Functions of saliva
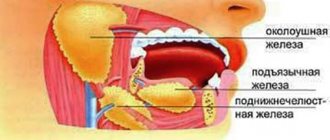
Saliva is one of the most important components of the digestive system. It is practically colorless and odorless, but has a slightly sour taste. Its production involves the salivary glands located around the jaw. One of the main functions of saliva is the initial digestion of food by softening it during chewing in the mouth before swallowing.
Saliva contains the enzyme amylase, which takes part in the breakdown of starch into simple sugars. Saliva also provides additional disinfection of food and enhances its taste. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for the production of salivary fluid, and the smell and taste of food is responsible for stimulating secretory function.
Salivation has a complex reflex nature
The role of saliva
As experts explain, saliva performs several important functions at once: it washes away food debris from the teeth, softens food, facilitating its subsequent digestion, and even supplies teeth with calcium, strengthening them. Indeed, chronic dry mouth is often a harbinger of caries. However, our body must produce exactly as much saliva as is necessary to ensure these important processes, and not a drop more. Drooling and the need to constantly swallow saliva can be signs of increased saliva secretion, which can cause a lot of discomfort.
What is hypersalivation?
An adult normally produces a moderate amount of salivary fluid: no more than 1 ml per 5 minutes. If drooling is increased, then significantly more saliva is produced (up to 5 ml during the same time), and a reflexive desire also arises to frequently spit out the secretions accumulated in the mouth.
Usually the sense of taste is reduced, in other cases the sensitivity of tastes may be too sharp or distorted. This mechanism works something like this. A person sees food, and in response to this, the amount of saliva in his mouth increases, especially when he is hungry.
If excessive salivation occurs during sleep or regardless of the feeling of hunger and other factors, it may be associated with disturbances in the functioning of the body, and therefore requires mandatory diagnosis by a doctor. In addition, this is an aesthetic problem, which inevitably causes discomfort in communication and provokes the development of complexes.
Excessive drooling is scientifically called hypersalivation. It comes in the following types:
- true - characterized by too intense production of saliva under the influence of external or internal factors;
- false - the problem lies in the difficulties associated with swallowing it. There are a great many reasons for this: from disorders in the functioning of the brain to injuries in the maxillofacial apparatus.
Increased secretion of the salivary glands occurs in the morning, afternoon and night. So, for example, salivation in the morning is considered a natural phenomenon, but a symptom that occurs mainly at night most often indicates problems in the functioning of the stomach and intestines, and the presence of worms.
Before and during meals, intense production of fluid in the mouth only indicates an increased feeling of hunger and good appetite. When the phenomenon becomes paroxysmal, this may indicate emotional overload.
| Types of hypersalivation | |
| Name | Description |
| True | Intensive work of the salivary glands under the influence of one of the etiological factors. |
| False | Swallowing is impaired. This happens for a number of reasons: disorders in the brain; when the facial muscles are atrophied; when you lose the ability to close your mouth; if the lips are damaged as a result of injury or illness (tuberculosis). |
| Night | The main provocateurs of increased salivation are worms and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. |
| Daytime | When copious salivation occurs at almost the same time, suspicion falls on a serious disease (heart, blood vessels, kidneys, etc.). |
| Morning | Most often, this phenomenon is considered the norm. |
| During meals, before meals or after meals | Food signals to the brain are associated with feelings of hunger. With this urge, saliva is released profusely. If the phenomenon is observed after eating, then it is worth checking for the presence of parasites in the body. |
| Paroxysmal | The body's response to stress and emotional overload. Excessive excitability affects the functioning of the brain, as a result of which the functioning of the salivary glands is disrupted. |
| Constant | Excessive salivation occurs for several reasons: due to inflammation and irritation of the oral mucosa; in case of digestive disorders; with mumps or inflammation of the salivary glands; due to a foreign body in the mouth. |
Hypersalivation or increased salivation - what is it?
Scientifically, the symptom is called “hypersalivation” - this is a pathological phenomenon, against the background of which there is an increase in the salivary glands and an increase in the intensity of their secretion. A similar condition is observed in infants, but as the child’s body grows, the symptom goes away on its own. If a similar problem is diagnosed in an adult man or woman, the reason may lie in disorders associated with the functioning of internal organs and systems. It is impossible not to notice the fact that such a symptom significantly reduces the quality of life and causes certain inconvenience to a person.
