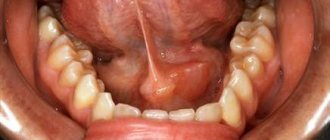
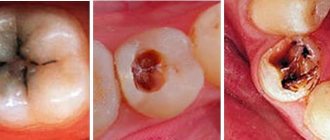
Professional dental care includes the removal of caries, cystic areas and many other procedures. In accordance with the protocol for providing medical care, the dentist is also required to monitor the condition of the salivary glands
. In clinical practice, their damage is quite rare. Most often, poor performance of the excretory ducts occurs due to injury or incorrect oral therapy. Quite often this happens due to insufficient hygiene.
Bougienage or treatment of the salivary gland involves intubation of a dental instrument or probe in order to examine the organ and administer appropriate substances. Saliva contains a large number of enzymes that take part in the processing of food and the removal of metabolites from the body. If appropriate manipulations are not performed, this can lead to an increased likelihood of developing caries, pain when eating and a malfunction in the digestive system.
Indications for use
Bougienage of the salivary gland ducts is performed with the following symptoms:
- Unpleasant painful sensations.
- Sharp pain when eating certain foods.
- An involuntary feeling of fullness in the mouth after eating.
In case of malfunction of the excretory duct, you must immediately contact a specialist. Otherwise, the clinical picture may worsen, and the pathological process will become chronic.
Salivary gland blockage
The salivary glands are ducts that secrete a special secretion into the oral cavity - saliva.
There are paired large salivary glands: submandibular, parotid, sublingual (they are closely related to the digestive system); as well as minor salivary glands: buccal, labial, molar, lingual, glands of the soft and hard palate. They are located in the submucosal layer of the cheeks, lips, palate, and tongue.
Kinds
According to the specificity of the secretion secreted by the glands, they are divided into protein, mucous and mixed. The largest paired salivary glands are the parotid glands, located in the back of the angle of the jaw, in front of the ears. The minor salivary glands are distributed throughout the oral cavity. If there is not enough saliva produced, the oral cavity becomes dry. In this regard, there is a high risk of developing caries, since with a deficiency of saliva, natural protection against such dental disease is no longer created.
Causes
It happens that the excretory duct of the salivary gland is blocked by various mineral deposits, which are also called stone. Blockage of the salivary gland provokes the normal outflow of saliva, as well as an enlargement of the gland. The cause of inflammatory phenomena can be infection with various bacteria and microbes.
When the duct is blocked, the swelling usually intensifies before eating, especially when eating pickled foods that have high acidity. It provokes salivation. When the ducts are blocked, saliva cannot be released freely. This often results in painful sensations.
A complication of blockage of the salivary gland is mucocele - the formation of a cyst, which is caused by the retention of secretions resulting from blockage of the outlet of the so-called Blandin-Nun gland.
Symptoms
Blockage of the salivary glands is manifested by swelling, a change in the color of the mucous membrane of the lips, which acquire a bluish tint. As a rule, this is how inflammation of the minor salivary glands manifests itself. If the major salivary glands are blocked, swelling and pain occur in the neck and cheeks, especially after eating.
Diagnosis and treatment
The Dento Style clinic network provides comprehensive diagnostics and treatment of various pathologies of the salivary glands. Our specialists have an individual approach to each patient. If the salivary ducts are blocked, the patient is examined and the affected area is palpated. Methods such as probing are used. It allows you to identify a salivary stone or a narrowing of the duct.
Hypo- and hypersalvation can be detected using sialometry (a method that allows you to measure the amount of secretion released per unit of time). X-ray and computed tomography are also highly effective.
As a treatment, the doctor prescribes the use of drugs that enhance salivation. In the case of an inflammatory process, antibacterial therapy is prescribed, as well as physiotherapeutic procedures.
The dentist first tries to mechanically squeeze out the stone by pressing on the duct. However, if such manipulation is not possible, surgical intervention may be required.
Diagnostic methods for bougienage of the salivary glands
- Sialometry. Allows you to conduct a quantitative and qualitative study of secreted unstimulated and stimulated saliva. With this technique, a special tube is inserted into the flow part.
- Radiosialography. The study is performed by filling the ducts with special substances. The saliva is then assessed for the presence of inflammation or an autoimmune disease. For contrast diagnostics, iodine-containing substances are often used.
- Pantomosialography. An innovative procedure that involves simultaneous contrasting of four salivary glands. With its help, it is possible to identify hidden pathological processes in the organ.
Additionally, X-ray diagnostics, thermosialography and other methods can be performed. It all depends on the symptoms of the disease and the characteristics of the inflammatory process in the oral cavity.
Causes
- The presence of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity
- Mechanical factors, for example, trauma to the ducts from sharp edges of teeth or crowns
- Stagnation of saliva secretion
Currently, there are four methods aimed at eliminating stones from the salivary glands.
1. Interventional sialendoscopy.
The doctor uses a special instrument with a camera at the end - an endoscope - to remove stones from the salivary ducts. This procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
2. Extracorporeal lithotripsy.
Under the influence of ultrasonic influence on stones, they are crushed.
Thanks to this method, it is possible to extract and wash the ducts with a special solution, which will prevent the development of the inflammatory process.
3. Dissection of the duct is done if the stone is large and cannot be removed using a simple method.
4. Extirpation of the salivary gland.
This operation is used only when irreversible changes are observed in the parenchyma of the gland. The doctor performs the procedure in a hospital setting under general anesthesia.
Common diseases of the salivary glands
- Narrowing of the flow channel. An inflammatory process or traumatic injury can lead to scarring of the tissue. As a therapy, a conical probe is inserted into the flow path. The number of sessions can range from 12 to 25 depending on the clinical picture.
