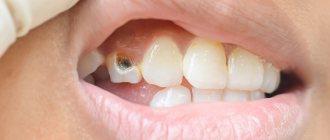
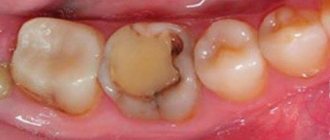
Cemental caries, or root caries, is less common than cervical caries, but is considered more dangerous and destructive to the tooth. The fact is that the root walls are thin and therefore caries destroys them faster and reaches the pulp. Root caries often becomes a complication of cervical caries or occurs as an independent disease. Its official name is cement caries, which indicates the location of the lesion - under the gum. This is precisely the problem. Ordinary caries can be seen with the naked eye by characteristic spots, but root caries is invisible.
Causes
The main cause of root caries is gum disease. With this disease, the gum does not completely adhere to the tooth and a pocket forms where food debris and plaque get trapped. As a result of plaque hardening, a stone appears, which becomes a provocateur for the development of caries. But there are other causes of the disease:
- cervical caries, which descends onto the exposed root;
- a poorly installed crown that lowers the gums and exposes the root;
- medications that increase salivation;
- poor oral hygiene;
- poor nutrition.
Root caries has another name - caries of the elderly. Age-related changes in the oral cavity, a decrease in local immunity and loss of skills in caring for the body and teeth in particular lead to the active proliferation of bacteria that easily penetrate to the root.
Caries
3934 16 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Caries: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Caries is an infectious lesion of the teeth in which demineralization and softening of the hard tissues of the tooth occurs with the formation of a defect in the form of a cavity. This is the most common disease of the dental system. Caries occurs among all age groups, but more often among adults over 35 years of age, where it accounts for 98-99%.
Causes of caries
In the oral cavity of any person there live a large number of microorganisms that are in balance and actively interact with the human body and with each other. This balance may change briefly under the influence of various factors, for example, after a teeth whitening procedure, but then the balance is restored again. If the body's defenses are reduced, the changes can be more significant and lasting.
Various bacteria, fungi and protozoa live on the oral mucosa, in the ducts of the salivary glands and in saliva, in gingival fluid and oral fluid, but most of them live in dental plaque - up to 90% of all microflora.
Dental plaque is a soft sticky deposit on the surface of teeth containing a large number of microorganisms, their metabolic products, epithelial cells, leukocytes, proteins and lipids of saliva. The formation of dental plaque is a natural process, and in the absence of timely and thorough dental care, it forms within 1-2 days. As a result of structural changes in plaque, dental plaques form quite quickly. Bacteria present in dental plaque and plaques actively “exchange information”, build a large number of connections, and then stick together, forming a microbial biofilm. In a biofilm, microorganisms exchange genetic material, nutrients, and remove metabolic products. The creation of such a biofilm protects bacteria from the body's defense cells and from the action of antibiotics. As a result of the vital activity of microbial biofilm, a large amount of organic acids is formed, under the influence of which demineralization of tooth enamel begins. Small defects form, microorganisms penetrate there, destroying the enamel further, resulting in the formation of a cavity in the tooth - caries.
Carbohydrates serve as food for microorganisms, so eating sweet foods contributes to the development of caries.
In addition, predisposing factors are a decrease in the body's defenses, smoking, poor oral hygiene, and taking antibiotics - all this leads to an imbalance in the oral microflora, resulting in the proliferation of streptococci and lactobacilli, which are responsible for the production of organic acids and the development of caries.
Classification of caries
Doctors classify caries depending on the stage and location of the lesion. The stage of initial caries, in which the process does not extend beyond the enamel-dentin boundary, is called the white or chalky spot stage. This is followed by the stage of dentin caries, in which the disease crosses the enamel-dentin boundary without affecting the pulp, and the stage of cement caries with damage to the exposed surface of the tooth root in the cervical region.
Focal demineralization of enamel is characterized by the appearance of a dark pigmented spot within the enamel and is called the stage of suspended caries.
Based on the location of the cavities, there are 6 classes of the disease:
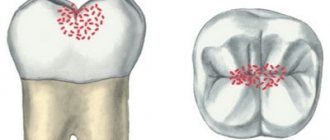
Class I - cavities localized in the area of grooves on the chewing surface of the teeth (fissures) and natural recesses of the incisors, canines, molars and premolars.
Class II - cavities located on the contact surface of molars and premolars.
Class III - cavities located on the contact surface of the incisors and canines without breaking the cutting edge.
Class IV - cavities located on the contact surface of the incisors and canines with a violation of the angle of the crown of the tooth and its cutting edge.
