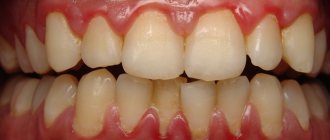
Human health is a very fragile and unpredictable thing, and diseases often appear out of nowhere. This also applies to oral diseases. If you are faced with such an unpleasant problem as a sore in the mouth, then you would probably like to know how to get rid of it.
The appearance of wounds on the human oral mucosa is usually accompanied by pain and causes discomfort while eating or talking. But many people, despite these symptoms, choose not to seek help from a doctor. Some people simply ignore the problem, while others try to self-treat the disease at home. Both of these approaches give positive results only in rare cases.
The presence of any wounds and damage covering the palate indicates health problems in an adult or child. This situation should not be left to chance; you should seek help from a dentist. Only he will be able to diagnose the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment. If you are concerned about wounds in your mouth, then you can contact the LeaderStom network of dental clinics to solve this problem. We will help you cope with the situation and will make every effort to quickly cure the disease.
— 15% on the first visit
Sores in the mouth as a sign of aphthous stomatitis
Wounds in the mouth can arise as a result of the development in a person of a separate independent disease of the oral mucosa, caused by the growth and development of pathogenic microorganisms. But, in addition, the cause of such wounds may also be hidden in the general somatic condition of an adult or child.
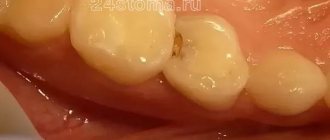
In most cases, mouth ulcers are symptoms of a disease such as canker sores. Stomatitis is a lesion of the human oral mucosa that occurs as a result of an atypical reaction of the immune system to foreign irritants. Depending on the nature and causes of the disease, stomatitis can be of various types: ulcerative, herpetic, allergic, vesicular, etc. But people most often have to deal with the aphthous form of this disease.
Let's name the main symptoms of aphthous stomatitis:
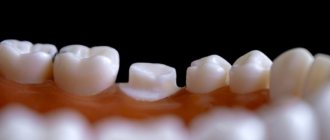
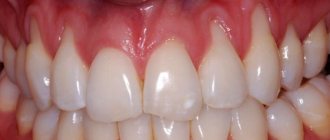
- The appearance of round ulcers (ulcers) in a person’s mouth, which are grayish in color and surrounded by a red, inflamed rim. Ulcers are located either separately or in groups and have different sizes.
- Painful sensations in the affected areas of the upper and lower palate of a person that occur during eating, drinking, or talking.
- Deterioration of a person’s general well-being, weakness.
- Temperature increase. But this is not a mandatory symptom; it occurs in most cases in children, since they are more difficult to tolerate aphthous stomatitis in the oral cavity.
- Enlarged submandibular lymph nodes. This symptom of aphthous stomatitis also occurs more often in children than in adults.
The mechanism of occurrence and symptoms of stomatitis
As noted above, the symptoms of stomatitis are ulcers that appear in the oral cavity (on the palate, in the cheeks or on the tongue), which bother a person, causing him pain. The mechanism of occurrence of such erosions is associated with the response of the human immune system to foreign irritants, which, for example, are viruses or bacteria.
Stomatitis manifests itself in such forms as herpetic, aphthous, allergic, vesicular, catarrhal, etc. In any case, the manifestations of stomatitis disease are expressed in lesions of the human oral mucosa or tongue, only depending on the variety they are of a different nature.
Why does aphthous stomatitis occur?
As noted above, the causes of aphthous wounds in a person’s mouth can be both local and general somatic in nature. Let's look at the main ones.
Local causes of aphthous stomatitis:
- Mechanical damage to the human oral mucosa. Such injuries occur as a result of a person eating hard and tough foods. Often, even a small scratch on the roof of the mouth can cause aphthous stomatitis.
- Thermal lesions of the human oral mucosa. The occurrence of wounds and the development of aphthous stomatitis in this case provoke burns of the mucous membrane, which a person could receive by consuming hot drinks or food.
General somatic causes of wounds in the human oral cavity:
- Heredity factors. The predisposition to the occurrence of aphthous stomatitis in the mouth may be determined by genetic reasons. Therefore, there is a risk of developing this disease and the manifestation of a chronic form of stomatitis (when ulcers on the mucous membrane appear regularly) in people whose parents also suffered from this disease.
- Somatic diseases. Aphthous stomatitis often develops in people who suffer from any secondary somatic diseases. For example, these could be diseases of the digestive system and gastrointestinal tract.
- Weak immunity. For this reason, children are susceptible to oral ulcers because their immunity is not yet fully developed. In a child, aphthous stomatitis is more severe than in an adult and is accompanied by an increase in temperature and a deterioration in general well-being. Against the background of colds, immunity is also often reduced, and aphthous stomatitis occurs in the person’s mouth.
