Mesial occlusion or occlusion is one of the types of defects in which the closure of the anterior dentition is disrupted. Outwardly, this manifests itself in the dominance of the lower jaw over the upper. With such a violation, not only an aesthetic defect is observed. This leads to abrasion of tooth enamel and changes in facial expression. Typically, malocclusion develops due to genetic predisposition or exposure to causative factors during a certain period of development.
Mesial occlusion can be corrected professionally. A competent approach, modern equipment and doctors will be able to restore the aesthetic appearance of the face. Dental clinic PROPRIKUS provides treatment of mesial occlusion without the use of surgical intervention. To correct malocclusion, we use aligners, including Invisalign. They are considered the most effective and help correct even complex cases of pathological occlusion.
Symptoms and causes of mesial occlusion
Patients with this pathology have a concave profile: the lower part of the face is increased in size due to a sharply protruding chin. The lower lip appears thicker than the upper lip, and the jaws are not closed properly. The lower row of teeth is pushed forward. In addition to external manifestations, deformation affects functionality:
- speech is disrupted;
- difficulty biting and chewing food;
- sometimes an open or crossbite develops.
Due to uneven load on the incisors of the jaws, early tooth loss is possible. In 50% of cases, the cause of the anomaly was disturbances in fetal development in the prenatal period. Among the main factors influencing the formation of malocclusion are: birth injuries, viral infections during pregnancy, rickets, osteomyelitis, incomplete development of the dentition. Today, the PROPRICUS clinic successfully corrects mesial occlusion in both adults and children of all ages.
Need some advice?
Enter your phone number and we will give you a free consultation
I want a consultation
*By making an appointment you consent to the processing of your data
How to identify distal bite in a child?
This type of teeth closure is always characterized by a discrepancy between the sizes of the upper and lower jaws. The upper molars may be displaced inward, and the incisors may be pushed forward at an angle. Sometimes the presence of three and diastemas (interdental spaces) is noticeable.
Distal occlusion as an independent type is rare. In 80% of cases, a combination of 2 pathologies is observed: prognathic and deep bites, when the upper incisors overlap the lower ones by more than half. As a rule, there is no contact between the front teeth on both jaws.
During diagnosis, the dentist examines not only the occlusion (closing) of the molars and incisors, but also the profile of the face.
Prognathia is accompanied by the following external signs:
- overly rounded face;
- the lower third of the face is visually reduced;
- half-open mouth;
- deep crease on the chin;
- “fan-like” arrangement of teeth;
- The lower lip is located behind the upper incisors.
Methods for correcting mesial occlusion in adults
Mesial occlusion, which is detected before the age of 12 years, is more treatable. Unfortunately, this does not always happen and often adult patients seek help in correcting their bite. Conservative orthopedic methods for correcting occlusion are sometimes ineffective. Often teenagers and adults complain of pain and discomfort when installing a corrective structure. But at the PROPRICUS clinic they use the most effective methods. Serious defects can be corrected with veneers, aligners, and mouth guards. We treat mesial occlusion in adults even in the most difficult situations, when it seems that it is impossible to return the teeth to their normal appearance.
Consequences of distal occlusion in adults
Prognathia should be eliminated in childhood, preferably before the age of 14. If this is not done, a person will experience a number of problems in adulthood:
- firstly, a violation of facial aesthetics - abnormal occlusion always affects the appearance, because of this, self-esteem decreases and complexes arise;
- secondly, deterioration in the function of chewing and swallowing - due to poor closure of teeth, a person has to make approximately 30% more chewing movements compared to the norm;
- thirdly, speech disorders - a “lisp” and other speech therapy abnormalities occur.
It should be taken into account that those with a distal bite have a greater risk of developing dental diseases - caries, gingivitis, and enamel erosion. This happens due to the increased load on individual dental crowns and periodontal areas. In addition, there may be problems with the jaw joint - pain when chewing and talking, deterioration in mobility.
Therefore, you cannot ignore the problem; you should contact your dentist in a timely manner. Treatment of distal bite in children and adults is carried out by an orthodontist. You can select such a specialist on our website through a convenient search system.
Types of mesial occlusion
Pathology is classified depending on the cause of origin and form.
There are the following types of occlusion in form:
- Dentoalveolar - accompanied by incorrect position of the teeth, corrected with the help of orthodontic structures;
- skeletal form - refers to more complex forms; malocclusion is formed due to pathology in the development of the jaws.