Before moving on to the question of what may be associated with increased salivation, it should be noted that in medical practice there are often cases of so-called false hypersalivation. This condition is a consequence of impaired swallowing function, and the cause of the problem is often a tongue injury or, for example, inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. In such a situation, the patient has the impression that there is too much salivary fluid in the mouth. To determine true or false hypersalivation, you need to understand why the pathological condition develops.
Increased salivation in children
In newborn babies, salivation is normally absent due to the underdevelopment of the salivary gland apparatus. However, often a mother may notice how, in the first hours of a child’s life, a colorless liquid, very similar to saliva, is actively secreted from his mouth.
Most often, this is how amniotic fluid comes out, which the baby managed to swallow while passing through the birth canal. Normally, this phenomenon should stop a few hours after birth. If drooling continues longer, it is better to inform your pediatrician (neonatologist) about this in order to exclude serious health problems.
Note: In general, in the first year of life, increased salivation in a child is a normal process.
At the age of about 2 months, a baby may experience profuse salivation, caused by the fact that the salivary glands finally begin to work at full capacity. It is at this age that a child may need his first bib to protect his clothes from getting wet.
Active salivation begins at 2 months of age
Closer to 3 months, children become active explorers of the world around them and taste everything. They put fingers, toys and any other objects at hand into their mouths.
The baby's body becomes acquainted with new microflora, which leads to increased secretion of saliva, which performs a protective function when various bacteria are removed from the oral cavity along with the fluid flowing out of the mouth.
The next time hypersalivation may bother the child during teething, closer to 6 months, and lasts up to 2 years. It is important to note that older children should not suffer from hypersalivation.
If a problem does exist, this may indicate certain disorders, for example, diseases of the nervous system, brain injury, worms, which is why it is extremely important to consult a specialist.
Elimination of hypersalivation
The best way to get rid of hypersalivation is to eliminate its cause. In many cases, changing medications or treating the underlying condition will help stop excess salivation. However, there are other methods that can help you reduce the amount of saliva your body produces.
For example, avoiding foods and drinks that can stimulate saliva production may help. Such irritants are different for everyone, but citrus fruits and alcohol, as a rule, temporarily increase salivation. Use an alcohol-free mouthwash because alcohol dries out your mucous membranes, which can signal your body to produce more saliva. In addition, it is useful to drink more liquid: this will make the saliva less viscous and easier to swallow.
Excessive salivation makes it difficult to speak, eat, and interact with others. Having eliminated the cause of hypersalivation, you can again look at mouth-watering foods without fear.
Causes of increased salivation in adults
Hypersalivation in adults is most often a pathology caused by a number of diseases. Moreover, it occurs with equal frequency in both men and women. Increased salivation always accompanies infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and pharynx - stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontitis, sore throat, acute respiratory viral infections.
Stomatitis is an inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa. As a rule, with this disease, the entire oral mucosa is covered with painful ulcers. As a result, it becomes painful to swallow, so the person stops swallowing the resulting saliva.
Gingivitis is no exception, leading to hypersalivation. This disease is characterized by inflammation of the gums. Whether with stomatitis or gingivitis, increased salivation is a protective function in diseases of the oral cavity, allowing timely removal of infectious agents, their toxins and tissue decay products.
This is also why excessive salivation is a sign of an incipient cold. Strong salivation in this case develops in response to mechanical irritation of the nerve endings of the oral cavity.
Disruption of digestive processes. Increased acidity of gastric juice, inflammation and irritation of its mucous membrane can cause a reflex increase in salivation and constant moderate hypersalivation.
With such diseases, increased salivation develops gradually and the patient gets used to the increased amount of saliva, not paying attention to the inconveniences associated with this condition. From the gastrointestinal tract, microorganisms can easily enter the oral cavity, where they irritate the salivary glands and gums and provoke the gradual development of hypersalivation.
Since it develops slowly, a person does not notice excess saliva production. An accurate diagnosis can only be made after fibrogastroduodenoscopy, because the symptoms of these diseases are similar.