- Avitaminosis. With an incorrect diet, a person does not receive enough substances necessary for the successful functioning of the body. Due to a lack of vitamins C and B or microelements such as selenium, folic acid, zinc or iron, in some cases aphthous stomatitis occurs in a person’s mouth.
- Allergy. An allergic reaction associated with eating foods such as citrus fruits, nuts (especially peanuts), chocolate, red berries (strawberries, wild strawberries) or foods containing gluten (cereals, pasta) in some cases leads to the appearance of canker sores. wound in a person's mouth.
- Stress. When a person finds himself in a stressful situation, he spends significant resources to cope with the current problem. This leads to a loss of strength, decreased immunity and a general weakening of the body, as a result of which wounds form in the person’s mouth and he develops aphthous stomatitis.
Causes of stomatitis and symptoms of the disease
Stomatitis on the oral mucosa and tongue occurs in humans for various reasons. Some of them are local in nature and are associated with the penetration of various bacteria or viruses into the oral cavity. In other cases, the formation of stomatitis ulcers on the tongue occurs against the background of decreased immunity and general weakening of the human body.
Let's name the most common causes of stomatitis in the tongue:
- Oral injuries. They can occur as a result of a person eating hot, hard or sour foods. Damage to the mucous membrane can trigger a stomatitis reaction and cause the formation of ulcers on the tongue, characteristic of this disease.
- Infections. Here we are talking about viral and bacterial diseases of the human oral cavity, which in themselves do not cause stomatitis. It is only the body’s reaction to the occurrence and development of these infections. In 90% of cases in such a situation, stomatitis caused by the herpes virus develops on the human tongue. It manifests itself in the form of small blisters that burst after 3 days, accompanied by severe pain and an increase in the person’s body temperature.
- Weakening of the immune system. Weakening of the immune system as a result of stress, acute illness (for example, a cold) or chronic diseases (helminthic infestation, giardiasis, etc.) provokes the formation of stomatitis ulcers in the human oral cavity.
- Poor oral hygiene. The surface of the human tongue provides an excellent environment for the growth and reproduction of bacteria. Therefore, daily brushing of teeth and treating the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions is the best way to avoid the development of infectious diseases that can provoke the appearance of stomatitis ulcers on the surface of the mucous membrane and tongue.
- Avitaminosis. Lack of microelements negatively affects the condition of the human body. Therefore, with a lack of vitamins A, B and C, folic acid, iron and other substances, the risk of stomatitis in a person’s mouth increases.
- Using toothpastes containing sodium lauryl sulfate. This substance is included in many products intended for human oral hygiene, since it promotes the formation of abundant foam. But sodium lauryl sulfate dries out the mucous membrane, as a result of which it becomes susceptible to damage, which can cause stomatitis.
Local and general causes of stomatitis are interconnected. One problem leads to another and causes a subsequent reaction. Thus, a weakened human immune system provokes the development of an infection, against the background of which stomatitis occurs on the tongue. Therefore, comprehensive measures are necessary to treat and prevent relapses of this disease.
How to get rid of sores in the mouth?
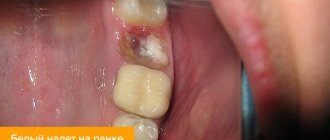
Stomatitis wounds that occur in the human mouth, in most cases, heal on their own within 7-10 days after formation. But timely treatment of aphthous stomatitis is necessary in order to prevent the formation of ulcers on the human oral mucosa again. The fact is that the acute form of stomatitis, which is characterized by the sudden appearance of wounds of various sizes on the upper and lower palate in a person’s mouth, if the problem is ignored or the wrong treatment is carried out, tends to develop into a chronic form of the disease. Wounds in the oral cavity with chronic stomatitis appear periodically and bother a person from time to time throughout life.
To exclude the possibility of aphthous stomatitis ulcers reoccurring, dentists perform the following treatment:
Local therapy
. It involves treating wounds on the oral mucosa with antiseptic agents: gels, ointments or sprays. During this treatment of stomatitis, a person is prescribed daily rinses with solutions such as furatsilin, chlorhexidine, miramistin, etc.
General therapy.
It includes a set of measures to cure this disease and at the same time strengthen the body. To strengthen the body, the doctor prescribes immunomodulatory drugs and vitamin courses to the person. To combat aphthous stomatitis, different drugs are used, depending on the nature of the disease and the causes of its occurrence: antihistamines, antivirals, steroids or antibiotics.
The selection of funds for the treatment of wounds with aphthous stomatitis is carried out only by a doctor and occurs after a visual examination of the person’s oral cavity, conducting the necessary diagnostic tests and making a diagnosis. The LeaderStom Clinic offers to use the services of our experienced doctors to carry out these operations.
How to cure stomatitis on the tongue?
