage.
To apply the procedure at home, gauze cloth is folded into 5-6 layers, moistened in hot water and applied to the injured area. Plastic film and thick fabric are placed on top of the fabric. The exposure time is 15-20 minutes, the number of procedures is 2 times a day.
The warming effect of the compress is enhanced by 40% ethyl alcohol, vodka, camphor or salicylic alcohol. They are diluted with hot water.
Massage
Reflex and mechanical influences with the hands stimulate contraction of the muscles and subcutaneous tissues of the face. This improves blood circulation, microcirculation and metabolism. As a result, the processes of resorption of infiltrate, edema and hematoma are accelerated, and the risk of muscle atrophy is reduced.
6-8 hours after the injury, begin massaging the areas adjacent to the affected area. To do this, deep stroking, kneading and vibration techniques are used. The duration of the procedure is 10 minutes, the quantity is 2 times a day.
Massage of the bruised surface can be done only 48 hours after the injury, provided there are no ruptures of large vessels and an extensive wound surface.
In this case, only superficial stroking and vibration are allowed. The duration of the procedure is increased to 15 minutes.
Diagnostics
A bruise is easy to diagnose, but only doctors can determine its severity and possible complications. Therefore, if for any reason the injured area is bothering you, it is better not to waste time and seek professional help. The diagnosis can be made:
- inspection;
- palpation;
- Assessment of symptoms and complaints;
- In some cases, an ultrasound or x-ray examination may be required.
Diagnosis consists of determining not only the presence of a bruise, but also its severity. There are four degrees:
- First degree. This is the easiest and least dangerous option, involving a slight change in the structure of the subcutaneous tissue. There is no bleeding or hematoma, but blue skin discoloration is quite possible. For the first degree of injury, visiting a doctor is usually not required. It is quite possible to limit yourself to home remedies, which, with the right approach, will help eliminate symptoms in 5-7 days;
- Second step. In this case, significant damage to the subcutaneous and muscle tissue occurs. Severe swelling, pain and even hematoma may appear. It is better to treat such a bruise with medications together with physiotherapeutic procedures;
- Third degree. It damages not only muscle tissue, but also tendons. In some cases, the integrity of the skin may be compromised. Since there is a risk of developing an infectious process, examination by a doctor is mandatory.
- Fourth degree. This is the most severe and dangerous degree of injury. It is always accompanied by injuries not only to soft tissue, but also to bone tissue. In this case, there is a high risk of developing various types of complications. It is imperative to seek qualified medical help.
Accordingly, the type of treatment will directly depend on the degree and nature of the bruise.
Consequences of fights and falls - concussion
We will try to answer this question in this not very long article!
There are few people in the world who have not heard anything about concussions. Most, both men and women, can talk about situations in which they have been and received various types of injuries. In some cases there were concussions, and maybe someone was on the verge of it. But no one can give a clear answer. They usually say that there was a severe headache and dizziness, but “I” did not turn anywhere.
Let's get creative! Imagine a decent-sized egg - it will be a human head, where the skull replaces the shell, the brain is the yolk inside, and the white is cerebrospinal fluid. Introduced? Now let’s shake the egg or hit it. The yolk floating inside collides with the shell, and each touch leaves marks on the yolk.
The same thing happens with the human brain (usually everyone has one!). He is very gentle and fragile. Any contact of the brain with the skull leads to a change in the shape of brain cells or a so-called concussion. The condition of a concussion is not a pleasant one. There are cockroaches rushing somewhere in my head all the time! But this is much better than if, upon impact, the integrity of the skull was not preserved.
The consequences of such injuries can be different. For example, loss of connection. This can occur selectively between any brain cells, and maybe between entire departments. There is poor interaction between the trunk and its identical opposite hemispheres.
Some symptoms of a concussion
Such symptoms include an increase in the size of the eye pupils, vomiting, even slight memory loss, partial or complete loss of taste and impaired sense of smell. But a head concussion does not always cause these symptoms, and if something bad happened to you, after which you have been dizzy for several days or have signs of a headache, contact the clinic. See a neurologist to examine your skull.
Concussion
Most concussions occur due to some kind of blow. And blows reach our heads in different ways and usually cause swelling and minor hemorrhages. These can, of course, include reckless fights, serious falls with injuries and, of course, accidents. A concussion occurs only due to a strong blow (the direction does not matter) to the head, because the brain must be displaced in such a way that a collision with the skull occurs. A weak impact does not cause a concussion.
