Mumps (mumps, behind the ears) is a contagious acute infectious disease of viral origin, in which the salivary glands behind the ears become inflamed in a child. Thus, when mumps occurs in children, treatment must be strictly carried out under the supervision of a doctor. At the SANMEDEXPERT clinic, the pediatrician will examine the little patient, tell you what medications should be taken and how to avoid complications.
This disease is called so because the child’s cheeks seem to puff out, and the little patient becomes like a pig. At risk are young unvaccinated children under seven years of age, most often boys. An adult suffers from the disease much worse than children.
Infants rarely suffer from a disease such as mumps - breast milk provides them with treatment and a kind of immunity from the disease; This immunity lasts up to 5 years. The peak of disease activity occurs in early spring (March, April).
The main cause of the disease is considered to be contact with a sick person, therefore most often they become infected through airborne droplets, but there are often cases when the disease affects a person through contaminated objects.
If a person has been ill with a disease such as mumps, the treatment has been completed, then he will never get sick again.
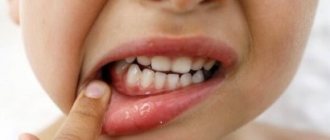
Symptoms of gum inflammation in a child
Symptoms of gum disease vary depending on the type and form of the disease. These include:
- bleeding and pain;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- purulent discharge;
- deposits of plaque or tartar;
- hypersensitivity.
Most often, childhood gum disease is associated with the development of gingivitis. The inflammatory process occurs due to poor oral hygiene (bacteria multiply).
REFERENCE! If you have problems with your gums, a visit to the dentist is required. Only a specialist will select an individual treatment algorithm based on the symptoms.
What are adenoids and where do they come from?
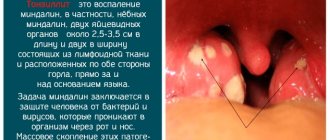
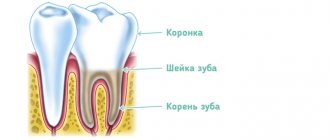
Adenoid vegetations (nasopharyngeal tonsil) are lymphoid tissue in the vault of the nasopharynx. It is present in all children without exception and is a peripheral organ of the immune system, part of the lymphoid pharyngeal ring. The main function of this anatomical formation is to fight bacteria or viruses that enter the child’s body. Its main difference from other tonsils is that the surface is covered with a special epithelium that produces mucus. An increase (hypertrophy) of adenoid tissue is provoked by frequent allergic and respiratory diseases of viral or bacterial etiology. Therefore, the peak of hypertrophy of adenoid tissue occurs precisely at the age of 3-7 years. Then the lymphoid tissue is gradually reduced at the age of 10–12 years. By the age of 17, only fragments of tissue often remain; in healthy adults, adenoid tissue is absent. Hypertrophy of adenoid tissue is usually divided into several degrees according to its volume in the nasopharynx, from the first, where the adenoids close the nasal passages (choanae) by 1/3, to the third or fourth degree, when complete obstruction of the nasopharynx occurs with the impossibility of nasal breathing.
Causes of gum inflammation in children
The abundance of causes that cause gum problems can be divided into two large groups.
Common ones include:
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- frequent colds;
- hormonal disorders.
Among the local causes, doctors identify:
- poor-quality fillings (they collapse and injure soft tissues);
- caries (infection from the tooth immediately spreads to the gum);
- incorrectly installed braces;
- crowding of incisors.
What are the reasons?
Among the infections that can cause mesadenitis in a child are bacteria such as:
- coli;
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- salmonella;
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
These may also be the following viruses:
- enterovirus;
- adenovirus;
- Epstein-Barr virus;
- cytomegalovirus.
Doctors often associate the development of mesadenitis in children with the presence of diseases such as:
- pneumonia;
- flu;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- tonsillitis;
- bronchitis.
After severe infectious diseases, a child is often diagnosed with reactive mesadenitis. In addition, this pathology often occurs in children as a specific reaction to vaccinations or uncontrolled use of certain types of medications.
Treatment methods
Some of the common childhood gum diseases include:
- stomatitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane due to a virus or fungus);
- periodontitis (advanced form of gingivitis);
- periodontal disease (associated with inflammation, rarely diagnosed);
- gingivitis (a consequence of injury or plaque, usually occurs in the catarrhal form, during the eruption or change of teeth).