Class V - cavities located in the cervical region of all groups of teeth.
Class VI - cavities located on the cusps of molars and premolars and the cutting edges of incisors and canines.
Symptoms of caries
Symptoms of the disease depend on its stage. A sign of initial caries is a change in the color of the tooth enamel in a limited area and the appearance of a chalky or gray stain, lacking shine - a focus of demineralization. Then an enamel defect develops, and then a cavity. Patients with caries at the stage of cavity formation note increased sensitivity of the tooth to chemical, temperature and mechanical irritants, while the painful sensations disappear immediately after the irritant is eliminated. A defect can be seen on the visible surface of the teeth.
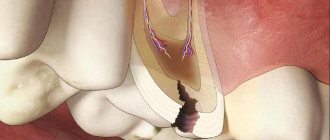
Further, tooth damage spreads to the underlying tissues - to the upper layers of dentin, after which, in the absence of treatment, the process captures the deep layers of dentin and approaches the pulp - soft connective tissue penetrated by blood vessels and nerve plexuses. At this stage, patients also note increased sensitivity to irritants and pain during chewing.
When the dental pulp becomes inflamed – pulpitis – severe toothache begins. If the disease is not treated, the pathological process can spread beyond the tooth into the bone tissue and periodontitis will develop.
Diagnosis of caries
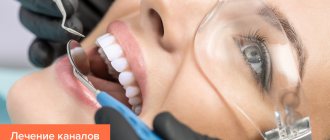
To make a diagnosis, the doctor examines the oral cavity, examining the mucous membrane, establishes the presence of fillings and the degree of their adherence, the presence of defects in the hard tissues of the teeth, and notes the number of teeth removed. The dentist carefully evaluates the condition of all teeth, determines the density of hard tissues, texture and degree of surface uniformity, checks pain sensitivity, and probes the identified carious cavity. If indicated, radiography is performed.
Which doctors should I contact?
Dentists treat caries.
Treatment of caries
The main goals of caries treatment are to stop the pathological process, restore the shape and function of the affected tooth, prevent the development of complications and restore the aesthetics of the dentition. If the carious lesion is limited to the enamel, then patients may be prescribed deep fluoridation of the hard tissues of the tooth to prevent further development of the process.
If a defect occurs in the hard tissues of the tooth, conservative remineralizing treatment does not have an effect; in this case, the altered tissues are removed and the tooth crown is restored using a filling.
Complications of caries
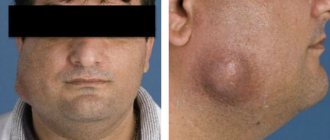
In almost half of patients aged 35-44 years, there is a need for filling and prosthetics of the affected tooth, and doctors have to resort to tooth extraction in almost a quarter of cases. With late treatment of caries, the pathological process can spread deeper into the dental pulp, and from the infected pulp, inflammation through the tooth canal penetrates further into the bone and under the periosteum of the jaw with the development of inflammation of the periosteum - periostitis or gumboil. Tooth extraction as a result of untimely treatment, which leads to complications, causes deformation of the dentition and can even lead to pathology of the temporomandibular joint.
Dental caries can cause problems with chewing function.
Prevention of caries
To effectively prevent the development of caries, it is necessary, firstly, to prevent the creation in the oral cavity of conditions conducive to the emergence of microbial films and the carious process, and secondly, to increase the caries resistance of dental tissues. The main methods of prevention are regular oral care with proper brushing technology, the use of dental floss, the use of fluoride toothpastes, mouth rinses, reducing sugar consumption and regular dental examinations (once every 6 months).
Sources:
- Clinical recommendations (treatment protocols) for the diagnosis of “Dental caries” Approved by Resolution No. 15 of the Council of the Association of Public Associations “Dental Association of Russia” dated September 30, 2014, updated on August 2, 2022.
- A.I. Khavkin, Yu.A. Ippolitov, E.O. Aleshina, O.N. Komarova. Oral microbiota: protective or pathogenic factor? // Issues of practical pediatrics. – 2015. – T. 10. – No. 4. – P. 49-54.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Diagnosis of cement caries
Unfortunately, it is impossible to diagnose the disease yourself. The patient can only feel a reaction to cold and hot drinks. This discomfort is fleeting and most people do not pay attention to it. And only a comprehensive dental examination will allow you to make the correct diagnosis.