- Chronic sialadenitis. In this case, the outlet flow channel does not work fully. This happens most often due to infection, the penetration of a pathogenic bacterial environment. Treatment involves drug therapy using antibiotics of the appropriate spectrum of action.
- Violation of the integrity of the duct. As a therapy, a probe is inserted into the cavity to prevent clogging of the duct and ensure normal patency.
These are the most well-known pathologies. There are other cases in clinical practice. Most often, a narrowing of the flow path with severe swelling is diagnosed. A full course of dilatation allows you to achieve the required therapeutic effect.
Maxillofacial Surgery
Maxillofacial Surgery
- a branch of medicine that deals with the treatment of various diseases and injuries of the head and neck. The range of these pathologies can differ significantly from each other depending on the specific medical institution and the competence of the individual doctor, which leads to the fact that not only patients, but also doctors of other specialties do not know where to refer a patient with a “non-obvious disease”.
We will try to briefly describe what pathologies we will deal with at the S.V. Center for Cosmetology and Plastic Surgery. Nudelman.
Diseases of the oral mucosa
, incl. both potentially malignant diseases (various erosive and ulcerative lesions, “white” and “red” diseases of the mucosa), and an established diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma.
Any ulcers, formations on the mucous membrane of the tongue, cheeks, lips, oropharynx, floor of the mouth.
Diseases of the salivary glands.
Benign tumors. Salivary stone disease. Systemic diseases associated with damage to the salivary glands (invasive diagnostics).
The appearance of formations or enlargement of large salivary glands - parotid (located “under the auricle, behind the lower jaw”), submandibular (under the lower jaw), sublingual (under the tongue).
Formation of soft tissues of the head and neck.
Skin formations and everything that is under it.
Congenital neck diseases.
The most common are thyroglossal duct cyst (median neck cyst), lateral neck cyst.
Long-term enlarged lymph nodes of the neck.
Diseases of the jaws. Cysts associated and not associated with tooth roots. Damages due to medication. Radiation damage to the jaws.
Abnormally positioned and supernumerary teeth.
Injuries of the upper and lower jaw, orbital walls, nasal bones.
Consequences of trauma to the bones of the facial skeleton and cranial vault.
Deformations and “retraction” of tissues and the eyeball (enophthalmos) due to a violation of bone anatomy.
Pain syndromes in the facial area.
Diseases of the temporomandibular joint.
Surgical treatment of endocrine ophthalmopathy.
A number of pathologies have a “vivid” clinical picture (for example, salivary stone disease), and a fairly clear and well-established treatment strategy. In other situations, it is necessary to “go to the diagnosis” for a long time and persistently, including invasive manipulations and operations to obtain cytological and histological material.
In all cases, the basis of treatment will be a correct diagnosis.
We actively discuss diseases that are at the “junction” of specialties, and there are definitely more than half of them. These consultations are carried out in our clinic and in some cases can be joint (neurologist, orthopedic dentist, orthodontist, ENT).
We carefully study imaging data (computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging) with the involvement of leading specialists.
It is possible to discuss the case with your attending physician (oncologist, dentist, neurologist, rheumatologist).
This surgical procedure is aimed not only at “selecting” patients for surgical treatment, but also at “strategic” planning and long-term observation of diseases that are chronic in nature and require monitoring (photo recording of clinical manifestations, biopsy, etc.).
Pathology of the bones of the facial skeleton
Jaw formations
Operation options: - incisional surgical biopsy (taking a section of pathological tissue for the purpose of subsequent histological verification, if without this it is impossible to immediately determine the extent of the operation) - cystectomy - removal of the cyst membrane (if the formation is of such a nature), may differ in significant variability in volume, complexity and duration - cystotomy (cyst marsupilization) - an operation to create an anastomosis of the cyst cavity with the oral cavity - used both as an independent surgical intervention and in combination with a biopsy.
— partial resection of the jaw along with the tumor
Chronic osteomyelitis of the lower jaw (in the absence of an acute inflammation phase), incl. radiation and drug-induced injuries (depending on a number of conditions, the operation can be performed both under local anesthesia and general anesthesia)
— necro- or sequesterectomy (removal of altered bone tissue)
Abnormally located and supernumerary teeth - removal of abnormally located and supernumerary teeth under anesthesia
Diseases of the temporomandibular joint - arthrocentesis, lavage of the temporomandibular joint
Surgical treatment of endocrine ophthalmopathy - bone decompression of the orbit (outer, lower, medial wall and their combinations)
Injuries of the upper and lower jaw, orbital walls - osteosynthesis of the lower jaw (mainly through intraoral access) - osteosynthesis of the upper jaw - plastic surgery of the orbital walls
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS, SPECIALIST CONSULTATION IS REQUIRED
Features of the procedure
If the flow channels are narrowed, appropriate therapy is prescribed using a probe to bougienage the salivary gland
. The procedure itself is as follows. First, an instrument is selected, a probe of the appropriate diameter, then it is inserted into the flow channel and left there for 12–16 minutes. In this case, the diameter of the probe increases each time. Thanks to this, it is possible to expand the duct as painlessly as possible. Before the procedure, the patient is advised to refrain from eating for 2.5 hours.
In order to consolidate the result, it is recommended to adhere to a special salivary diet; in addition, electrophoresis with potassium iodide and the required physiotherapeutic manipulations may be prescribed. The recovery period takes from several weeks to several months.
The specialists of the AlfaDent clinic will help solve any dental problem. Doctors use high-quality pharmaceuticals and advanced techniques. Timely detection of pathology and its treatment will help maintain the elements of the dental system and salivary glands in a healthy condition. We will help you get rid of any disease painlessly and with minimal time.