For treatment, local administration of various medications and rinsing with antiseptics may be prescribed. Additional measures: sanitation of the oral cavity and removal of tartar. In the chronic form, physiotherapeutic methods are used.
Diagnosis and treatment
The doctor makes the diagnosis based on external symptoms and accompanying complaints of the patient. Most often, the disease affects the glands on both sides. Sometimes the symptoms of the disease practically do not appear, except for inflammation of the salivary glands. Once ill, a small patient may refuse to eat, he may experience dry mouth and inflammation behind the ears.
The child is hospitalized only in case of complications or an epidemic. At home, the patient must be isolated from family members for 10 days and kept in bed.
It is necessary to adhere to a dairy-vegetable diet, grind food to reduce pain when swallowing, eat in small portions and drink plenty of warm teas, decoctions, and fruit drinks. You should avoid sour juices and fatty foods.
Doctors often prescribe:
- antipyretic,
- antihistamine,
- vitamins.
Gargling with a soda solution and dry warm compresses applied to the throat area are indicated. To relieve pain, you can tie a warm scarf around your neck and make a warm oil compress with heated vegetable oil.
In some cases, the doctor prescribes physical therapy, for example, ultraviolet radiation, diathermy. In severe cases, intravenous detoxification therapy with glucose solution is prescribed.
You can get a referral for them and undergo them at the children's clinic or at the SANMEDEXPERT clinic in Moscow Central Administrative District at the Baumanskaya metro station.
Prevention
To avoid mumps, a vaccination is necessary, which is done in any children's clinic according to the vaccination calendar, that is, after a year, often together with the measles and rubella vaccine. However, if a child has a decrease in immunity, for example, with leukemia, then the vaccine is contraindicated. Vaccinations for small allergy sufferers are given with special care. Normally, vaccination should be carried out under the supervision of an allergist.
Prevention
The main preventative rule is daily brushing of teeth twice a day (morning and evening). It is important not to forget about the palate and tongue. Please also pay attention to the following recommendations:
- caries is immediately healed (it is advisable not to start the disease in the early stages);
- it is also necessary to treat the disease that could provoke gum inflammation;
- malocclusion needs correction;
- with the help of good nutrition and taking multivitamin complexes according to age, they strengthen the immune system;
- during teething, use a special fingertip to massage the gums;
- food and drink for the baby cannot be too hot or, conversely, cold;
- They explain to their son or daughter that food is always experienced on both sides.
REFERENCE! It is the parents' responsibility to monitor how thoroughly and correctly the child brushes his teeth.
Our specialists at modern pediatric dentistry “Avesta” believe that timely preventive measures help minimize the development of a serious disease. This is the easiest way to keep your baby's gums and teeth healthy.
Mumps symptoms
So, the following symptoms indicate the need for treatment for mumps:
- the temperature rises sharply (sometimes up to 40 degrees),
- joint and muscle pain,
- headache,
- chills and fever (but this symptom does not always appear),
- pain behind the ears, in front and behind the earlobe,
- weakness and lethargy,
- sharp pain when swallowing and chewing food,
- increased salivation.
But the main marker of the disease is gumboil and swelling behind the ears, and sometimes under the jaw. The sublingual glands can also be affected by the disease. Inflammation persists for up to 10 days; flux usually reaches its maximum on the 3rd day. The child remains contagious until the 10th day of illness. If mumps symptoms are detected early, treatment is faster and without possible complications.
Complications
Treatment of mumps in children can be complicated by secondary diseases. Glandular organs are considered weak points when mumps is affected, so common complications are:
- pancreatitis (pancreas),
- oophoritis (ovaries),
- atrophy, orchitis, priapism, infertility (testicles),
Meningitis, encephalopathy, otitis media, hearing loss, and sometimes complete deafness also occur. These diseases are characterized by the following alarming symptoms:
- vomiting and stomach pain,
- apnea,
- convulsions,
- increased drowsiness,
- prolonged fever
- enlargement and pain in the testicles.
Clinical manifestations
Inflammation of the adenoid tissue is called adenoiditis. Its course can be acute, subacute and chronic. Let's briefly touch on the main symptoms that parents should pay attention to:
1. Runny nose, most often it has a protracted course.
2. Predominant breathing through the mouth. Caused by difficult nasal breathing. The degree of difficulty directly depends on the degree of hypertrophy of the adenoid tissue. Nasality often appears. With a long course of chronic adenoiditis and breathing through the mouth, changes in the facial skeleton are possible, which later manifests itself as a persistent violation of speech pronunciation.