For diagnosis, a Family Dentistry specialist:
- cleans the gums and removes subgingival deposits using hand instruments, ultrasonic instruments and Air Flow treatment;
- isolates the root from saliva secretion using a rubber dam - a special latex membrane;
- probes the root surface with a sharp probe to detect roughness characteristic of caries;
- prescribes radiovisiography, which will detect even the smallest subgingival and perigingival defects and carious processes at any stage;
After a set of examinations, the dentist may prescribe additional ones to confirm the diagnosis of cement caries and refute suspicions of pulpitis or periodontitis. This can be thermometry (checking the tooth’s reaction to hot and cold), EDI (checking the pulp’s reaction to current), etc.
How do you know if you have early stage caries?
If you have had caries at least once, then you probably know that the symptoms of the disease may vary. It depends on how deeply the tooth is affected. Caries is a progressive process, and in its development it goes through several stages, each of which is characterized by different symptoms.
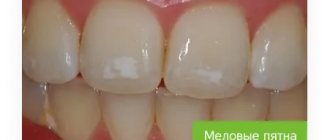
The disease begins at the spot stage and is asymptomatic at first. Therefore, without a dentist, it is difficult to notice that you have caries. The teeth do not hurt, there are no carious cavities, there is no discomfort while eating. The only sign of pathological changes at an early stage is white spots or stripes on the surface of the tooth enamel. If you notice such changes in the color of the enamel, consult a doctor immediately. These signs most likely mean that you have tooth decay. The disease at this stage is best treated because you can do without anesthesia, drilling and filling.
Treatment
The stages of treatment of dental caries are generally similar to the stages of treatment of ordinary caries:
- excision of affected tissue;
- treatment with medicinal and antiseptic drugs;
- the root is filled to recreate the shape.
The difference arises in the difficulty of accessing the site of the disease. First you need to clean the pocket and expose the root. As a rule, treatment takes place in two steps - on the first day, carious tissue is removed and the cavity is filled with a temporary glass ionomer filling. At the second appointment, the doctor examines the gums for healing and installs a permanent filling. To treat cement caries, Family Dentistry uses materials that are not affected by saliva, blood and gingival fluid - composites and glass ionomers.
If cement caries is not treated, pulpitis and periodontitis may develop, which will lead to tooth loss. To avoid such consequences, you should visit the dentist once every six months. During the consultation, the doctor will be able to detect signs of caries and, with little effort, get rid of this problem.
Treatment of caries
Improving existing ones and introducing innovative methods for diagnosing and prescribing appropriate therapy for dental caries makes it possible to qualitatively treat and maintain healthy teeth and gums. More recently, when advanced caries was detected, a tooth had to be removed, but now dentists perform special operations to save the tooth.
When is treatment for dental caries indicated?
Treatment of a carious tooth should begin when visible changes are detected (visual) or if there is discomfort.
In the first case, the appearance of stains on tooth enamel, darkening of the cervical part of the tooth, chips, darkening around the filling, or the appearance of a carious hole will be an indication for contacting a doctor.
Tactile indications include the appearance of pain from sweet, salty or sour foods, as well as the appearance of sharp acute pain due to temperature changes.
Conservative therapy without preparation
At the initial stages of the development of dental caries, it is possible to treat using non-invasive methods, when even a drill is not required. The goal of such treatment is to prevent progress in the development of the disease and, most importantly, to preserve the tooth. Only a person who regularly visits the dental office can be treated in this way: the doctor will notice the slightest deviations from the norm, signs of an incipient disease, and prescribe the necessary therapy in a timely manner.
The essence of the non-invasive technique is that soft plaque is removed and tooth enamel is mineralized. You will need to undergo a medical examination for diagnostic purposes, a gum isolation procedure and the application of medicinal drugs. This takes about an hour, it all depends on the equipment used and the professionalism of the attending physician.
Our clinic uses Icon and Clinpro technology.
Types of caries according to its location
This classification was highlighted by researcher Black from America:
- Class I: cavities in the area of fissures and cavities on the teeth are affected;
- Class II: cavities on the contact surfaces of molars are affected;
- Class III: cavities on the surface of the canines and incisors are affected, the corners and cutting edges are not involved in the process;
- Class IV: cavities on the surface of the canines and incisors are affected, the corners and cutting edges are involved in the process;
- Class V: cavities in the area of the tooth necks are affected;
- Class VI: cavities with atypical locations are affected.
Types of caries according to the severity of the process
There are the following types of caries process according to the speed and form of the disease:
- The compensated form is due to the slow development of the disease. Thus, the process usually develops with chronic caries;
- Subcompensated form - develops with average intensity, which is typical for a specific age group;
- Decompensated form (“acute caries”) - when compared with the average indicators of the age group taken, the symptoms of caries in this form are more pronounced, the disease develops quickly. When almost all the teeth in the area between the crown and roots are affected, this is the last form of acute carious process.