After such a strong blow, damage occurs and sometimes even destroys some of the nerve cells that are responsible in the body for the passage of impulses to the brain. There comes disorder in their work, you can call it a neural storm in the brain. It is cellular rabies that leads to significant loss of vision and loss of memory (full or partial), vomiting and nausea, headaches, etc.
The brain heals us!
It's good that our amazing brain itself is engaged in our treatment. He voluntarily begins the process of pacifying rebellious neurons by increasing glucose production. After all, with the help of glucose, blood vessels contract, and this means the work of the brain slows down. And the restoration process will end only when everything returns to its normal appearance.
Self-medication usually takes several weeks. The only requirement: do not receive new concussions or negative impacts during this period. Otherwise, new damage may not be reversible and will lead you to dementia. The main medicine in this situation is peace and only peace!
Lie down and rest in silence, preferably without TV.
So as not to disturb the nerve cells. If you notice similar symptoms, consult a doctor, as rest alone may not be enough! You may need treatment with medications, because the head is not to be trifled with! Take care of your health! Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Treatment
Treatment methods for bruises can be divided into two large groups: traditional in the form of drugs and treatment methods, and non-traditional in the form of traditional medicine. Ideally, you can combine techniques from both groups. This solution will help you get rid of bruises in less time.
Medication
If the situation does not require hospitalization, the bruise is treated using standard methods. Namely:
- Preparations for external use: gels, ointments, creams;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures. These include electrophoresis, heating, laser therapy. All these procedures are aimed at eliminating subcutaneous clots and stimulating skin regeneration.
Creams, ointments, and other treatments for bruises are widely available.
In every pharmacy you can find a huge selection of such products. But when choosing, it is important to pay attention to the composition, influence and age restrictions. Not all products are suitable for children.
With regular and correct use of the ointment, you can get rid of bruises and swelling within a few days. And if you supplement your treatment with physical therapy, you can expect results even faster.
Traditional methods
Bruises and bruises can also be treated with traditional medicine. The only rule is that you can start using them a few days after the injury.
Among the folk recipes for bruises and bruises on the face it is worth mentioning:
- Cabbage leaf or raw potato. They should be applied to the damaged area. Thanks to this, swelling quickly decreases;
- Honey. Has a good laxative and anti-inflammatory effect. You can even not limit yourself to the area of the bruise, but apply honey all over your face, creating the appearance of a mask;
- Camphor oil. To obtain the effect, it must be applied with light rubbing movements;
- Compresses. It is best to cook them with onions or salt;
- Alcohol-based compresses. In this case, the rosemary plant can be the basis. Has a warming and antiseptic effect;
- Arnica decoction. This measure is applied not externally, but internally. It not only strengthens the immune system, but also stimulates regenerative processes.
Applications with honey are a folk method for treating bruises of the soft tissues of the face.
And, of course, one should not underestimate the influence of standard massage measures in the form of light stroking and rubbing.
Severe brain contusions
Such an injury poses a threat to human life. The consequences of a severe brain injury are serious, and recovery takes several months. Often the victim never fully recovers.
The following signs indicate a severe brain injury:
- loss of consciousness, after which the person is in stupor or a state of stupor;
- temperature rise to 41°C;
- psychomotor agitation, convulsive syndrome;
- disturbances in the respiratory and circulatory system (up to the need for artificial ventilation);
- neurological symptoms (dilation or constriction of pupils, “floating” eyeballs, difficulty swallowing, paralysis, loss of speech);
- pronounced meningeal signs.
Severe brain effects regress extremely slowly. Recovery takes a long time. In some cases, the patient becomes disabled.
The most common consequences of brain contusions are:
- inflammation of the meninges;
- epilepsy;
- atrophy (decrease in tissue volume) of the brain;
- hydrocephalus accompanied by intracranial hypertension;
- scars on the meninges and tissues;
- cerebrospinal fluid cysts;
- post-traumatic porencephaly;
- liquorrhea (due to a skull fracture).
These conditions are accompanied by movement disorders, dizziness, impaired coordination, speech, mental disorders, headaches, decreased intelligence, and convulsive seizures.