3. Night snoring, restless sleep.
4. Morning cough caused by choking on mucus draining from the nasopharynx overnight.
5. Hearing loss, recurrent otitis due to mechanical obstruction of the auditory tubes by adenoid vegetations. In this case, hypertrophy can be 1-2 degrees, when the adenoids are located near the mouths of the auditory tubes, which are responsible for ventilation of the middle ear through the auditory tube. The child begins to constantly ask questions or watch cartoons too loudly.
6. Fatigue, apathy. Caused by constant oxygen starvation of the brain, especially in chronic adenoiditis. There may be a lag behind peers in mental and physical development.
Types of gingivitis in children
So that the doctor can create the most complete picture, there are several classifications of the disease. Each type has its own clinical characteristics, methods of care and arises due to various factors. After treatment, strict monitoring is required to avoid relapse. This is especially true for children, because they are not able to carry out hygiene and other procedures on their own, so all the doctor’s recommendations fall on the parents.
Catarrhal
It is associated with age-related changes. Most often occurs during primary eruption or in the presence of a concomitant infectious disease. It can be recognized by pain when eating and bleeding when cleaning. An unpleasant odor and loss of taste sensitivity appear. The child may complain of burning and itching in the mouth. On examination, you can see redness.
Marginal
Most often observed in children with abnormal dentition and malocclusion. Because of this, it may be impossible to thoroughly clean all hard-to-reach places where plaque begins to accumulate and pathogenic microflora multiply. Bleeding is noticeable, and in the early stages there is virtually no pain or redness. The attachment of the gums to the teeth is not disturbed. In advanced cases it can become chronic.
Desquamative
The appearance is associated with hormonal disorders and most often occurs during puberty. May occur against the background of other diseases:
- lichen planus;
- pemphigus vulgaris;
- permanent infections.
In the early stages, other than bleeding during cleaning, no symptoms are observed. During the transition period, the gums swell greatly and acquire a bright shade and shine. In complex and advanced cases, purulent ulcers and erosion appear.
Hypertrophic
A complicated form that occurs against the background of a long-term inflammatory process that has entered the chronic stage. The redness will be pronounced, it is impossible to miss or not notice it during examination. The taste of food will be practically lost due to constant bleeding and the taste of blood in the mouth.
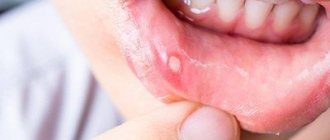
Ulcerative
Appears if there has already been primary inflammation in the oral cavity - stomatitis. Concomitant factors include severe hypothermia and decreased immunity. At the same time, the child’s condition worsens sharply; he feels pain in his gums and cannot swallow. Due to the inflammatory process, not only the gum tissue, but also the tonsils can swell. Upon examination, you can see ulcers with a serous putrefactive coating.
Atrophic
It often manifests itself as a medical error during poor-quality orthodontic treatment. An abnormal attachment of the frenulum may also be a provoking factor.
The child's condition will be stable, there are practically no signs of inflammation. You may notice only mild redness, exposed teeth and increased sensitivity to hot foods.
Methods for studying adenoid vegetations
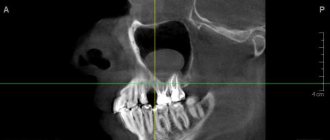
In its normal state, it is impossible to see this tonsil without additional optical devices. There are a number of studies that help determine the extent of adenoid vegetations: digital examination, posterior rhinoscopy with a mirror, radiography of the nasopharynx, endoscopy of the nasopharynx, three-dimensional X-ray examination or CT scan of the nasopharynx. The most modern methods today are:
- endoscopy of the nasopharynx and nasal cavity. The procedure is performed in our clinic under local anesthesia during an appointment with an ENT doctor. It is completely painless and allows you to assess not only the degree of adenoid vegetations, but also the nature of inflammation, the condition of the mouths of the auditory tubes, and also examine the posterior parts of the nasal cavity.
- three-dimensional X-ray examination / CT scan of the nasopharynx. The methods are significantly more informative than conventional X-rays of the nasopharynx, since they allow one to determine not only the size, but also the ratio of adenoid vegetations to other structures of the nasopharynx (the mouths of the auditory tubes, choanae, etc.). The radiation dose is almost 3 times less (0.009 m3v), and the duration of the study is no more than 2 minutes. You can undergo this study at the clinic on Usacheva.