By nature of occurrence:
- micrognathia of the jaws - characterized by their increase or decrease in size;
- prognathia of the lower jaw - normal closure of the jaws is impossible due to individual teeth;
- retrognathia - characterized by a normal jaw size, but its incorrect position;
- macrodentia and microdentia.
If parents are diagnosed with this disorder, then it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the child’s teeth. Genetic predisposition and exposure to adverse factors increase the risk. It is important to take your child to see a dentist every six months. Early loss of primary incisors due to trauma or caries is dangerous for the development of mesial occlusion in the future, even with correct occlusion. The pathology can be noticed at an early age - by an enlarged lower jaw and lower incisors overlapping the upper ones.
Diagnostics
To draw up a complete clinical picture and treatment plan, you need high-quality diagnostic data of several types:
- Visual examination of teeth and face by an orthodontist. Usually occurs at the first consultation. The doctor evaluates the position, size and condition of the teeth. If necessary, refers to additional specialists.
- Assessment of jaw position and size using CBCT. Only a 3D image of the entire skull will give the doctor an accurate idea of how the jaws are positioned relative to each other and the condition of the temporomandibular joint. Based on these data, a plan for moving the teeth is drawn up, and the need for surgical intervention or additional treatment of joint dysfunction is assessed.
- Assessing the position, relationship and closure of teeth using impressions.
- A detailed photo protocol for drawing up a treatment plan and further monitoring the dynamics of treatment.
Causes of mesial bite
In the early stages of development:
- genetic predisposition - congenital anomalies in the structure of the skull and facial bones occur;
- illnesses suffered during pregnancy, deficiency of vitamins and nutrients, living in unfavorable conditions;
- increased size of the child's tongue;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland, rickets;
- short frenulum, improper breastfeeding.
During the period of milk and permanent teeth:
- insufficient wear of primary teeth in children 3-6 years old;
- premature loss of teeth in the upper jaw due to caries or impact;
- late appearance of teeth on the upper jaw;
- bad habits - resting your chin on your hand, sleeping in a position with your head bowed to your chest.
Most often, abrasion is disrupted on temporary canines due to the late period of physiological change. This prevents the closure of the dentition, and therefore mesial occlusion is formed. The correction scheme depends on the severity of the deformity. Therefore, PROPRICUS dentistry uses several treatment methods. The patient undergoes a detailed diagnosis by several specialists to understand how to correct the mesial bite.
Treatment
Treatment methods for mesial malocclusion depend on the patient’s age and the shape of the malocclusion (skeletal or alveolar). Earlier treatment is usually faster and more effective because the jaws, teeth and alveolar bone tissue are in the growth phase.
Treatment in milk and mixed dentition
When diagnosing mesial occlusion in a child with primary or mixed dentition, first of all, it is necessary to exclude factors that aggravate the pathology:
- bad habits. Special jaw appliances will help make it easier to wean yourself from a bad habit and adapt to the correct position of the jaws.
- improper swallowing or mouth breathing. To eliminate breathing problems, you will need to consult an ENT doctor.
- forced position of the jaw due to interfering tubercles or cutting edges of individual teeth. In this case, the teeth are ground to a safe extent for normal closure.
If the lower jaw is shifted forward slightly, then massage of the alveolar process (the place where the teeth grow) from the side of the palate in the anterior part of the upper dentition is indicated for correction. The general position of the jaw is corrected with removable devices.
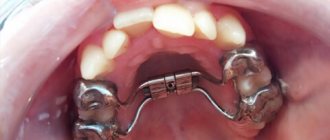
In case of deep incisal overjet, the Brückle apparatus is used in the mixed dentition. It moves the upper teeth forward, and the bite block helps to release the bite on the anterior teeth.
Jaw development can be further hampered by pressure from the lips, tongue, and cheeks on the alveolar bone and teeth. The type 3 Frenkel function regulator normalizes the position and relationship of the teeth, tongue and cheeks.
Bruckle apparatus
Frenkel apparatus type 3
Studies show that it is impossible to restrain the growth of the lower jaw, therefore, in the primary and mixed dentition, orthodontic treatment is focused on stimulating the growth of the upper jaw. To do this, a partial bracket system “4+2” is installed on the permanent incisors and first molars. The action of braces helps to expand and lengthen the upper jaw.
Partial bracket system for mesial occlusion"
Treatment in permanent dentition of dentoalveolar form
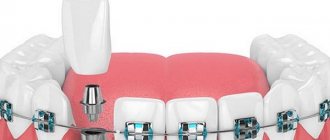
In the dentoalveolar form, the mesial bite is formed due to the incorrect position of the teeth. To correct it, it is enough to install a braces system. Treatment is carried out with the mandatory use of intermaxillary traction - elastics, which help to pull the lower dentition back. In case of severe anomaly, the lower eighth teeth (wisdom teeth) are removed, and mini-screws are connected to extend the dentition. Mini-screws or micro-implants are small screws that become absolute support.