With an ulcer, salivation is accompanied by pain and nausea, and most often this occurs on an empty stomach; with gastritis, heaviness and pain appear immediately after eating. Duodenitis leads to the same symptoms, but 1-2 hours after eating. Also, increased salivation in men and women can be observed in acute pancreatitis, caused by excessive production of enzymes by the pancreas.
If bitter belching is added, especially in the morning, the liver and gall bladder should be checked. Saliva can also accumulate in the mouth when there is esophageal spasm, scarring, or tumors that make swallowing difficult.
Involuntary secretion of saliva occurs with facial paralysis (this can also be a symptom after a stroke); in this case, the person cannot swallow at all, even liquid food. Paralysis of the muscular system in the maxillofacial area is a consequence of damage to the facial nerve.
Pathologies of the nervous system. Hypersalivation can also be caused by diseases associated with the central nervous system. Such pathologies include cerebral palsy, Parkinson's disease and its initial stage, irritation of the trigeminal nerve, as well as ailments that cause frequent nausea, such as migraines.
Patients may have problems with swallowing and nasal breathing that are not under their control. Often such patients complain of salivation when talking, which interferes with normal communication with others. A similar situation arises against the background of malfunctions of the vestibular apparatus.
FGDS helps to understand the causes of increased salivation
The main symptom of pseudobulbar or bulbar syndromes. This disease is characterized by damage to the cerebral cortex. As a rule, the amount of saliva produced directly depends on the severity of the disease. With poliomyelitis, syringobulbia or vascular pathologies, patients also experience hypersalivation.
Disorders of the thyroid gland. When the hormonal balance is disrupted, all functions of the organs and systems of the body are disrupted. The symptom can be triggered by diabetes mellitus or hormonal changes - during menopause or puberty.
Chemical poisoning, long-term use of potent medications. The symptom is often caused by long-term drug therapy with potent drugs. The most common drugs that have this effect are nitrazepam, pilocarpine, muscarine, physostigmine and lithium. After stopping the course, the secretion of the salivary glands returns to normal.
Note: It happens that the cause of all troubles is poisoning with iodine, mercury or pesticides.
Causes of hypersalivation in men
Increased salivation in men can be caused by all of the reasons listed above, but there is one more factor. As a rule, men are more likely than women to abuse bad habits, among which smoking and drinking alcohol are the leading ones. Inhaling smoke containing nicotine and tar has a negative impact on the condition of the oral cavity.
The mucous membrane is constantly injured. To reduce irritation, the salivary glands reflexively begin to produce more fluid - this increases the amount of saliva produced. Because of this, hypersalivation is especially common among smokers. If a person quits smoking, then salivation, after a certain time, returns to normal.
Why do women salivate?
For many women, the cause of hypersalivation is pregnancy, or more precisely, the resulting toxicosis. According to experts, it is in the early stages of pregnancy that many women notice primary signs of hypersalivation.
Increased salivation may accompany early toxicosis of pregnancy
The thing is that a woman is constantly trying to suppress attacks of nausea and vomiting, thereby she begins to involuntarily swallow less often. As a result, there is a feeling that there is actually more saliva than there should be. Heartburn often accompanies increased salivation during pregnancy.
In this case, the body conditionally receives a signal to soften the acid with saliva, which, due to its high bicarbonate content, is classified as an alkaline environment. Sometimes hypersalivation occurs due to the same factors as in ordinary adults. In such a situation, pregnant women are advised to inform their doctor about this to rule out obvious causes of the problem.
Another reason for increased salivation in women is the onset of menopause. In this case, it is accompanied by severe sweating and frequent flushes of blood. This is a natural process that will gradually disappear.
Treatment of hypersalivation
There is no single treatment method for all cases. However, you can use methods to reduce the activity of the salivary glands - sometimes they are recommended by doctors as an addition to complex therapy.
- Reception of sorbents: activated carbon, polysorb, etc.
- Taking medications prescribed by a doctor.
- Exercise therapy, massage (most often prescribed for children).
- Botulinum toxin injections.
In rare exceptions, the salivary glands are partially removed, but the downside is that there is a risk of damaging the facial nerve.