How caries progresses depends on individual characteristics. If the patient has a history of a serious illness associated with the immune system or the endocrine system, then from 5 to 20 teeth can be simultaneously affected in a short time. This form is called acute or decompensated. But the course of the disease may not be progressive. This type of caries will be a chronic or compensated form. But most often there are patients who develop a subcompensated form.
Symptoms of the disease
Initially, the disease is practically asymptomatic. During this period, a barely noticeable white or brown spot appears on the tooth. This is the first sign of superficial destruction of the enamel, but its integrity has not yet been compromised. Later, a carious cavity appears at the site where the spots formed.
If unpleasant sensations appear during the process of eating, and at the end of the chewing process they disappear, this indicates the presence of a carious process. If the pain does not disappear after the end of exposure to the irritant (food, liquid), perhaps the first stage of caries has ended and pulpitis has begun.
In some cases, the onset of the disease may be indicated by an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, you need to visit a dentist.
Types of caries by location
It is mainly the location that indicates the cause of the pathological process. Depending on the location, there are the following types of caries:
- Fissure. It begins in the grooves and pits of the chewing surfaces of the teeth (fissures), where microorganisms from food particles remain. Carious destruction occurs quickly, since the enamel layer here is much smaller;
- Contact. The most poorly diagnosed type of caries. Occurs on the distal surface, i.e. located on the edge of the tooth, which faces the adjacent one. Develops when food debris and plaque accumulate. A person turns to a dentist in advanced cases due to the fact that pain appears at a late stage of the disease;
- Cervical. The most common variety. It appears at the point of contact between the tooth and gum from the accumulation of food particles that form plaque, where microorganisms multiply. Erosion destroys the cementum of the tooth root. The disease is quite dangerous and requires mandatory treatment;
- Circular. A complex type of cervical caries, it seems to form a circle at the junction between the gum and the tooth itself. If the disease is not treated in time, crown destruction may occur. This is a common type of caries in primary teeth. It affects the front teeth and labial surface in children under 3 years of age with reduced immunity. Gradually spreads and covers the palatal surface and is localized around the entire crown of the tooth.
Complications of caries -
If the deep form of caries is not treated in time, then the infection penetrates into the pulp of the tooth. In this case, inflammation of the nerve in the tooth develops, which is called pulpitis. If, in turn, pulpitis is not treated in a timely manner, then the inflammation extends beyond the boundaries of the tooth - into the tissue surrounding the tips of the roots of the diseased tooth. In this case, granulomas or cysts (purulent sacs) appear at the tops of the roots. This disease is called periodontitis.
Classification of dental caries
This dental disease can be classified in different ways. The World Health Organization has identified the following types of caries:
- Enamel caries - characterized by softening of tooth enamel. Such caries begins after teething;
- Dentin caries - damage occurs to both enamel and dentin;
- cement caries - the tooth root is exposed, the cement is damaged;
- caries that has stopped - a dense dark spot appears, the process itself is stabilized;
- odontoclasia - occurs when the roots of baby teeth are reabsorbed;
- other and unspecified caries.
How are caries treated in dentistry?
At the initial stages of development of dental caries, the problem can be successfully solved using one of the modern non-invasive methods of therapy. The goal of this approach is to prevent progression of the disease and save the affected tooth. Progressive caries must be treated in the classical way.
Read more about the stages of invasive treatment and modern methods of getting rid of caries.