Treatment of gnathic permanent dentition
The skeletal form of the bite, that is, fixing the bite at the level of the skull bones, requires additional surgical intervention. An orthognathic surgeon corrects the size and position of the jaws after installing braces and adjusting the position of the teeth. After the operation, the orthodontist details the position of the teeth for a perfect smile.
Methods for treating mesial occlusion
Aligners are one of the most practical, convenient, safe and effective correction methods. They are made from polymer materials according to the patient’s individual impression. Therefore, the risk of the structure shifting is completely eliminated. Aligners follow the anatomical shape of the teeth and jaw. They cannot be seen on the teeth due to the complete transparency of the trays. Patients observe minor defects within 2-3 days after installation. They do not interfere with chewing, drinking, or brushing your teeth. You should remove your aligners before performing oral hygiene and eating.
Sign up for free 3D modeling of your future smile!
Make an appointment
*By making an appointment you consent to the processing of your data
Advantages of aligners:
- do not stain;
- not visible to others;
- soft and elastic;
- safe for health;
One of the most advanced foreign bite alignment systems is Invisalign. This is an innovative product from an American company that is used in our clinic. Therapeutic mouth guards create pressure on the teeth, causing them to return to their normal position. We use only original products and are completely confident in the effectiveness of orthodontic treatment with aligners.
During the initial examination, the doctor assesses the condition of the patient’s oral cavity, diagnoses the condition of the jaw system, draws up a treatment plan and names its cost. Before the treatment plan is approved, the patient is shown what the oral cavity will look like after treatment. After agreeing on the details and signing the contract, the doctor performs sanitation of the oral cavity, if there is an indication for this. Therapeutic mouth guards take 2 weeks to make. The elements will have to be changed and will have to be changed every 2-3 weeks. The average duration of treatment with aligners is 6 months to 1.5 years.
Types of abnormal bite
An abnormal bite is characterized by incorrect location of the alveolar openings of the molars or incisors, the presence of congenital anomalies of the bone structure of the head, and post-traumatic violation of occlusion. To correct it, trainers, braces are used, and surgery is performed.
Deep bite
The front upper incisors cover the upper ones by more than ⅓. In severe situations, their end ends at the gums of the lower teeth. The contact between the incisors and molars is disrupted. An alternative name for occlusion is traumatic, frontal overbite, decreasing, disocclusion.
A person develops “bird-like” facial features. The upper half flares out, so the chin looks abnormally narrow. The lower lip is turned outward, the mouth is small. With a deep bite, difficulties arise when chewing food, injuries to the mucous membranes, and thinning of the enamel.
Often pathological occlusion leads to deterioration of the oral cavity:
- severe headaches;
- decreased tone of the chewing muscles;
- dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint;
- friction of the mucous membranes of the cheeks, the appearance of wounds.
Deep occlusion can in most cases be corrected with long-term retainer therapy.
Open bite
The pathological process is characterized by a strong vertical displacement of the dentition of the jaws. An open bite develops due to sucking on pacifiers and fingers. Bad habits gradually shift the dentition. The sucking reflex can be traced even in adulthood: unconscious sucking or biting of the tongue.
Pathological occlusion is diagnosed when the molars are in close contact, but a large gap forms between the lower and upper incisors. Surgery is performed in the presence of speech therapy disorders or pain during eating.
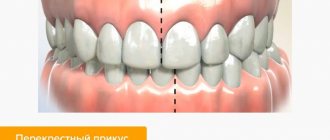
Crossbite
Crossed occlusion occurs in people who use only one side of the jaw or incisors to chew food. The development of a pathological process can be provoked by a congenital anomaly of the jaw, a mechanical injury, as a result of which the chin is shifted to the left or right.
This type is considered one of the most severe dental diseases. Unilateral cross occlusion can be diagnosed if one or more of the upper incisors extend beyond the lower ones. A bilateral violation is accompanied by a displacement of the entire jaw, in which the dentition does not close simultaneously on the left and right sides.
Occlusion in childhood can be provoked by:
- rickets;
- cleft palate;
- lack of calcium and vitamin D;
- cleft lip;
- inflammatory process in the temporomandibular joint;
- disturbances in the development of cranial bones during embryonic development.