Which doctors will help you cope with this disease? Dentist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, neurologist, infectious disease specialist, etc.
Increased saliva production during sleep
When a person sleeps, saliva production slows down and becomes less intense. But sometimes the salivary glands “wake up” before their owner, and then in the morning you can find a wet spot on the pillowcase. If this is only a periodic phenomenon, there is nothing to be afraid of (for example, when a person has a runny nose or a cold).
However, such a symptom can also be the result of an incorrect bite or loss of part of the teeth - here you need the help of a dentist. Normally, in a healthy person, salivation decreases sharply at night. A couple of drops of saliva on the pillow in the morning is just evidence that the body woke up earlier than its owner.
Factors that provoke excessive salivation during sleep:
- mouth breathing;
- malocclusion, in which the mouth remains open at night - for example, with open, mesial and distal bites;
- sleep disturbances - for example, too deep sleep, similar to an unconscious state, during which control over the body is completely lost.
A wet pillow in the morning can be either normal or a symptom of a serious illness.
Characteristic symptoms
Increased salivation is usually accompanied by other symptoms, which can help roughly determine the source of the problem. Thus, in medical practice, various forms of hypersalivation are distinguished, aggravated by other pathological phenomena - let’s look at the main ones.
Increased saliva production during sleep
When a person sleeps, saliva production slows down and becomes less intense. But sometimes the salivary glands “wake up” before their owner, and then in the morning you can find a wet spot on the pillowcase. If this is only a periodic phenomenon, there is nothing to be afraid of. This may be associated with a mild cold and runny nose, which makes it difficult to breathe through the nose. However, such a symptom can also be the result of an incorrect bite or loss of part of the teeth - here you need the help of a dentist.
There can be different reasons for salivation during sleep.
When the symptom is complicated by gagging
When hypersalivation is accompanied by frequent vomiting, this may indicate injury to the vagus nerve, inflammatory processes in the pancreas, the development of gastritis and stomach ulcers. Also, a similar combination of symptoms occurs in women during pregnancy against the background of toxicosis. To determine the exact cause, you must consult a doctor.
Hypersalivation after eating
The production of saliva becomes more intense before and during meals - this is a completely natural phenomenon. It’s another matter if the symptom does not go away even after a meal. This often indicates the presence of worms in the body. Parasites can affect virtually any organ, from the stomach and intestines to the lungs, heart and brain. Other characteristic symptoms include loss of appetite and increased fatigue.
Uncontrolled secretion of the salivary glands in combination with belching
This condition is usually observed when there is a problem with the functioning of the stomach. In this case, the belching may be sour or with a bitter taste, and is often combined with the release of mucous fluid. If the passage of the food tract is obstructed, excessive salivation is aggravated by a feeling of a lump and difficulty swallowing. Here you definitely need the help of a specialist.
Sometimes this condition occurs due to problems with the functioning of the stomach.
When the symptom is combined with a sore throat
This combination of symptoms is characteristic of lacunar tonsillitis. Other signs of the disease include high temperature, fever, general loss of energy and severe headache. During the examination, the doctor may detect redness and swelling of the tonsils, whitish plaque, and enlarged lymph nodes.
Increased salivation during a conversation
Sometimes the problem is associated with dysfunction of the oral muscles - this situation occurs with cerebral palsy and certain neuralgic disorders. If you produce too much saliva during communication, in some cases this signals a hormonal imbalance - thyroid disease, disruptions of the endocrine system, including diabetes.
Features of the development of hypersalivation in women
In the first stages of menopause, many women encounter this unpleasant phenomenon. Along with intense secretion of the salivary glands, increased sweating and hot flashes are observed. This is due to hormonal changes in the female body, and all inconveniences go away on their own, usually without requiring the intervention of specialists.
When menopause occurs, many women experience this unpleasant phenomenon.
Hypersalivation in infants and older children
It was already mentioned above that excessive drooling in the first year of a child’s life is a normal situation that does not require medical help. The reason for this is an unconditional reflex factor, and over time the problem goes away on its own. Next time, hypersalivation may overtake the child during teething. In all other cases, excessive secretion of salivary fluid will indicate certain disorders, for example, diseases of the nervous system, brain injury, gliss.