Stages of caries treatment
Otherwise, the classic method of caries removal is called surgical. The doctor removes the affected tissue (fragments of enamel and dentin) and then fills the resulting cavity until the anatomical shape of the unit is completely restored. The process includes several successive steps:
| Cleaning a tooth from plaque | To remove tartar, which will hinder a successful recovery, the dentist uses a surgical instrument, ultrasound. Air abrasive cleaning can remove plaque. |
| Determination of tooth color using a special scale | This stage is very important when treating teeth in the smile area. The doctor will have to give the patient a filling that will not differ in color from natural enamel. For these purposes, the dentist uses the standardized Vita scale. |
| Anesthesia | For the comfort of the patient and the doctor, an anesthetic is administered to the patient. Depending on the method of administration and duration of action, there are several types of anesthesia. Before using a specific pain reliever, a good dentist will make sure that the patient is not allergic to the active ingredient. |
| Drilling out carious tissues | At this stage, the doctor drills out damaged dental tissues - eliminates destroyed dentin and enamel edges hanging over the cavity. If the drilling technology is violated and some of the affected fragments are preserved under the installed filling, there is a high risk of developing secondary caries. |
| Isolation of tooth from saliva | This measure is necessary to ensure that moisture does not get under the filling, otherwise its survival rate will be low and the filling will soon fall out. A special rubber scarf with a hole for the teeth helps to properly isolate the work area. It's called a rubber dam. |
| Medical treatment of carious cavity | To isolate the tooth from saliva, the doctor treats the dental cavity with antiseptic drugs to destroy all bacteria and prevent inflammation under the filling. |
| Restoring the contact point between teeth | The contact point is the place where adjacent teeth come into contact. It is important to restore it to prevent damage to the interdental space, accumulation of food between the elements and the development of caries. At this stage, the dentist uses tools to restore the point of contact: matrices, wedges, metal rings, cones, attachments, etc. |
| Etching enamel with acid | In order for the adhesive, which the doctor will apply at the next stage, to penetrate deep into the dental tissue, the enamel must be etched with a special gel. The product contains an acid based on phosphorus. After etching the surface, the dentist washes off the gel and dries the work area. |
| Treatment of dentin and enamel with adhesive | Cleaned dentin and enamel are covered with a layer of adhesive - a composition that promotes better adhesion of the filling to the walls of the tooth. |
| Applying a gasket under the filling | The doctor installs a gasket at the bottom of the cavity, which acts as an insulator for the future filling from the tooth surface. |
| Sealing | At this stage of therapy, the dentist uses a photopolymer composite material from which he forms a filling. The material must be applied in layers to ensure high-quality fixation. Each layer is followed by illumination of the composition with a special lamp. The technology allows the doctor to determine the location of the polymer and dry the material well. |
| Grinding and polishing of teeth | The caries treatment process cannot be completed without grinding and polishing: the primary photopolymer filling has a rough surface and stands out against the background of natural enamel. The doctor completes the therapy using a drill and special attachments. Afterwards, all that remains is to cover the surface of the tooth with a special composition that will allow the enamel to quickly recover. |
Modern methods of caries treatment
It is not necessary to remove the affected dental tissue and fill the cavity in all cases. If a patient consults a doctor with initial symptoms of caries, the problem can be solved using one of the gentlest methods. These methods are used to treat caries in adults and children.
Remineralization
Modern methods are applicable when detecting initial caries. The doctor treats the surface of the damaged unit with a special composition that contains fluorine, calcium and phosphorus.
Infiltration method using ICON technology
Chemical-mechanical method of treating caries. The therapeutic measure is applied only at the primary stage of the disease, when spots appear on a smooth surface or between units. The dentist covers the local area of the tooth with a gel, which breaks down the injured enamel layer. Then the inflammatory focus is dried using ethyl and air flow. To fill the pores of damaged enamel, the doctor coats the area with a polymer resin. Treatment of caries in this way lasts no more than 15 minutes.
Ozone therapy
The principle of the therapeutic technique is simple - ozone, as a natural antibacterial agent and oxidizing agent, destroys bacteria, the activity of which leads to the development of caries. In addition to the antibacterial effect, ozone therapy also demonstrates a restorative effect (strengthens the enamel layer).
When using ozone therapy for caries, the doctor uses a special device that converts oxygen into ozone and delivers it to the local area. Once the ozone kills the bacteria, it turns back into oxygen.
A gentle method of therapy allows you not to injure healthy cells, affecting only damaged ones. Another advantage of the approach is that there is no need to administer an anesthetic. The procedure lasts about a minute and is successfully used in the treatment of caries at the white spot stage and as a preventive measure for the disease.
Air abrasive method
In this case, caries is treated without a drill, but using an alternative device that delivers a powerful stream of abrasive elements. The technique allows you to literally “knock out” superficial caries with an abrasive. The air-abrasive flow affects only softened (damaged) dental tissues; anesthesia is not required.
Gentle therapy “insures” against the formation of microcracks in the enamel after classical treatment. In the case of superficial caries, the technique is not applicable in all clinical cases.
Laser therapy
This method of therapy is recognized as effective for superficial and even moderate caries. In practice, the technique is recommended for pregnant women and children. The procedure is painless due to the use of a bactericidal solution that cools the tooth. The equipment itself does not create vibrations that could increase pain.
The laser beam acts on the damaged area, evaporating the affected tissue, and additionally disinfects the formed cavity, while reducing the risk of relapse of the disease.
ART technique
Step-by-step treatment of caries, during which the dentist, using a professional instrument, cleans the affected tissue and fills the formed cavity with dental cement. This method of therapy appeared in third world countries, and is sometimes used in developed countries. Manual work ensures precision and allows you to preserve healthy dental tissue to the maximum extent.