At the first signs of stomatitis, specialists at the LeaderStom clinic recommend contacting a dentist for diagnosis and prescribing appropriate treatment. A person’s attempt to cope with a stomatitis disease that appears on the tongue on his own may not only not lead to the desired result, but on the contrary, increase the symptoms of the disease. The drugs that are used to treat stomatitis on the tongue can be divided into local therapy drugs and medicinal formulations that have a general effect on the human body. Let's take a closer look at each of these forms.
Treatment of stomatitis with local therapy:
- Treatment of stomatitis ulcers on the human tongue with antiseptic gels, ointments and sprays.
- Rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions, which can be purchased at the pharmacy (chlorhexidine, miramistin, etc.) or prepared yourself using medicinal herbs such as chamomile or calendula.
- In order to relieve the pain symptom, doctors recommend using local preparations containing lidocaine for a person with stomatitis formations on the tongue.
General therapy for stomatitis:
Depending on the cause that provoked the stomatitis disease, antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal or antihistamines are used. Such drugs are prescribed to a person only by a dentist or therapist. To relieve the symptoms of stomatitis, modern antipyretic and painkillers are used.
Taking vitamin complexes allows you to compensate for the lack of essential microelements in the body, which for one reason or another a person does not receive with food, and vitamin deficiency, as is known, is one of the factors that can provoke stomatitis on the oral mucosa and tongue.
For stomatitis, immunomodulatory drugs are also used - drugs that increase human immunity. They can be of both plant and medicinal origin. All patients, regardless of the reasons that caused stomatitis on the tongue, are recommended by doctors to take these medications.
Drugs are also used to treat somatic diseases. The use of such remedies is necessary if the cause of stomatitis on the tongue lies inside the body. Chronic diseases of certain systems, and especially the human gastrointestinal tract, weaken the body and contribute to the launch of an immune reaction, manifested in the formation of stomatitis ulcers on the palate and tongue.
What can be done to prevent sores in the mouth from appearing again?
Completing a course of timely treatment for aphthous stomatitis will reduce the risk of a similar disease of the human oral mucosa in the future, but in some cases it will not completely eliminate this possibility. This especially applies to situations where a person has a hereditary tendency to develop aphthous sores in the mouth, suffers from autoimmune diseases, and is prone to allergies.
In such cases, preventive measures are required:
- Enhanced oral hygiene. It involves not only daily brushing of a person’s teeth and gums twice a day, but also rinsing the oral mucosa with solutions of antiseptics or medicinal herbs in order to prevent stomatitis.
- Balanced diet. Reviewing the diet and diet will help saturate the human body with essential vitamins and microelements and reduce the risk of allergies that can cause aphthous wounds in the human mouth.
- Taking vitamin complexes. If it is not possible to compensate for the lack of nutrients in the body with nutrition, then to prevent stomatitis a person can regularly take vitamin complexes, the composition of which, doses and duration of administration will be determined by your attending physician, based on the results of the tests.
- Taking immunomodulatory drugs. Today, there are many remedies that stimulate the immune system and encourage the body to resist diseases. They can be either of plant origin or synthesized in the laboratory. The selection of such drugs is individual for each person and is carried out by a doctor.
- Compliance with preventive measures, timely treatment of the disease and following the recommendations of the attending physician will help a person avoid relapses of aphthous stomatitis and the reappearance of wounds in the mouth in the future. Be attentive to yourself and your health, listen to the signals that your body gives, and at the first signs of disease in the oral mucosa, seek help from a dentist.
You should not self-medicate stomatitis and use the advice of friends or information found on the Internet, since the exact cause of sores in the mouth and stomatitis can only be identified through diagnostic methods. And the selection of treatment is determined in accordance with the diagnosis, and in each case it is individual. Dentistry "LeaderStom" offers its assistance in the treatment of aphthous stomatitis and other diseases of the oral mucosa. Contact us and we will help you identify the cause of the disease and select medications accordingly.
Result of common diseases
Some diseases have a systemic effect on the body. This means:
- Tuberculosis. When the lungs are affected, negative symptoms can spread to the mucous membranes of the mouth. This occurs due to the penetration of the pathogen into the oral cavity through damaged epithelium. Then the patient develops ulcers on the cheeks and under the tongue. First, these are always specific tuberculous tubercles, and then aphthae. They grow quite quickly. At the same time, an increase in the amount of plaque on the tongue, weakness, and loss of body weight are recorded.
- Syphilis. Pathology caused by Treponema pallidum. During the incubation period, which lasts about three weeks, aphthae occur. They are round or oval. Their edges are usually raised, swollen, and the color is red. Such damage takes a long time to heal - up to three months. Syphilis erosions are not as painful as tuberculosis ones. After their healing, retracted scars form.
- HIV infection. It has been noticed that every third HIV-infected person has inflamed oral tissues. In this case, therapy must be specific. It is not the dentist who is responsible for its implementation, but the infectious disease specialist. As soon as the patient’s health improves and the immune system is strengthened, the aphthae will disappear on its own.