To treat crossover anomalies, the Herbst device and metal braces are used. In case of congenital diseases, plastic surgery is performed to restore the palate.
Distal bite
Such occlusion is diagnosed when the upper jaw is highly developed, and the lower jaw is narrowed and small in size. The teeth on top move forward, almost completely covering the bottom ones. The root elements do not close, and vertical cracks form. Distal occlusion is diagnosed with various types of prognathia.
Along with the anomaly, speech disorders are formed. Speech therapy disorders prevent a person from speaking normally: pronouncing hissing consonants and guttural sounds. When occlusion occurs, the shape of the face changes. Due to a strongly protruded jaw, the lower lip sinks, the chin looks massive and heavy.
Mesial bite
An alternative name is reverse, progeny. Pathological occlusion is detected with pronounced development of the lower jaw. At the same time, the orthodontist notes that it is moving forward greatly. In this position, closure of neither the molars nor the anterior incisors is possible.
The situation is the opposite of an orthognathic bite - the lower jaw overlaps the upper jaw. In severe cases, gaps form between the incisors, which prevents normal biting and chewing of solid food. The gap between the teeth is clearly visible when a person smiles. The main load falls on the chewing molars.
Immediate surgical intervention by an orthodontist is required only in cases where traumatic occlusion is diagnosed using x-rays. In this position of the jaws, the development of constant bleeding is observed. Regular injuries to soft tissues lead to chronic gum disease, because the lower ones completely cover the upper incisors.
Against the background of the reverse, cross and open occlusion occurs. In this case, it is difficult to implant prostheses. When progeny occurs:
- three and curvature of the lower dentition;
- crowding;
- formation of tartar, caries, inflammation of soft gum tissue;
- early loss of canines and molars;
- thinning of cartilage tissue, pain, difficulty in chewing movements.
Causes of progeny and prognathia
All children are born with a distal malocclusion. But in the process of natural feeding, the child actively trains the lower jaw, and over time the bite becomes normal.
At older ages, prognathia occurs for the following reasons:
- artificial feeding;
- prolonged pacifier sucking;
- mouth breathing (for chronic ENT pathologies);
- previous rickets;
- early removal of baby teeth;
- incorrect posture;
- incorrect position of the body and head during sleep.
Progeny can develop due to congenital or acquired factors. Here is a complete list of reasons:
- unfavorable heredity;
- taking certain medications during pregnancy;
- severe illnesses suffered by the mother while carrying a child;
- birth injuries;
- underdevelopment of the jaw bone;
- pathology of the alveolar processes;
- bad habits (finger or upper lip sucking);
- long-term use of the pacifier;
- respiratory system diseases;
- late change of teeth;
- macroglossia (too large tongue);
- complications after surgery in the maxillofacial area.
Classification
Now the authors have identified a number of classifications of occlusion. Depending on this, the type of treatment and preventive measures may vary greatly.
According to the degree of morphological changes
Depending on this, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Gnathic. It is formed against the background of a violation of the development of facial bones. In particular, it occurs as a result of a disturbed location or size of the jaws.
- Dentoalveolar . Occurs when the buds of the teeth are incorrect, as well as a significant difference in the size of the jaws. Sometimes the disease can appear against the background of a violation of the shape of the process of the upper jaw.
Some authors identify a mixed form of the disease, in which signs of both forms are noted.
Is it possible and how to straighten teeth at home without the participation of a specialist?
Visit here to learn more about the stages of permanent dentition formation.
At this address https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/okklyuzii/pri-smennom-prikuse.html we will discuss what difficulties may arise when forming a mixed bite.
By localization
In this case, experts distinguish partial and general forms of the disease . For the general type, violation of the location of both lateral and frontal teeth.
In case of partial violation, only the contact of the anterior units suffers.
According to etiological factor
According to the etiology, progeny can be true or false:
- True is a condition in which both the front and lateral teeth are positioned incorrectly, and with central occlusion, a space is formed between the front elements.
This form of the disease is characterized by severe disruption of the jaws. Thus, patients cannot bite and chew food normally, and the jaw itself protrudes forward quite strongly, which causes severe psychological and aesthetic discomfort. - For false progeny, only a few front teeth are in the wrong position. Basically, this form of the disease is observed in older people, or against the background of improper surgical treatment.
- Some authors also highlight forced progenic occlusion. This type of disease occurs when there are temporary bumps in the lower jaw.
At the same time, the dentition remains normal. At rest, no manifestations of pathology are visible, however, when the teeth close together, signs of a progenic bite appear.