In children, this problem often occurs during teething.
When the problem occurs during pregnancy
Many women develop toxicosis during pregnancy, which is often accompanied by hypersalivation. Other accompanying symptoms include heartburn, dizziness, and nausea.
“I had this happen around 35 weeks. I began to notice that too much saliva was forming in my mouth. In the mornings it was a total nightmare, the pillow was all wet. Heartburn also began to plague me often. But the doctor reassured me, said that everything would go away on its own, and didn’t find any problems. She prescribed vitamins and said that you need to be less nervous..."
Alenka25, Moscow, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
The problem can also be caused by insufficient intake of vital vitamins and microelements into the body and, as a result, a drop in immune defense. Taking a multivitamin complex prescribed by a doctor, as well as proper nutrition, will help restore balance.
Complications and prevention
The consequences of ignoring such a symptom can be:
Symptoms of salivary gland disease
- violation of adequate taste perception, food aversion;
- sudden weight loss;
- dehydration of the body;
- psycho-emotional disorders, insomnia;
- deterioration of the condition and color of the skin due to the constant influence of saliva and the bacteria in it;
- infectious lesions.
In order to prevent pathologies that provoke increased salivation, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- perform hygiene procedures in a timely manner, including the oral cavity;
- once every six months, undergo a preventive examination at the dentist, have your teeth professionally cleaned;
- review your diet, use more fresh vegetables and fruits to enrich the body with vitamins and microelements (you should give up salty, smoked and fatty foods);
- lead an active lifestyle, relax in nature, visit fitness centers;
- to refuse from bad habits.
If excessive salivation is a symptom of any disease, you need to undergo medication prescribed by your doctor. Eliminating the problem in this case depends on complete recovery.
A healthy lifestyle is an excellent prevention of increased salivation
Excessive salivation during pregnancy
During pregnancy, hormonal changes occur in the female body. The main reasons why an expectant mother’s salivation increases.
- Heartburn. When the acid-base balance in the stomach is disturbed, the body begins to produce a lot of saliva. This is a defensive reaction.
- Reaction to medications.
- Toxicosis. To stop gagging, the expectant mother tries to swallow saliva less often. Therefore, it may seem that there is more saliva in the mouth than usual.
A large amount of saliva does not threaten the fetus, however, if this is a consequence of any disease, then the pregnant woman should monitor her condition.
What complications are possible?
- Impaired taste perception of food.
- Dehydration of the body.
- Insomnia, disturbance of psycho-emotional state.
- Deterioration of the skin condition on the face and body.
- Infectious diseases.
Diagnostics
Initially, with complaints of increased salivation, the patient should contact a therapist or pediatrician. If necessary, other highly specialized specialists are involved in the diagnostic search: neurologist, phlebologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist, infectious disease specialist, oncologist, gastroenterologist, dentist.
The survey usually involves the following steps:
- External examination, finding out in a conversation with the patient or his relatives about the time of the problem, the presence of concomitant diseases, and other signs of the disease.
- Exclusion of other pathologies, the symptom of which may be hypersalivation. In children, it is important to distinguish ptyalism, as a symptom of teething, from ARVI.
- Identifying signs confirming the disease. For this purpose, laboratory blood tests, functional tests, and bacteriological seeding of biological material are carried out.
- Hardware diagnostic methods include X-ray, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound scanning of the affected organ, electroencephalography of the heart, and Doppler ultrasound of blood vessels.
- Additional examination by a dentist, psychiatrist and neurologist to identify possible indirect causes.
General information
Hypersalivation (syn. sialorrhea, ptyalism, drooling) is increased production/secretion of saliva caused by high activity of the salivary glands or insufficient utilization of it.