Consequences
Complications with bruises are quite possible. It all depends on the nature of the injury and which area of the face was damaged. Possible consequences include:
- Nerve damage. completion. This is quite dangerous, since it is not always possible to fully restore their functionality. This means that the affected part of the face may stop moving;
- Deterioration of vision. If the area around the eyes is bruised, there is also the possibility of damage to the nerve responsible for visual functions. Again, the outcome depends on the nature of the injuries. Both partial and complete loss of vision is possible, which is much less common;
- suppuration at the site of the bruise in the form of an abscess;
- bleeding that, if not treated immediately, may lead to fainting or shock;
- Cyst formation in the presence of hematomas.
In case of serious injuries, the bruise may be accompanied by a concussion, deformation of the bones of the nose or jaw. As a result, a person may later suffer from conditions such as sinusitis or sinusitis.
Mild brain contusions
They are not accompanied by a threat to life and manifest themselves with the following symptoms:
- loss of consciousness, lethargy, drowsiness, memory loss;
- dizziness, vomiting;
- changes in heart function, increased blood pressure;
- neurological disorders (tremor of the eyeballs, lack of pupillary response to light, decreased muscle tone, anisocoria);
- meningeal symptoms (neck muscle tension, Brudzinski and Kernig symptoms).
There are no serious consequences for mild brain contusions. The prognosis for the patient is favorable. Symptoms disappear within 3 weeks.
Main services of Dr. Zavalishin’s clinic:
- consultation with a neurosurgeon
- treatment of spinal hernia
- brain surgery
- spine surgery
Prevention
Almost all of us have had bruises on the soft tissues of our faces in our lives. Unfortunately, this cannot be completely prevented. However, in order to at least minimize the risk, it is necessary to take basic precautions and safety measures. When it comes to children, it is important to teach them from an early age how to avoid traumatic situations.
If facial bruises do occur, do not leave it unattended and take appropriate measures. You can do this yourself or seek medical help.
How to remove a bruise from a blow?
Hematomas from blows can be removed in two ways: using medicinal drugs and compounds or by masking .
The choice of method depends on the extent of the damage and how quickly the injury needs to be removed.
First aid
Keep in mind! Direct treatment should always be preceded by first aid.
The further process of resorption of the bruise depends on this, so after injury, the following steps should be performed as soon as possible:
- Apply something cold to the bruise . Ideally, this is ice, but in “field” conditions you can use any frozen product from the freezer, a bottle of cold water, even ice cream purchased at the nearest store, and any cold metal object. The main thing is to ensure cooling of the damaged area within the next half hour. Cold should be applied not only directly to the hematoma, but also to the entire cheek to avoid the spread of internal hemorrhage to adjacent tissues.
- Limit heat exposure . Excessive heat during the first day can provoke an increase in bruising, for this reason it is forbidden to warm the damaged areas with compresses - this will be needed in subsequent days.
- Stop nosebleeds . If an eye injury is accompanied by such a symptom, you should not blow out excess blood, as this can lead to the spread of the hematoma to the area near the nose and to the cheek.
The next day, if there are no open wounds in the bruise area, you can perform warming .
Remember! Any methods are suitable for this - from a freshly boiled egg to heated salt wrapped in natural fabric or in a bag made of it.
It is optimal to perform warming in the morning and evening throughout the healing period.
Medications for bruises
Elimination medications and ointments are often found in home medicine cabinets.
And if you don’t have them, you can buy such products at any nearest pharmacy.
Among these medications, the most common are the following:
- Heparin ointment. Contains the active substance heparin, which promotes rapid blood clotting and eliminates swelling and inflammation. When applying this ointment daily to a bruise twice a day, the effect is visible after the second day. The course of treatment can last differently - it depends on the severity of the damage and the condition of the tissue.
- Badyaga. Can be used both in the form of a powder, which is diluted with water, and in the form of a gel. In both cases, it is enough to smear the bruise once a day for a week.
- Lyoton. Another product based on heparin, but in a higher concentration, resulting in a faster result. The ointment must be applied three times a day.
- Bruise-Off . A modern product in the form of a gel based on an extract from leeches, which is often used by athletes. The active ingredients promote rapid resorption of hemorrhages and neutralize the color of the bruise. At the same time, the cream has a shade characteristic of normal skin, so this drug has a slight additional masking effect.
- Troxevasin. Elimination of bruises is not the main purpose of such an ointment, but due to its absorbable effect, this remedy is successfully used in this direction. Additionally, troxevasin helps strengthen the walls of blood vessels, which leads to rapid healing. It is enough to apply this ointment only during the first day from the moment the bruise forms, but every hour.
You can read more about other creams here.