Saliva is an important biological fluid in the human body, ensuring the maintenance of homeostasis of the oral cavity, including the condition of the mucous membrane, periodontal tissues and teeth, enhances the chemosensory functions of the oral mucosa (taste perception), and supports the communication function (pronunciation of sounds). Saliva is also actively involved in the digestive process (preparing the food bolus for digestion and ensuring the initial phase of hydrolysis of carbohydrates/proteins), performs a protective (bactericidal) function, negatively affecting pathogens entering the oral cavity. Ptyalism can be both a physiological phenomenon characteristic of certain age periods or conditions of an adult, and one of the manifestations of pathology/diseases of various origins. Hypersalivation, as a physiological phenomenon, develops in children during the active growth of primary/permanent teeth. In women during pregnancy , which is associated with changes in hormonal levels (decreased levels of corticosteroids and increased estrogen levels), especially with the development of early toxicosis of pregnancy. with reflex stimulation of the center.
The appearance of salivation is caused by reflex irritation (stimulation) of the salivation center. Normally, in adults, the salivary glands (sublingual, submandibular and parotid) secrete an average of 1500-2000 ml of saliva per day.
At the same time, the rate of secretion is uneven and is determined by such factors as age (slow salivation after 60 years), the strength of the food stimulus, the state of the nervous system (excitement), the circadian cycle (saliva secretion during sleep decreases 8-10 times and increases during wakefulness) . The rate of salivation outside stimulation varies between 0.05-0.5 ml/min, and during stimulation the rate increases to 2.0-2.5 ml/minute.
The secretion of the salivary glands, released into the oral cavity, mixes and forms saliva. The secretion released from the ducts of the salivary glands differs from mixed saliva in the presence of specific microflora, desquamated mucosal epithelial cells, leukocytes and mucus coming from the nasal cavity. The specificity of the salivary glands is double innervation. Therefore, the process of stimulating salivation is triggered by activation of the parasympathetic system (the main mechanism) and the sympathetic system. At the same time, not an antagonistic, but a synergistic effect is noted. Parasympathetic stimulation results in increased saliva production in large volumes, while sympathetic stimulation produces viscous/thick saliva in small volumes.
With hypersalivation, the flow of saliva from the oral cavity can reach large volumes (10-12 l), which leads to damage (maceration) of the soft tissues of the lips and chin. This negatively affects the psychological well-being of patients and their everyday/social activities.
Long-lasting and abundant hypersalivation can lead to dehydration (dehydration) and metabolic disorders. With copious ingestion of saliva, there is a decrease in the acidity of gastric juice/development of achylia , which causes disruption of the digestion process in the stomach. Severe hypersalivation disrupts night sleep and causes speech problems.
Tests and diagnostics
Making a diagnosis of hypersalivation is not difficult. It is much more difficult to determine its cause, that is, to establish a disease/pathology accompanied by drooling. The diagnostic search includes collecting a medical history, studying complaints, physical examination, instrumental/laboratory diagnostic methods:
- General clinical examinations - general blood test, clinical urine test, stool test for helminth eggs, coprogram.
- Biochemical analysis of saliva.
- Instrumental techniques: plain radiography, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, MRI/CT of the brain, electroneuromyography.
Gestures
A person who wants to lie is always nervous, even if he knows how to control himself. There are several signs that give it away:
- touching the bridge of the nose with the index finger; rubbing the earlobe;
- lightly rubbing a finger under the nose above the upper lip or touching the tip of the nose with the index finger;
- covering his mouth with his hand, as if he is surprised;
- rubbing the lower eyelid with the index finger as if in thought;
- chin propped up by hand and biting fingers;
- if during a difficult conversation a person reaches out to stroke the back of his neck with his palm (just below the back of the head) or tries to free his neck from a tie, scarf, etc.);
- hands tightly clenched into a fist or vice versa, fingers often clenching and unclenching;
- hands in pockets;
- openly voluptuous, defiantly free behavior may also indicate a lie.
Consequences and complications
Complications of severe hypersalivation are:
- Rapidly developing dehydration of the body, accompanied by a violation of the acid-base state/electrolyte balance. Swallowing saliva in large volumes neutralizes gastric juice, reduces the bactericidal effect, and accelerates the process of evacuation of food from the stomach to the intestines, which can contribute to the rapid development of malabsorption syndrome .
- Inflammation and maceration of the skin and around the mouth.
- Flow of saliva into the respiratory tract, which is accompanied by the risk of infection by oral microflora.
- Night sleep disturbance.
- Impaired communication (speech problems).